Definition of Regional Bell Operating Company in the Network Encyclopedia.
What is the Regional Bell Operating Company?
The Regional Bell Operating Company, also known as RBOC, is one of the regional telcos that was created as a result of the breakup of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T), or one of their successors. AT&T, which was also known as the Bell System (or “Ma Bell”), was divested in 1983 to end its monopoly control and was broken up into several dozen Bell Operating Companies (BOCs), each of which was to supply telephone services to local loop subscribers in a given geographical region.
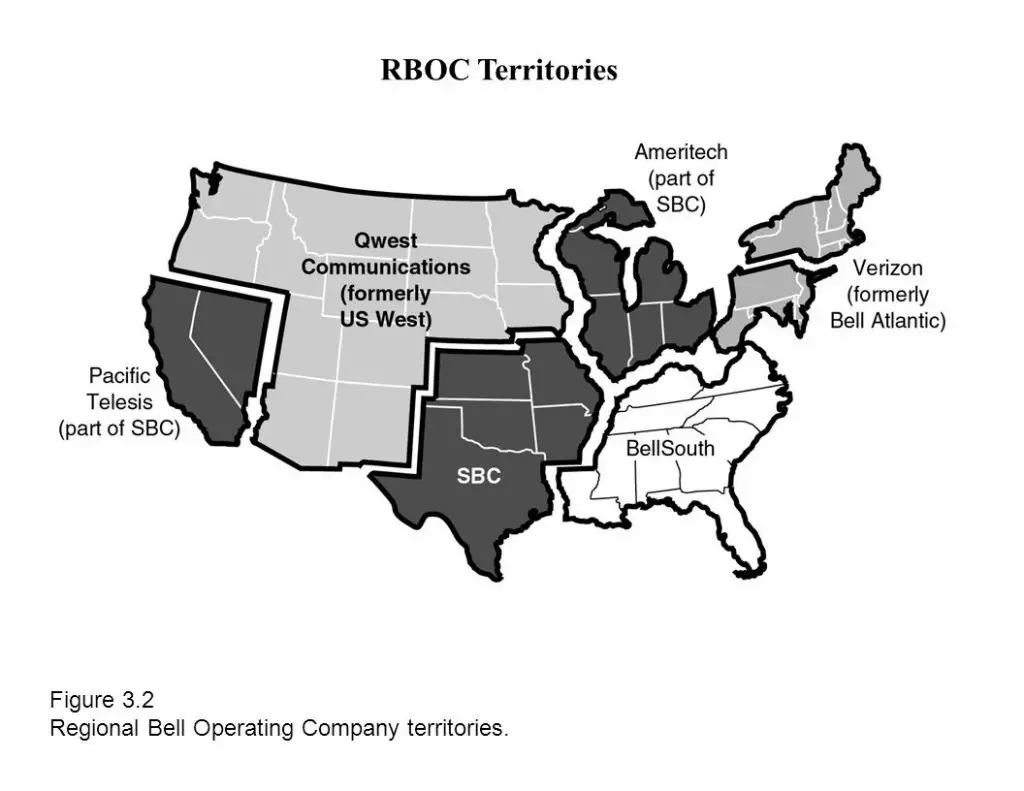
Seven Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs) were also created, each consisting of two or more BOCs. The seven original RBOCs were Ameritech, Bell Atlantic, BellSouth, NYNEX, Pacific Bell, Southwestern Bell, and U S WEST. RBOCs provided local loop services to much of the United States by functioning as local exchange carriers (LECs), while AT&T was left to provide long-distance carrier services and to function as an inter-exchange carrier (IXC). In addition to the RBOCs, dozens of independent LECs serviced different areas.
The telecommunications landscape changed with the passage of the Telecommunications Act of 1996. The act allowed RBOCs and independent LECs to compete with existing IXCs for long-distance carrier business, allowed mergers, and essentially opened up the telecommunications market to all kinds of companies, including cable television companies. Of the seven original RBOCs, only five remained in 2000.
US Telcos today
Many of these companies have since merged; by the end of 2000, there were only three of the original Baby Bells left in the United States. After the 1984 breakup, part of AT&T Corp.’s Bell Labs was split off into Bellcore, which would serve as an R&D and standards body for the seven Baby Bells. In 1997, Bellcore was acquired by Science Applications International Corporation where it became a wholly-owned subsidiary and was renamed Telcordia.
- AT&T Inc – Southwestern Bell Corporation, which changed its name to SBC Communications in 1995, acquired Pacific Telesis in 1997, SNET in 1998, and Ameritech in 1999. In February 2005, SBC announced its plans to acquire former parent company AT&T Corp. for over $16 billion. SBC took on the AT&T name upon merger closure on November 18, 2005. SBC began trading as AT&T Inc. on December 1, 2005 but began re-branding as early as November 21. In 2006 AT&T Inc. purchased BellSouth.
- Verizon Communications – In 1997, NYNEX was acquired by Bell Atlantic (taking the Bell Atlantic name), which later, in 2000, acquired GTE, the largest independent telephone company, and renamed itself Verizon. In 2005, following a protracted bidding war with rival RBOC Qwest, Verizon announced that it would acquire long-distance company MCI. The Verizon and MCI merger closed on January 6, 2006.
- CenturyLink – CenturyLink was originally Century Telephone (CenturyTel), and took its current name in 2009 when it acquired Embarq, the former local operations of Sprint Nextel, which also includes the former operations of Centel. The company, as CenturyTel, had acquired some Wisconsin Bell lines from Ameritech in 1998. CenturyLink announced in April 2010 its intent to buy Qwest for US$10.6 billion. The transaction was completed in April 2011. In August 2011, the Qwest branding was retired and replaced by that of CenturyLink. Qwest, a Denver-based fiber optics long-distance company, had taken over US West in 2000.