Category: Letter P
-
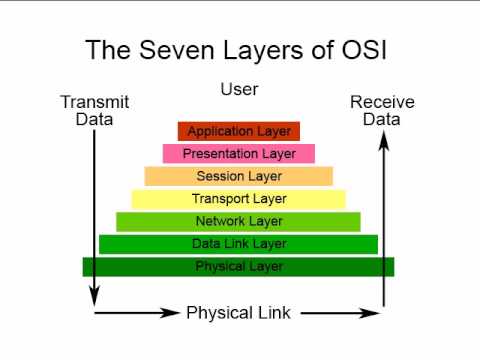
Physical Layer
Physical Layer is the first Layer (or the PHY layer) of the Open Systems Interconnection reference model, also known as the OSI Model or the Seven Layer Model.
-
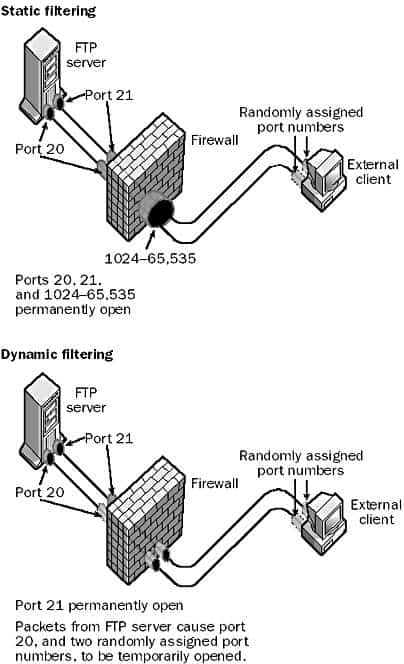
Packet Filtering
Packet Filtering is the process of controlling the flow of packets based on packet attributes such as source address, destination address, type, length, and port number.
-
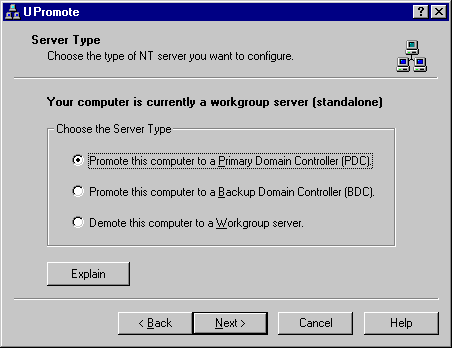
Primary Domain Controller (PDC)
Primary Domain Controller is a Microsoft Windows NT domain controller that contains the master copy of the Security Account Manager (SAM) database.
-

Private Branch Exchange (PBX)
Private Branch Exchange, also known as PBX, is a telephone switch at the customer premises that supports multiple independent telephone extensions.
-
Patch Cable
Patch Cable is a short cable, usually unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling, that connects a port on a patch panel to a port on a hub or a switch.
-
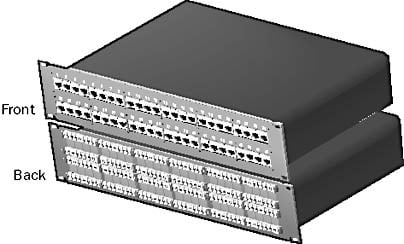
Patch Panel
Patch Panel is a rack-mounted panel with a series of connectors that provides a branching-out point for network cabling to leave the wiring closet and make horizontal runs to wall plates in the work areas.
-
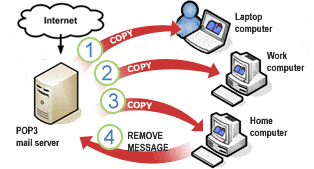
Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3)
Explore the ultimate guide to POP3: Post Office Protocol version 3. Learn about its history, functionality, advantages, disadvantages, and more!
