Definition of Dual Boot in the Network Encyclopedia.
What is Dual Boot?
Dual Boot is a computer that can boot one of several operating systems by means of a startup menu.
You can have multiple operating systems installed on a single PC. Having two operating systems installed – and choosing between them at boot time – is known as “dual-boot.”
An example is a machine on which Windows 98 and then Windows NT has been installed. The user can utilize the Windows NT boot loader menu to choose which operating system to run at startup.
The computer’s operating system is generally installed on its internal hard drive. When we boot our computer, the BIOS loads the boot loader from the hard drive and the boot loader boots the installed operating system.
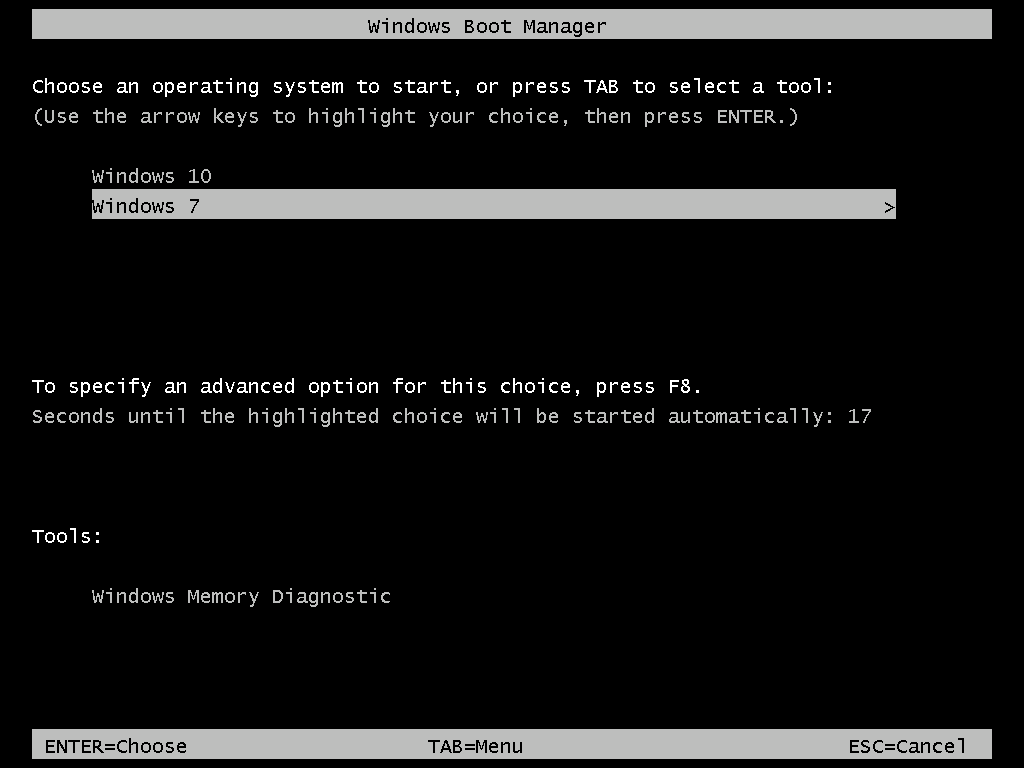
Windows NT supports dual booting with other operating systems, but this is neither recommended nor supported by Microsoft. Dual boot systems are typically used in hobbyist and test networks in which a variety of operating systems are used to test different networking functions, or when the number of available machines is fewer than needed to perform the tasks.
Setting Up a Dual-Boot System
Setting up a dual-boot system is fairly easy. Here’s a quick overview of what to expect:
- Dual Boot Windows and Linux: Install Windows first if there’s no operating system installed on your PC. Create Linux installation media, boot into the Linux installer, and select the option to install Linux alongside Windows. Go to Ubuntu’s web site to download the latest image.
- Dual Boot Windows and Another Windows: Shrink your current Windows partition from inside Windows and create a new partition for the other version of Windows. Boot into the other Windows installer and select the partition you created. Read this article to learn about dual boot with Windows 7 and 8.
- Dual Boot Linux and Another Linux: You should be able to dual-boot two Linux distributions by installing one first and then installing the other. Choose to install the new Linux system alongside your old Linux system. Resize your old Linux partitions in the installer and create new ones to make space if the installer won’t do this automatically.
- Dual Boot Mac OS X and Windows: The Boot Camp utility included with Mac OS X allows you to easily set up a Windows dual-boot system on your Mac.
- Dual Boot Mac OS X and Linux: Boot Camp doesn’t allow you to set up a dual-boot Linux system, so you’ll need to do a bit more footwork here. Follow this guide to installing Linux on a Mac for more details.