Have you ever wondered how large-scale systems manage to organize their network resources so efficiently? The answer often lies in directory services like X.500, and today, we’re diving into one of its pivotal components—Directory Access Protocol (DAP).
In this article:
- What is the DAP Protocol?
- Key Components of DAP
- Communication Mechanisms
- Operations Supported by the DAP Protocol
- Understanding DAP Messages
- Directory Access Protocol Security Features
- Advantages and Limitations of the DAP Protocol
- DAP vs LDAP
- Alternative Protocols
- Real-World Applications
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- References
1. What is the DAP Protocol?
So, you might be asking, what exactly constitutes the DAP Protocol? The DAP Protocol is a set of rules and conventions for how applications and services interact with X.500 directory services. These rules define the format, timing, sequencing, and error-handling procedures for data exchange. Essentially, the DAP Protocol is the “rulebook” that standardizes how Directory User Agents (DUAs) and Directory System Agents (DSAs) communicate.
The protocol is designed to handle complex queries and modifications, making it ideal for intricate systems where high granularity of data access is required. When you initiate a directory query or update, the protocol takes care of everything from packaging your request to ensuring the reliability and security of the data transfer.
What is X.500?
Before we can fully appreciate DAP, we need to understand its parent—X.500. X.500 is a series of computer networking standards covering electronic directory services. These standards came about in the 1980s and have provided the backbone for a variety of applications requiring directory services.
How Does DAP Fit Into X.500?
DAP serves as the communication layer between the user’s system and the directory service in X.500. Imagine it as the interpreter that translates human queries into a language the directory system can understand.
2. Key Components of DAP
Two main agents work hand in hand within DAP:
Directory User Agent (DUA)
This is the client-side component. Whenever you query a directory service, DUA takes your request, translates it, and sends it off to the server.
Directory System Agent (DSA)
Think of DSA as the gatekeeper at the server end. It receives the requests, processes them, and returns the results to DUA.
3. Communication Mechanisms
When it comes to the communication framework within DAP, there are two key aspects that deserve attention: Data Encoding and Transmission Techniques.
Data Encoding
The use of Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) in DAP isn’t just a random choice. ASN.1 provides a level of abstraction, allowing for consistent data formatting across multiple platforms and programming languages. This is crucial because directory services often need to operate in heterogeneous environments, where multiple different systems need to interact seamlessly.
Transmission Techniques
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model serves as the transport mechanism for DAP. The OSI model, with its seven-layer protocol stack, allows DAP to be highly interoperable and flexible. Specifically, DAP usually operates at the application layer of OSI, providing a way to abstract the lower-level networking complexities. This enables developers to focus more on directory operations and less on networking hurdles.
4. Operations Supported by the DAP Protocol
DAP supports a variety of operations that facilitate interactions with the directory services. Let’s dig into them:
- Read: This operation allows users to retrieve existing information from the directory. With a Read request, you can fetch user profiles, network configurations, or any other data stored in the directory.
- Modify: The Modify operation empowers you to alter data in the directory. This could range from changing a user’s email address to updating security protocols.
- Add: Want to include a new user or a new network node? The Add operation allows you to introduce new entries into the directory service.
- Delete: This operation is pretty self-explanatory; it enables you to remove existing entries from the directory service. Whether you’re de-provisioning a user or decommissioning hardware, the Delete operation has you covered.
5. Understanding DAP Messages
The interaction between the client (DUA) and server (DSA) in DAP is facilitated through a series of request and response messages. Here’s what you need to know:
- Request Messages: These are initiated by the DUA and contain specific instructions for the kind of operation the client wishes to perform—be it Read, Modify, Add, or Delete.
- Response Messages: Once the DSA receives a request, it processes it and sends back a response message. This message contains the outcome of the operation—success, failure, or any other status information.
Each of these messages is encoded in ASN.1 format, maintaining consistency and interoperability.
6. Directory Access Protocol Security Features
When we talk about security in DAP, it isn’t just a side note; it’s a robust, built-in feature set designed to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
Authentication
DAP employs strong authentication mechanisms, typically in the form of digital certificates. These certificates are used to verify the identity of both the client and server, reducing the risk of impersonation or man-in-the-middle attacks.
Encryption
To maintain confidentiality, DAP uses high-level encryption algorithms. The data that travels between the DUA and DSA is encrypted, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to decipher it.
7. Advantages and Limitations of the DAP Protocol
Let’s look at the two sides of the coin—the good and the not-so-good aspects of DAP.
Advantages
- Robustness: DAP is designed to handle complex queries and directory structures, making it incredibly powerful for large-scale and intricate systems.
- Security: With its built-in authentication and encryption mechanisms, DAP offers a secure environment for data exchange.