-
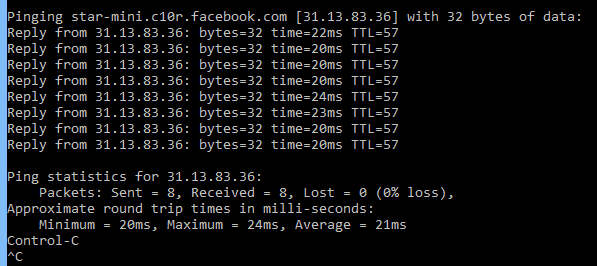
ping
Unlock the secrets of the Ping command—a must-know tool for network diagnostics. Learn how it works, options, examples, security risks, and alternatives.
-
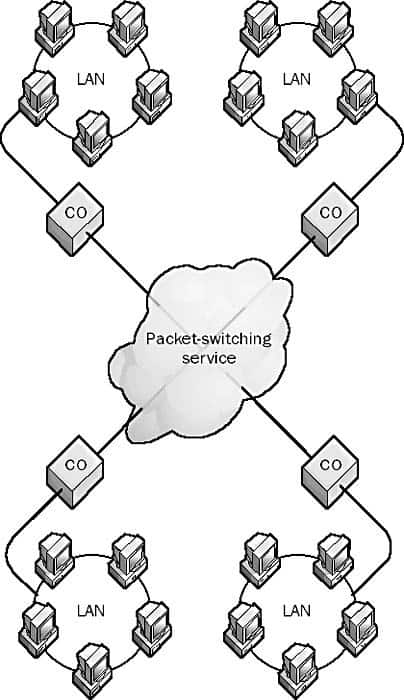
Packet-switching Services
Packet-switching Services are telecommunications services provided by telcos and long-distance carriers that route packets of data between local area networks (LANs) in diverse geographical locations to form a wide area network (WAN).
-
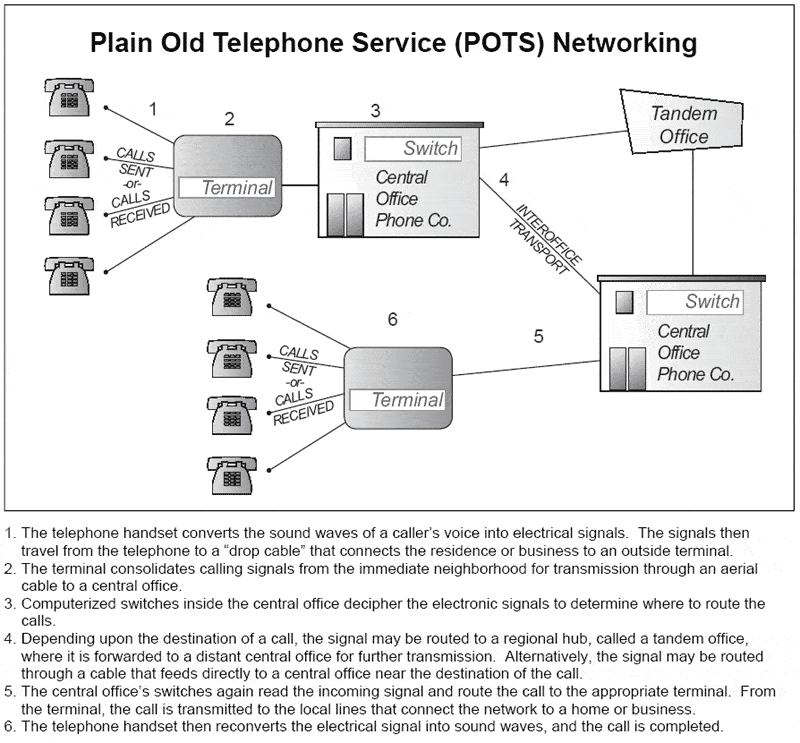
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS)
POTS stands for Plain Old Telephone Service and it is the basic analog telecommunications service provided by a local telco.
-
Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor is a system tool for monitoring the performance of a Microsoft operating system. (In Windows 9x, Windows 2000, and Windows XP this tool is called System Monitor.)
