In the world of computer networking, the term “Homogeneous Network” refers to a network architecture where all nodes, devices, and communication protocols are uniform and consistent. This uniformity simplifies management, improves compatibility, and often enhances security. This article delves into the definition of a Homogeneous Network, contrasts it with its counterpart, the Heterogeneous Network, and discusses the implications of such a network setup.
Jump to:
- What is a Homogeneous Network?
- Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Networks
- Implementing a Homogeneous Network
- The Role of Homogeneous Networks in Modern Infrastructure
- Conclusion
- References
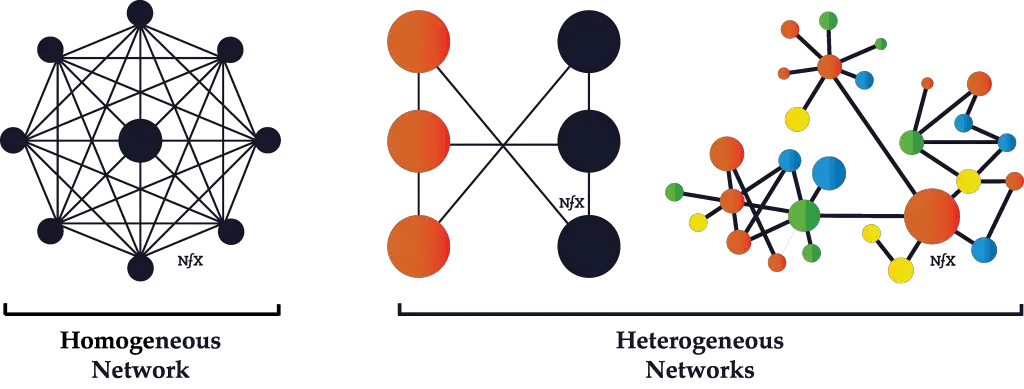
1. What is a Homogeneous Network?
Definition and Fundamentals
A Homogeneous Network is characterized by the use of identical network devices and protocols. It means that the computers, switches, routers, and software standards are consistent across the entire network infrastructure. This homogeneity leads to a network where each component seamlessly interacts with the others, often resulting in a more straightforward setup and fewer compatibility issues.
Advantages of Homogeneity
- Simplified Configuration: With uniform components, configuration is standardized, which can significantly decrease the time and expertise needed to manage the network.
- Easier Troubleshooting: Diagnosing issues becomes less complex when all network devices are the same, as the number of variables in play is reduced.
- Enhanced Security: Standardizing network components can make it easier to apply uniform security measures and policies.
Considerations
- Scalability: Homogeneous networks can sometimes face challenges with scaling, as the addition of different devices or technologies may be required to meet growing needs.
- Flexibility: While uniformity offers simplicity, it can also limit the flexibility to integrate diverse technologies that may offer better performance or features.
2. Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Networks
Contrasting Network Types
A Heterogeneous Network is the antithesis of a Homogeneous Network, containing a mix of computers, operating systems, protocols, and device manufacturers. The diversity within a Heterogeneous Network can offer flexibility and resilience but also introduces complexity in network management.
Comparison Points
- Interoperability: Heterogeneous networks are often designed to be more flexible and can support a broader range of devices and protocols.
- Management: Homogeneous networks are generally easier to manage due to the uniformity of devices and configurations.
- Cost: Homogeneous networks may have lower initial costs due to standardization, while heterogeneous networks can incur higher costs due to the need for additional tools to manage diversity.
3. Implementing a Homogeneous Network
Strategic Planning and Assessment
Implementing a homogeneous network demands a rigorous planning phase. The initial step involves assessing the current and future needs of the organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes understanding the bandwidth requirements, server capacity, network traffic patterns, and potential expansion plans. Decisions made during this phase directly influence the choice of networking equipment and the design of the network architecture.
Vendor Selection: A Critical Decision
Choosing a single vendor or a set of compatible vendors is a pivotal aspect of establishing a homogeneous network. The selected vendor’s technology stack must align with the organization’s performance expectations and budget constraints. Long-term considerations, such as vendor stability, support services, and the frequency of updates, play a crucial role in this selection process. Organizations must evaluate the trade-offs between vendor lock-in and the benefits of a standardized network environment.
Standardization and Deployment
Once the planning is complete, the deployment phase involves standardizing network hardware and protocols. This includes the installation of networking devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls that are identical in model and firmware versions. Consistency in software protocols and configurations is equally critical, ensuring that devices communicate efficiently and adhere to the planned network design.
Training and Documentation
Training for IT staff is essential to effectively manage a homogeneous network. Comprehensive documentation of the network setup and configurations also plays a crucial role in maintenance and troubleshooting. Such documentation acts as a guide for current and future personnel, promoting a consistent understanding and approach to network management.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Post-deployment, continuous monitoring is imperative to ensure the network operates as intended. Evaluation of network performance should be ongoing, with periodic reviews to verify that the homogeneous network continues to meet the organization’s requirements. Monitoring tools can assist in detecting anomalies that may indicate hardware failures or configuration issues, prompting timely interventions.
4. The Role of Homogeneous Networks in Modern Infrastructure
Cloud Integration and Homogeneity
In contemporary IT environments, the integration with cloud infrastructure highlights the role of homogeneous networks. These networks facilitate a more seamless extension to cloud services, ensuring that on-premises equipment is compatible with cloud-based resources. The uniformity in protocols and networking standards simplifies the hybrid cloud models, enhancing the overall efficiency of IT operations.
Homogeneity in the Age of IoT
The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has brought about challenges in network management due to the vast array of devices and protocols. Within this complexity, homogeneous networks serve as a stable backbone in specific layers, such as the data center, where managing a uniform set of technologies enables better security and data processing capabilities.
Evolving Security Dynamics
Homogeneous networks have a significant impact on an organization’s security posture. While they offer the advantage of streamlined security protocol deployment, they also require robust security measures to protect against uniform vulnerabilities that could be exploited across the network. Implementing advanced threat detection systems, enforcing strict access controls, and ensuring regular updates are fundamental to maintaining the security integrity of a homogeneous network.
5. Conclusion
Implementing a homogeneous network can lead to a more controlled and manageable IT environment. The consistency in equipment and protocols allows for streamlined processes, from deployment to maintenance. However, the implementation of such a network must be approached with careful planning, and cognizant of the potential risks and limitations.
As the IT landscape continues to evolve with cloud integration and IoT proliferation, homogeneous networks must adapt, balancing the benefits of uniformity with the need for agility and comprehensive security. The ultimate goal remains to provide a robust, reliable, and secure network that supports the organization’s operations and growth ambitions.
6. References
- “Computer Networks,” Andrew S. Tanenbaum, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall
- “Network Management: Principles and Practices,” Subramanian, M., Addison-Wesley
- “Network Security Essentials: Applications and Standards,” William Stallings, Pearson Education.
- “Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Networks: A Comparative Study,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications
- “Designing and Deploying 802.11 Wireless Networks: A Practical Guide to Implementing 802.11n and 802.11ac Wireless Networks For Enterprise-Based Applications,” Jim Geier, Cisco Press.
- “Enterprise Network Testing: Testing Throughout the Network Lifecycle to Maximize Availability and Performance,” Andy Sholomon, Tom Kunath, Cisco Press.
- “Cloud Networking: Understanding Cloud-based Data Center Networks,” Gary Lee, Elsevier Science