Definition of Request for Comments (RFC) in Network Encyclopedia.
What is RFC (Request for Comments)?
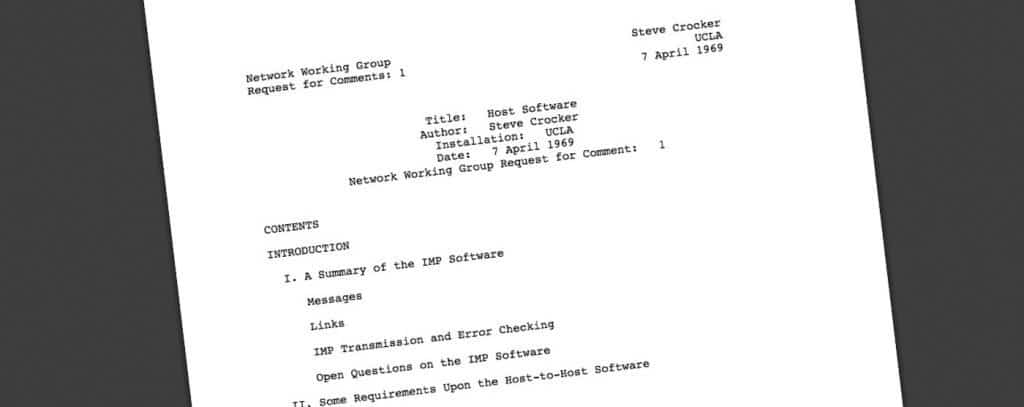
RFC (stands for Request For Comments) is a document that describes the standards, protocols, and technologies of the Internet and TCP/IP. Since 1969, about 2400 Requests for Comments (RFCs) have been published on various networking protocols, procedures, applications, and concepts. The first RFC was published by Steve Crocker and was entitled “Host Software.”

Internet and TCP/IP standards are generated by consensus rather than by committee. Any member of the Internet Society (ISOC) can submit an RFC for consideration, although submission is usually done through the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Once published, an RFC is reviewed by various technical groups and given one of five classifications:
- Required
- Recommended
- Elective
- Limited Use
- Not Recommended
Once an RFC is classified, it is published as an Internet Draft and is discussed and tested by research and technical groups and individuals. It might eventually go through the following stages of development:
- Proposed standard: Stable, well understood, and generally considered useful
- Draft standard: Stable enough to develop implementations of the standard in applications and networking technology
- Internet standard: Technically mature, widely implemented, and significantly beneficial to the Internet community
RFCs are sequentially numbered and published by the RFC Editor at the Information Sciences Institute at the University of Southern California.
NOTE
Old RFCs are not updated, so several RFCs might relate to the same Internet protocol or technology, and some of them might be obsolete. To find the current RFC for a protocol or technology, see the Internet Architecture Board (IAB) Official Protocol Standard published quarterly by the IAB. The following table shows some of the important RFCs for commonly used Internet protocols.
Some Important RFCs for Internet Protocols
| Protocol | RFC(s) |
| ARP | 826 |
| DHCP | 2131, 2132 |
| DNS | 1034, 1035 |
| FTP | 959 |
| HTTP-1.1 | 2068 |
| ICMP | 792 |
| IGMP | 1112 |
| IMAP4 | 2060 |
| IP | 791, 919, 922, 950 |
| IPv6 | 1883 |
| Kerberos | 1510 |
| LDAPv3 | 2251 |
| MIME | 2045, 2046, 2047, 2049 |
| NetBIOS | 1001, 1002 |
| NNTP | 977 |
| OSPFv2 | 2328 |
| POP3 | 1939 |
| PPP | 1661, 1662 |
| PPP-CHAP | 1994 |
| PPP-MP | 1990 |
| RADIUS | 2138 |
| RMON | 1757 |
| RSVP | 2205 |
| SMTP | 821, 822, 974, 1869, 1870 |
| SNMP | 1157 |
| SNMPv2 | 1441 |
| TCP | 793 |
| Telnet | 854, 855 |
| UDP | 768 |