Incremental Zone Transfer is a method of updating zone information in newer implementations of the Domain Name System (DNS). In this article, you can also learn what an AXFR Request is.
What is Incremental Zone Transfer?
Also known as IXFR, is a method of updating zone information in newer implementations of the Domain Name System (DNS).
How IXFR works
Incremental zone transfer is a more efficient method of propagating zone updates than the earlier standard DNS method of transferring the entire zone file using the AXFR request.
Incremental zone transfer is defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 1995 and uses the IXFR request to transfer only the minimal information needed to keep the DNS servers within a given zone of authority in synchronization.
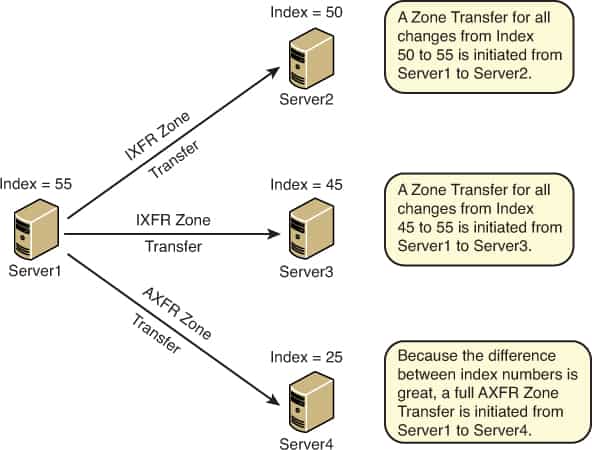
In incremental zone transfer, every primary or master DNS server maintains a full copy of the up-to-date zone file plus an additional version history that records any changes to resource records that occurred during recent updates of the zone file. When a secondary DNS server makes an IXFR request to a primary or master DNS server, the master server compares the zone version number of the secondary server’s zone to its own current version number.
The zone version number is the serial number stored in the start of authority (SOA) record of the DNS server. If the master server has a newer version number and incremental zone transfers are supported, the master server sends to the secondary server only those changes to resource records that have occurred in the time interval between the two version numbers.
If the version numbers of the master and secondary servers match, no zone transfer takes place. And if incremental zone transfer is not supported, the normal full zone transfer takes place instead.
AXFR Request
AXFR Request is a type of Domain Name System (DNS) request in which a secondary DNS server requests the update of information from a master DNS server. An AXFR request always results in a full zone transfer.
This can take time and use considerable network bandwidth if the zone files are large. An alternative to AXFR is the incremental zone transfer protocol described in Request for Comments (RFC) number 1995.
Incremental zone transfers use an IXFR request and transfer only those portions of the zone file that have been changed. Incremental zone transfers are supported by the DNS service running on Microsoft Windows Server Systems.