In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, there’s one term you’ve likely heard bouncing around more than others: 5G Network. Whether you’ve caught snippets of its promised lightning-fast speeds on the morning news or overheard animated discussions about its potential at the local café, it’s clear that 5G is more than just the latest buzzword—it’s the next big leap in our digital journey.
In this article:
- What is 5G Network?
- Brief History of Mobile Networks
- How 5G Works
- Comparing Generations: 5G vs. 4G
- 5G Network Infrastructure and Deployment
- Safety, Health, and Environmental Concerns
- 5G Devices and Hardware
- Beyond 5G Network: What’s Next?
- Further Reading
Have you ever been in the middle of a gripping online game, or deep into a video call with a dear friend, only for the connection to stutter or drop entirely? Frustrating, right? Well, the pioneers of the 5G Network envisioned a world where these digital hiccups are a thing of the past. But what is this 5G magic, and why is everyone talking about it?

What is 5G Network?
In the simplest terms, 5G network stands for the fifth generation of mobile network technology. As the successor to 4G, it promises not only faster speeds but a revolution in how devices connect and communicate. But before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s take a stroll down memory lane and explore how we got to this pivotal moment in tech history.
Brief History of Mobile Networks
Tracing the trajectory of mobile networks provides an illuminating perspective on technological evolution. The first generation, or 1G, marked the infancy of wireless communication, facilitating analog voice calls. However, as robust as it was for its time, it had its share of limitations, not least of which was susceptibility to interference and eavesdropping. With the inception of 2G, we transitioned to digital transmission, bringing forth not just voice but the advent of SMS and basic data services. 3G then ushered in an era of higher data rates, enabling mobile internet browsing, video calling, and multimedia streaming.
Yet, the real game-changer was 4G, with its broadband-like speeds, low latencies, and efficient IP-based architecture. This paradigm allowed the proliferation of mobile applications, cloud integration, and enhanced user experiences. Now, with 5G, we’re not merely iterating; we’re redefining the entire infrastructure, topology, and potential of wireless communication.
How 5G Works
Delving into the mechanics of 5G requires understanding its foundational shift. Instead of merely amplifying the existing architecture, 5G employs a multi-band spectrum approach, utilizing both the sub-6 GHz frequencies and the millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies, which are north of 24 GHz. This spectrum expansion allows for larger bandwidths, translating to vastly higher data rates.
Furthermore, 5G incorporates Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) technology. Unlike traditional antennas, Massive MIMO arrays can have hundreds of individual antenna elements. This, combined with beamforming, allows the network to focus the signal, creating ‘beams’ directed towards specific users instead of broadcasting in all directions. This leads to a significant enhancement in capacity and efficiency.
On the architectural front, 5G uses network slicing, allowing the creation of multiple virtual networks atop a shared physical infrastructure. Each slice can be tailored to specific needs—be it IoT devices requiring low power and bandwidth or virtual reality systems demanding high throughput and ultra-low latency. In essence, 5G is not just an evolution in speed or capacity—it’s a holistic redesign of how wireless communication is conceptualized and realized.
Comparing Generations: 5G vs. 4G
The progress from 4G to 5G isn’t merely a case of offering faster internet speeds. The leap entails a fundamental restructuring of how our networks operate and what they offer to the end-user. Let’s delve deeper into the primary differences that set 5G apart from its predecessor, 4G.
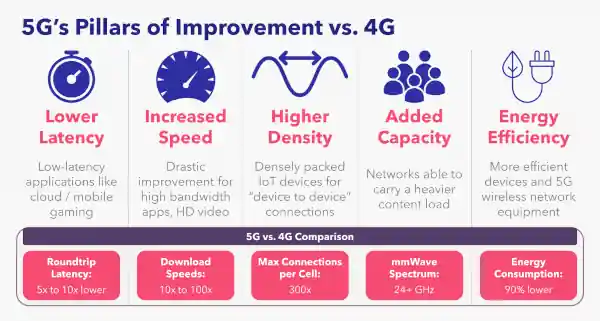
Speed and Latency:
4G: With 4G, we witnessed data transfer rates that were up to ten times faster than its predecessor, 3G. Download speeds on 4G average anywhere from 12-30 Mbps, with peak speeds reaching up to 100 Mbps in some regions. However, the latency on 4G networks typically hovered around 30-50 milliseconds. While this was efficient for most applications and tasks, it wasn’t optimized for real-time experiences like augmented reality or autonomous driving.
