Definition of Defense Messaging System in the Network Encyclopedia.
What is Defense Messaging System (DMS)?
Defense Messaging System, also known as DMS, is a program established by the U.S. Undersecretary of Defense (Acquisition) to develop an integrated, global messaging system for transferring classified and unclassified data.
The Defense Messaging System (DMS) will replace the existing Automatic Digital Network (AUTODIN) system currently in use by the U.S. Department of Defense.
Microsoft Exchange DMS, a version of Microsoft Exchange Server, complies with the DMS specification. It is suited for government agencies that are required to use DMS-compliant products and for companies that do defense business with the U.S. government.
Exchange DMS technology can be purchased only through Lockheed Martin Federal Systems.
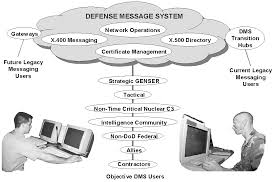
Defense Message System components
DMS includes interfaces to the messaging systems of other Government Agencies, Allies, Defense contractors, and other approved activities. DMS Transition Hubs (DTH) through FY 2003 provided legacy, non-DoD, and allied interoperability. The MROC defines the primary DMS objective as reducing costs and staffing requirements for DoD messaging services. Secondary objectives are to improve messaging security and service.
DMS capabilities have evolved over time since the initial Release 1.0 version to the current fielded version of Release 3.0 Gold. These releases introduced new capabilities and requirements, sometimes with actual new components, including randomly upgraded security solutions. Release requirements are defined by the Services and Agencies, the direction of COTS and Government-Off-The-Shelf (GOTS) technology, including the updates and fixes introduced via service packs.
Release 3.0 Gold has been fielded for some time with periodic updates occurring via Field Engineering Notices (FENs) and Information Assurance Vulnerability Alerts (IAVAs). Updated Release 3.0 Gold capabilities are under test and will be introduced to the users as Maintenance Release FENs.
Defense Message System deployment
The deployment of DMS Release 3.0 Gold presented some technical challenges. The most significant challenges were:
- The transition from MISSI v1 certificates to X.509 version 3 certificates,
- The deployment of a directory infrastructure capable of supporting ACP 120 attributes with no disruption of the existing Message Security Protocol (MSP) 3.0 system, and
- The initial implementation of MGS coexistent with DMS HGS.
The requirement to upgrade every organizational user’s software at the desktop, including upgrading servers and the backbone infrastructure, increased the challenge of deploying Release 3.0 Gold. The DMS Release 3.0 Deployment Methodology concentrated on providing the logical steps and sequences of events that enabled a successful deployment of DMS Release 3.0. Ultimately the successful deployment was dependant upon each individual’s skill and knowledge base.
Medium Grade Services coexist with DMS HGS with the installation of DMS Release 3.0 in that the DMS User Agent will contain coexistent High Grade Service and Medium Grade Service capability. MGS will use DoD PKI class 3 certificates for security services, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) as the transport protocol, and the Global Directory Service. The transport for MGS will be the DISN network, but not as part of the DMS Message Transfer System (MTS). The directory and security services are provided separately. Although MGS implementation is a DMS site issue, the DMS program office will assist in ensuring that messaging, directory, and security services are available to DMS MGS users, but is not directly responsible for the implementation of these services.