Definition of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) in Network Encyclopedia.
What is Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)?
PPTP is a data-link layer protocol for wide area networks (WANs) based on the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) and developed by Microsoft that enables network traffic to be encapsulated and routed over an unsecured public network such as the Internet. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) allows the creation of virtual private networks (VPNs), which tunnel TCP/IP traffic through the Internet.
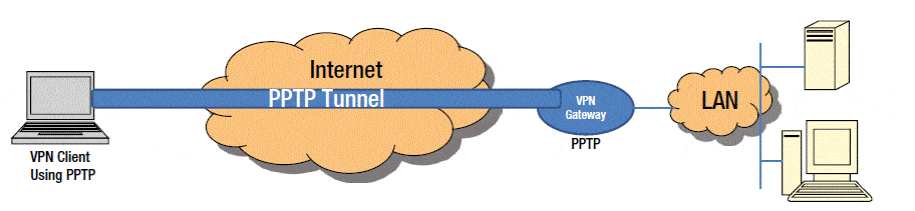
Remote users can securely access corporate local area network (LAN) resources using the Internet instead of having to use direct modem connections over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) or dedicated leased-line connections.
How It Works
PPTP is an extension of PPP and is based on PPP negotiation, authentication, and encryption schemes. PPTP encapsulates Internet Protocol (IP), Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), or NetBEUI packets into PPP frames, creating a “tunnel” for secure communication across a LAN or WAN link. The PPTP tunnel is responsible for authentication and data encryption and makes it safe to transmit data over unsecured networks.
PPTP supports two types of tunneling:
- Voluntary tunneling: Initiated by the PPTP client (such as Microsoft Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, or Windows 2000). This type of tunneling does not require support from an Internet service provider (ISP) or network devices such as bridges.
- Compulsory tunneling: Initiated by a PPTP server at an ISP. This type of tunneling must be supported by network access servers (NAS’s) or routers.
No matter which type of tunneling you use, you must use a PPTP server. Corporations can set up dedicated PPTP-enabled servers on their networks using Windows NT Server.
RAS supports PPTP
Microsoft’s Remote Access Service (RAS) supports PPTP through both dedicated and dial-up Internet connections. To enable Windows Server to act as a PPTP server, click Network in Control Panel, click the Advanced button on the TCP/IP property sheet, and select Enable PPTP Filtering.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol troubleshooting
Because PPTP supports multiple network protocols, including IP, IPX, and NetBEUI, two computers can establish a tunnel over the Internet only if they are running the same network protocol. To troubleshoot PPTP over a TCP/IP connection, use ping to determine whether you are connected to your PPTP server. Also, be sure that you have trusted credentials in the domain of the PPTP server, and be sure that you don’t have an active Winsock Proxy client that might be redirecting PPTP packets to a proxy server instead of to your VPN.
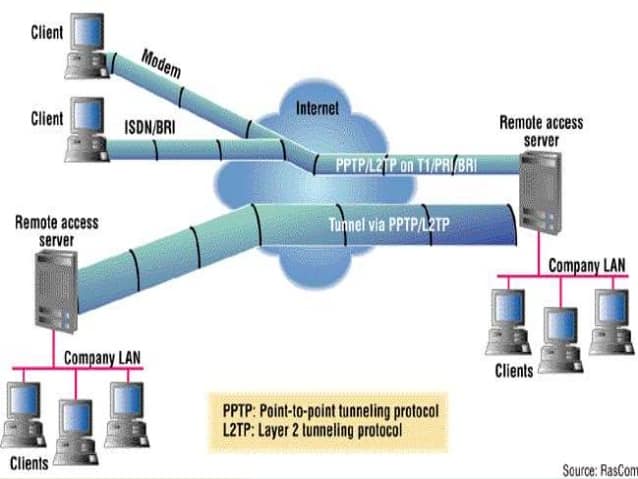
In spite of its age and security shortcomings, PPTP is still used in some network implementations – mostly internal business VPNs in older offices. The advantages of PPTP are that it’s easy to set up, it’s fast, and because it’s built-in on most platforms, you don’t need any special software to use it. All you need to set up a connection are your login credentials and a server address.
However, the fact that it’s easy to use doesn’t mean you should use it, especially if having a high level of security is important to you. In that case, you should use a more secure protocol for your VPN network, such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPSec, or IKEv2/IPSec.