5G: When it comes to speed, the 5G network is in an entirely different league. It promises peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, although real-world speeds will be contingent on various factors. Most users can expect gigabit speeds in optimal conditions. Even more impressively, latency is reduced to under 10 milliseconds in optimal scenarios, with potential end-to-end latencies of 1 millisecond for specific applications. This transformative reduction ensures near-instantaneous reactions, critical for applications like real-time gaming, telemedicine, and connected vehicles.
Coverage and Connectivity:
4G: The 4G network was primarily designed with humans in mind—our smartphones, tablets, and computers. It employed large cell towers to cover vast areas, making it efficient for widespread coverage. However, these large cell towers often faced challenges in dense urban areas or intricate landscapes, leading to coverage blackspots.
5G: 5G takes a different approach. Instead of relying solely on massive towers, it uses a combination of large cells and smaller, dense cells known as ‘small cells’. These small cells can be placed on streetlights, rooftops, or other urban infrastructure. This design ensures that 5G can offer a more consistent and reliable connection, even in densely populated areas. Moreover, the 5G Network is designed not just for humans but for machines as well. With the proliferation of IoT devices, 5G’s connectivity matrix can handle billions of devices seamlessly.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
4G: The 4G architecture, while revolutionary in its time, wasn’t particularly energy efficient. As our hunger for data grew, so did the power consumption of 4G infrastructure. While advancements were made over its tenure, energy efficiency wasn’t a focal point of its design.
5G: Sustainability is at the core of 5G’s ethos. The network’s ability to handle more data, more reliably, and at higher speeds doesn’t come at the cost of power. Advanced algorithms and technologies like network slicing mean that 5G can allocate resources dynamically, depending on the demand. This dynamic allocation reduces power wastage. As a result, 5G networks are expected to be up to 90% more energy efficient per traffic unit than their 4G counterparts.
In conclusion, while 4G played a pivotal role in shaping the digital age we know today, 5G is set to redefine it. It’s not just about faster download speeds, but a holistic improvement in how we interact with the digital world. Whether it’s the Internet of Things, real-time gaming, autonomous driving, or smart cities, 5G stands at the cusp of powering the next generation of technological evolution.
You must also read this: “Choosing the Right Network for Your Business!“
5G Network Infrastructure and Deployment
Understanding the transition to 5G means looking beyond the devices in our hands to the extensive network infrastructure that underpins this transformative technology. As we navigate through the intricacies of 5G deployment, we’ll explore not just the foundational components but also the current status of its rollout and the collaborations powering this advancement.
Network Infrastructure Essentials:
Small Cells
Contrary to the massive towers commonly associated with previous generations, 5G leans heavily on ‘small cells’. These compact, low-power stations are integral to achieving the low latency and high speeds characteristic of 5G. Strategically positioned in urban landscapes—on buildings, streetlights, or other fixtures—they facilitate dense network coverage, especially in populated areas.
Massive MIMO
This is one of the bedrocks of 5G’s increased capacity. MIMO, which stands for Multiple Input, Multiple Output, uses numerous tiny antennas to serve multiple users simultaneously. 5G ramps this up with ‘Massive MIMO’, deploying potentially hundreds of antennas on a single array.
Edge Computing
To achieve the ultra-low latencies that certain applications demand, 5G incorporates edge computing. By processing data closer to its source (i.e., near where it’s generated), 5G can significantly reduce response times.
Global Rollout Status and Challenges:
Status
In August 2023, 5G was in varying stages of deployment across the globe. Many developed nations had initiated extensive 5G rollouts in urban centers, with plans to expand further.
Challenges:
- Spectrum Availability: One of the pivotal challenges is securing the appropriate spectrum bands for 5G, as it requires specific high-frequency bands to deliver its promised speeds.
- Infrastructure Costs: Deploying small cells en masse is capital intensive, demanding significant financial resources.
- Geographical Limitations: Regions with complex terrains or sparse populations pose unique challenges for 5G deployment due to the network’s reliance on densely populated cell sites.
