IP Address (Internet Protocol address) is a 32-bit logical address for a host on a TCP/IP network (IPv4) or 128-bit (IPv6). Each host on a TCP/IP network needs a unique IP address for communication to take place reliably on the network.
How IP Address works
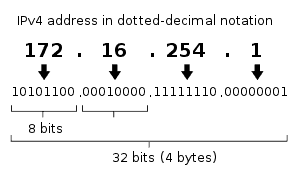
IP addresses are usually expressed in four-octet, dotted-decimal form – w.x.y.z – in which each octet ranges in value from 0 to 255 (with some restrictions). The IP address of a host is partitioned by the network’s subnet mask into two parts, a network ID and a host ID.
IP addresses belong to certain classes according to their first octet, as defined in the following table. The actual distinguishing feature of each class is the pattern of high-order bits in the first octet, but it is easier to remember these classes by their first octet decimal numbers.
IP Address Classes
| IP Address Class | Possible First Octet | Used For |
| Class A | 1–126 | Very large networks |
| Class B | 128–191 | Medium to large networks |
| Class C | 192–223 | Small networks |
| Class D | 224–239 | Multicasting |
| Class E | 240–255 | Reserved (experimental) |
IP addresses whose first octet is 127 represent the loopback address and are used for troubleshooting purposes only, not for naming hosts.
Public IP Addresses
Networks that are directly connected to the Internet must have their IP addresses assigned by the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC) or some other authority. Businesses usually obtain these addresses through their local Internet service provider (ISP). However, firewall and proxy server combinations, which are popular on today’s networks, hide a network’s IP addresses from other hosts on the Internet. These private networks can use any IP addresses they choose, although InterNIC recommends the following IP address blocks for private networks:
- Class A networks: 10.x.y.z
- Class B networks: 172.16.y.z through 172.31.y.z
- Class C networks: 192.168.0.z through 192.16.255.z
Valid IP Address examples
Note the following considerations for valid IP addressing:
- The network ID cannot be 127.
- The network ID and host ID cannot both be 255.
- The network ID and host ID cannot both be 0.
- The host ID must be unique for a given network ID.