Group Policy is a group of settings that are applied to a subset of Active Directory objects in Microsoft Windows Operating Systems.
What is Group Policy?
A group of settings that are applied to a subset of Active Directory objects in Microsoft Windows. Group policies are created and assigned using Group Policy, a snap-in for the Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Group policies are typically used to simultaneously configure the desktop working environments of a group of users, but they have many other uses as well. Group policies can be used to:
- Manage applications – for example, by configuring policies to allow users to install applications published in Active Directory, or to automatically install or upgrade applications on their machines
- Redirect folders from the Documents and Settings folder on a user’s local machine to a share on the network
- Assign scripts for startup, shutdown, logon, and logoff events
- Manage security – for example, to control users’ access to files and folders, control user logon rights, and configure account lockout restrictions
- Manage software – for example, to configure user profiles such as desktop settings, Start menu, and other common settings
Group policies can be assigned to domains, sites, or organizational units (OUs). To create and configure a group policy, use Group Policy to create a new Group Policy object (GPO). Group policies are applied to users when they log on and to computers when they boot up. If two policies apply to a user or computer, and they do not conflict, they are applied in a cumulative fashion. Users are subject to group policies that apply to them as users and to group policies that apply to the computer at which they are working.
For advance information about Group Policy in Active Directory check this Technet article: Understanding the Structure of a Group Policy Object
Local Group Policy
Each computer running Windows 2000, Windows XP Professional, Windows XP 64-bit Edition (Itanium), or a Windows Server 2003 operating system has exactly one local Group Policy object. In these objects, Group Policy settings are stored on individual computers, whether or not they are part of an Active Directory environment or a networked environment. For more information, see Security Settings extension to Group Policy, Folder Redirection, and Group Policy Software Installation overview.
Local Group Policy objects contain fewer settings than nonlocal Group Policy objects, particularly under Security Settings. Local Group Policy objects do not support Folder Redirection or Group Policy Software Installation.
Because its settings can be overwritten by Group Policy objects that are associated with sites, domains, and organizational units, the Local Group Policy object is the least influential object in an Active Directory environment. In a non-networked environment (or in a networked environment that does not have a domain controller), the Local Group Policy object’s settings are more important, because they are not overwritten by other Group Policy objects.
To edit the local Group Policy object that is stored on your local computer, use the Group Policy Object Editor snap-in.
- Press Windows Key + R on your keyboard to launch Run prompt. Enter gpedit.msc and hit Enter to open Local Group Policy Editor.
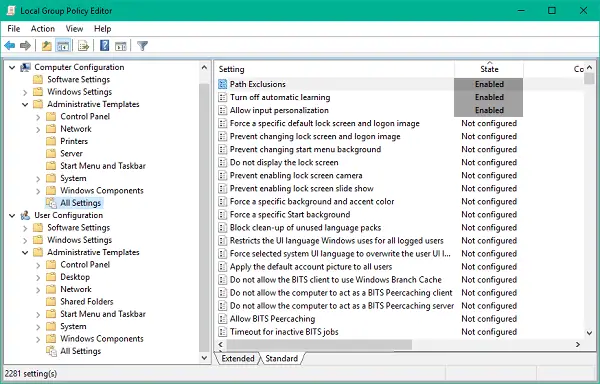
- Navigate to the following path on the left side pane of Group Policy Editor window:
- Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > All Settings
- Proceed with careful
- Now, on the right side window, sort the policy settings by State column so that all those policies which are Enabled/Disabled currently can be accessed on the top.
TIP
A typical use for group policies is to enforce a written company policy across all users in a specific site or domain.