- Security Concerns: With heightened connectivity comes increased vulnerability. Addressing these security concerns is paramount to ensure the safe operation of 5G networks.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
The enormity of the 5G transition necessitates collaborative efforts.
1. Telecom Operators and Tech Giants
Major telecom providers have collaborated with technology giants to facilitate 5G’s rollout. Partnerships, like those between Verizon and Samsung or AT&T and Nokia, underscore the blend of telecommunication and technology expertise required.
2. Government Initiatives
Many governments have recognized the strategic importance of 5G, facilitating public-private partnerships to expedite its deployment.
R&D Collaborations
Research into optimizing 5G technologies has often been a collaborative endeavor. Universities, tech companies, and independent research bodies have jointly ventured into several projects to refine and enhance 5G capabilities.
In essence, 5G’s transition isn’t just about a leap in speed or connectivity—it embodies a global movement, redefining how we conceive and interact with digital spaces. The blend of innovative infrastructure, ongoing global deployment, and myriad collaborations promises a future where 5G becomes as ubiquitous as the air we breathe.
Safety, Health, and Environmental Concerns
In the realm of technology, especially one as groundbreaking as 5G, concerns about safety, health, and the environment are inevitable. As 5G permeates our lives, it’s crucial to address these concerns head-on, differentiating between fact and fiction.
Addressing Health Myths:
Radiation Concerns
One of the most pervasive myths about 5G is that it uses harmful radiation levels that could adversely affect human health. However, the radio frequencies used by 5G fall within the non-ionizing range, meaning they don’t possess enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules or to damage DNA directly.
World Health Organization’s Stance
The WHO has classified radiofrequency electromagnetic fields, like those used by 5G, as possibly carcinogenic to humans, in the same category as pickled vegetables and talcum powder. It’s crucial to note that this classification is based on limited and inconclusive evidence.
Heat Concerns
Another myth revolves around 5G causing harmful levels of heat. While radio frequencies can produce heat, the levels produced by 5G are too low to raise temperatures in human tissue.
Environmental Impacts of 5G:
Energy Consumption
5G networks are designed to be up to 90% more energy-efficient per traffic unit than 4G. However, the sheer volume of 5G base stations could raise overall energy consumption. Strategies to make base stations more energy-efficient are ongoing.
E-waste
As consumers transition to 5G-compatible devices, there’s a potential increase in electronic waste. Manufacturers and policymakers are urged to establish robust recycling programs to mitigate this.

5G Devices and Hardware
As 5G networks unfurl across the globe, hardware manufacturers are in an arms race to produce devices that can harness the full potential of this revolutionary technology.
Latest 5G Smartphones:
Samsung Galaxy Series
As of 2021, Samsung’s Galaxy S21 and Note series were among the flagship phones offering 5G capabilities, with the promise of faster downloads, seamless streaming, and instant sharing.
Apple iPhone
The iPhone 12 and subsequent models rolled out with 5G compatibility, ensuring that Apple aficionados aren’t left behind in the 5G transition.
OnePlus
Known for their performance-centric phones, OnePlus’s latest models, like the OnePlus 9, come 5G-ready.
Routers and Hotspots:
Netgear Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot
This has been a popular choice for those wanting to experience 5G speeds on the go. With an impressive battery life and the ability to support multiple devices, it’s a testament to 5G’s potential.
Huawei 5G CPE Pro
Designed for home or office use, this router seamlessly converts 5G signals into super-fast Wi-Fi.
5G-Compatible IoT Devices:
Connected Cars
Many automobile manufacturers are integrating 5G into their latest models, ensuring that vehicles can communicate in real-time with other devices, enhancing safety and functionality.
Smart Cities Infrastructure
From traffic lights to surveillance cameras, urban infrastructure is undergoing a transformation with 5G-enabled IoT devices.
Healthcare Devices
5G-compatible wearable devices and monitors allow real-time health tracking and quicker data transfer, paving the way for telemedicine’s future.
The proliferation of 5G-compatible devices is just the beginning. As the technology matures and becomes more ubiquitous, the devices we use daily—whether it’s our smartphones, cars, or household appliances—will become more interconnected, smarter, and more efficient, all thanks to 5G’s unparalleled capabilities.