Limitations
- Complexity: While its robustness is an advantage, DAP’s complexity can be a downside too. The steep learning curve and intricate setup processes can make it less appealing for small or straightforward applications.
- Resource-Heavy: DAP’s rich feature set comes at the cost of high resource consumption, making it less ideal for resource-constrained environments.
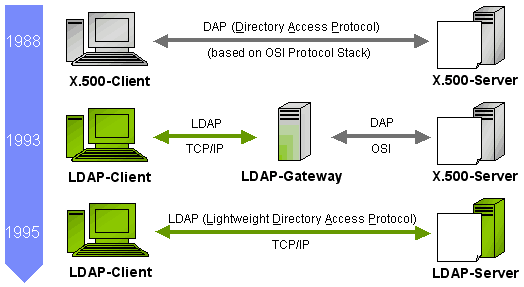
8. DAP vs LDAP
If you’ve dabbled in directory services before, you’ve likely heard of LDAP—Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. So how does DAP stack up against LDAP? Let’s break it down.
Complexity
DAP is known for its complexity and robustness, which comes with both advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, it can handle more complicated directory architectures and security requirements. However, this often results in a steeper learning curve and can be overkill for simpler applications.
LDAP, as the name suggests, aims to be a lightweight alternative to DAP. It simplifies many operations, making it easier to implement and manage but less suitable for complex directory structures.
Resource Utilization
DAP, with its extensive feature set, typically demands more system resources. It’s not uncommon for DAP-based solutions to consume more memory and CPU, which might be a concern for resource-constrained systems.
LDAP, on the other hand, is optimized for lower resource utilization, making it a more viable option for smaller systems or applications where performance is a top priority.
Security Features
Both DAP and LDAP offer robust security mechanisms, but DAP goes above and beyond when it comes to built-in security features like encryption and authentication. These features make DAP particularly suitable for environments where high-security measures are needed.
LDAP also offers various security options but usually requires additional configuration and third-party extensions to reach the same level of security offered by DAP out-of-the-box.
Adaptability
While DAP is inherently tied to the X.500 standard, LDAP offers more flexibility and is often used with various directory services, not just X.500. This makes LDAP a more adaptable option if you’re working with different types of directory services.
9. Alternative Protocols
When it comes to directory services, DAP isn’t the only game in town. There are other protocols you might want to consider, depending on your specific needs.
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
We’ve touched on LDAP earlier, but it’s worth mentioning again as it’s perhaps the most widely used alternative to DAP. Its lightweight design makes it easier to implement and manage. LDAP is often used in internet-facing applications and is supported by many commercial products.
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
While not a directory access protocol per se, SOAP can be used for similar purposes. SOAP is a messaging protocol that allows programs to run on disparate operating systems to communicate using HTTP and XML.
JSON-RPC and RESTful APIs
Modern directory services are increasingly offering RESTful APIs or JSON-RPC interfaces, which use JSON-formatted messages. These methods are particularly popular for web-based applications and services due to their simplicity and ease of use.
10. Real-World Applications
Understanding the theoretical aspects of the Directory Access Protocol is great, but how is it actually used in the real world?
Enterprise Directory Services
In large organizations with complicated directory structures, DAP can serve as the backbone for robust enterprise-level directory services.
Telecommunications
The telecommunications sector uses DAP for its phone number directories and customer databases. The protocol’s robust security features are particularly beneficial here to ensure customer data is kept secure.
Healthcare Systems
Healthcare organizations often have complex and sensitive directory needs. DAP’s strong authentication and encryption make it a viable option for such critical applications.
Government and Defense
Given its high level of security and robustness, DAP is often employed in highly sensitive governmental and defense systems where data integrity and security are of utmost importance.
11. Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Directory Access Protocol (DAP)?
- The Directory Access Protocol, or just DAP, is a protocol for accessing information in a directory service, typically based on X.500 standards.
- How does DAP differ from LDAP?
- DAP is more complex and robust, whereas LDAP is a lightweight alternative designed for simpler applications.
- What are DUA and DSA in DAP?
- DUA (Directory User Agent) is the client-side component, and DSA (Directory System Agent) is the server-side component in DAP.
- Is DAP secure?
- Yes, DAP offers robust security features including authentication and encryption.
- Where is DAP commonly used?
- DAP is often used in large enterprise solutions and specialized systems requiring robust directory services.
12. Conclusion
So there you have it—a deep dive into the DAP Protocol and how it empowers X.500 directory services. Whether you’re setting up an enterprise-level network or working on an IoT project, understanding DAP can be your key to unlocking more effective directory services.
13. References
- RFCs
- Books
- “Understanding LDAP – Design and Implementation” by IBM Redbooks