The evolving landscape of networking often involves juggling between different types of cables, signals, and devices. One essential but often overlooked component that aids this interconnection is the Balun—a device that converts between balanced and unbalanced signals. Understanding how Baluns work can significantly impact the effectiveness and reliability of your network, especially in mixed environments that require both types of connections. In this article, we’ll explore what Balun is, its various types, and why it’s crucial for today’s networking needs.
Jump to:
- What is a BALUN?
- Balanced and Unbalanced Signals
- Why Use a Balun?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
1. What is a BALUN (in networking and telecommunication)?
Stands for bal anced un balanced. BALUN is a device used to connect balanced lines and unbalanced lines. Balanced and unbalanced lines have different electrical characteristics. A balun matches these characteristics by providing impedance transformation between the two different lines.
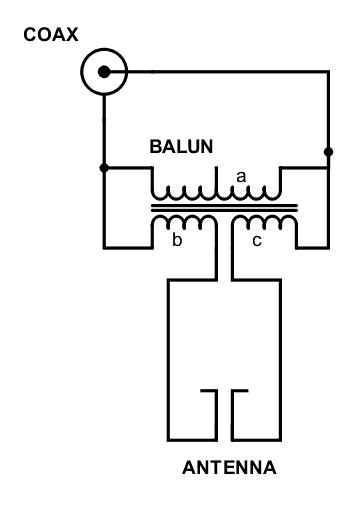
2. Balanced and Unbalanced Signals
- Balanced Signal: In a balanced signal, two conductors are used, and both carry opposite phases of the signal. This design helps to cancel out noise and is commonly found in twisted-pair cables like Ethernet.
- Unbalanced Signal: In an unbalanced signal, one conductor carries the signal while the other serves as a ground reference. This kind of signaling is usually found in coaxial cables and is more susceptible to electrical noise.
3. Why Use a Balun?
Using a balun allows you to connect devices that use balanced connections with those that use unbalanced connections without causing signal degradation or introducing additional noise. For example, you may need a balun to connect a device with a coaxial output (unbalanced) to a device with a twisted-pair input (balanced).
Types of Baluns
- Impedance-matching Baluns: These baluns not only convert between balanced and unbalanced signals but also match the impedance levels of the connected devices.
- Voltage Baluns: These baluns are designed to ensure that the voltage levels remain consistent between the balanced and unbalanced sides.
- Current Baluns: These baluns aim to maintain the same current on both the balanced and unbalanced sides of the connection.
Common Uses
Baluns have been pivotal in making diverse types of networking connections possible. Their versatility extends not just to different types of cables, but also to various kinds of data signal requirements. Here are some common uses of Baluns, incorporating both traditional and more modern applications:
Traditional Uses:
- Twisted-pair cabling to coaxial cabling: One of the classic uses of Baluns is to connect 10BaseT networks with IBM 3270 equipment running on coax or twinax networks. This allows for seamless data flow between fundamentally different cable systems.
- Twisted-pair cabling to token ring cabling: Baluns can be used to match token ring Type 1 cabling to standard unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cabling. This helps in integrating 10BaseT or faster hubs or adapters with RJ-45 ports into a token ring network, thus extending its usability.
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) cabling to token ring cabling: In campus backbone networks, Baluns can be utilized for connecting high-speed ATM hubs to token ring networks. This allows for the amalgamation of high-speed data transmission lines with legacy systems.
Modern Uses:
- Home Entertainment Systems: With the prevalence of smart homes, Baluns are used to connect modern home entertainment systems that use balanced HDMI signals with older, unbalanced coaxial cable networks in the house.
- CCTV and Security Systems: Baluns are often used in modern security systems to convert the balanced signal from the camera to an unbalanced signal that can be transmitted over long distances via coaxial cables, without significant loss of quality.
- Broadcast and Streaming Services: In media production, Baluns can be used to adapt professional-grade, balanced audio and video connections to unbalanced connections, facilitating easier integration with existing infrastructure.
- Industrial Automation: In factories and production lines that employ a mixture of new and legacy systems, Baluns are used to connect modern Ethernet-based control systems with older serial or coaxial systems.
By understanding these common uses, you’ll appreciate how Baluns continue to play a critical role in making various networking configurations compatible, even as technology evolves.
4. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What does Balun stand for?
A: Balun stands for “Balanced-Unbalanced,” indicating its role in converting between balanced and unbalanced signals.
Q: Why would I need to use a Balun in my network?
A: Using a Balun allows for the interconnection of devices that utilize different types of signaling, helping to preserve signal integrity and reduce noise.
Q: Are there different types of Baluns?
A: Yes, there are various types, including impedance-matching, voltage, and current baluns, each serving specific needs in balancing signal and impedance levels.
Q: Can a Balun reduce noise in a system?
A: Yes, converting an unbalanced signal to a balanced signal using a Balun can help minimize electrical noise.
Q: Is a Balun necessary for every type of networking cable?
A: No, a Balun is generally used when you need to connect devices that use different types of signals (balanced and unbalanced) or different types of cables like coaxial and twisted-pair.
5. References
Books:
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall – Provides comprehensive coverage of networking basics, including the role of Baluns.
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan – Offers an in-depth look at network devices and technologies, including Balun.
Websites:
- Cisco’s Official Website – Contains various resources and articles that discuss the technical aspects of Baluns in networking. Cisco Official Website
- Network Engineering Stack Exchange – A community-driven platform that often discusses the practical applications and troubleshooting involving Baluns. Network Engineering Stack Exchange