Beyond 5G Network: What’s Next?
The digital renaissance catalyzed by 5G is just the beginning of a broader technological evolution. While we’re still in the midst of grasping 5G’s transformative potential, visionaries and innovators are already gazing beyond the horizon, contemplating what the post-5G era might look like. The future appears to be a cohesive blend of enhanced connectivity, intelligent algorithms, and a vision of truly global communication.

Integrating AI and Machine Learning:
Self-Optimizing Networks
Imagine networks that can self-diagnose and repair, optimizing their performance based on real-time feedback. With the fusion of AI and 5G, networks will become more autonomous, making real-time decisions to optimize traffic flow, reduce latency, and enhance user experience.
Personalized User Experiences
Machine learning thrives on data. With 5G’s enhanced data transfer capabilities, devices can learn from users’ behaviors and preferences faster, ensuring tailored experiences. Whether it’s content recommendations, targeted advertising, or health insights, the convergence of 5G and machine learning promises a world where technology anticipates our needs.
Advanced Security Protocols
The integration of AI with 5G can revolutionize cybersecurity. AI algorithms can detect anomalies in data patterns, flagging potential security threats in real-time, making digital spaces more secure.
Potential for Global Connectivity:
Bridging the Digital Divide
Despite our interconnected age, significant portions of the global population remain offline. The next step beyond 5G aims to bridge this divide, ensuring that remote and underserved regions get connected. Projects like satellite internet, helmed by initiatives like SpaceX’s Starlink, envision a world with truly ubiquitous internet coverage.
Seamless Connectivity Across Platforms
The post-5G world might redefine our notion of networks. Instead of distinct cellular, Wi-Fi, and satellite networks, we might witness a convergence, ensuring seamless transitions and constant connectivity, regardless of location or platform.
Interconnected Devices on a Global Scale
With the enhanced capabilities of post-5G technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) will not just be a network of devices but a global ecosystem. Devices across continents will communicate in real-time, making our world more synchronized and responsive.
In conclusion, while 5G is redefining our present, the visionaries of tech are sculpting a future that promises even more profound transformations. The nexus of ultra-fast connectivity, intelligent algorithms, and a dream of a globally connected world will shape the digital tapestry of tomorrow. The journey beyond 5G beckons, promising wonders we’re just beginning to fathom.
Further Reading
The fascinating journey through the world of 5G is just the tip of the iceberg. For those with an insatiable curiosity, the depth and breadth of resources available are boundless. From technical papers to comprehensive books, let’s delve into some of the most recommended resources that can satiate your thirst for knowledge on the 5G network.
Books:
“The 5G Myth: And Why Consistent Connectivity is a Better Future” by William Webb
This insightful read challenges popular notions about 5G and sheds light on what connectivity can truly mean for the future.
“5G Explained: Security and Deployment of Advanced Mobile Communications” by Jyrki Penttinen
A comprehensive guide that goes into the intricacies of 5G’s security challenges and its deployment strategies.
“5G for the Connected World” edited by Devaki Chandramouli and Rainer Liebhart
This is a compilation of contributions from various experts, offering a wide perspective on 5G’s potential and challenges.
Websites:
- GSMA: As the global body representing mobile operators, GSMA regularly updates with reports, news, and insights on the latest in 5G developments.
- 5G.co.uk: This website offers updated news, guides, and analysis of 5G in the UK and around the world.
- RCR Wireless News: A reputable source for the latest telecom news, including in-depth features and reports on 5G technology.
Papers & Journals:
“A Survey on 5G: The Next Generation of Mobile Communication”
Published in Physical Communication.
This paper provides a detailed overview of the potential technologies that could shape the evolution of 5G. [Read the Abstract]
“5G Spectrum Research”
From IEEE Communications Magazine.
An exploration of the crucial role of spectrum allocations in the realization of global 5G services. [Read the Abstract]
“Challenges in 5G: How to Empower SON with Big Data for Enabling 5G”
In IEEE Network.
This paper merges the world of Big Data with 5G, examining the challenges and possibilities therein.
[Read]
These resources are just a starting point. The world of 5G is expansive and constantly evolving. Regularly visiting academic journals, attending webinars, and staying updated with industry news can provide a holistic understanding of this dynamic field. Happy reading!