Definition of WEBCASTING in Network Encyclopedia.
What is Webcasting?
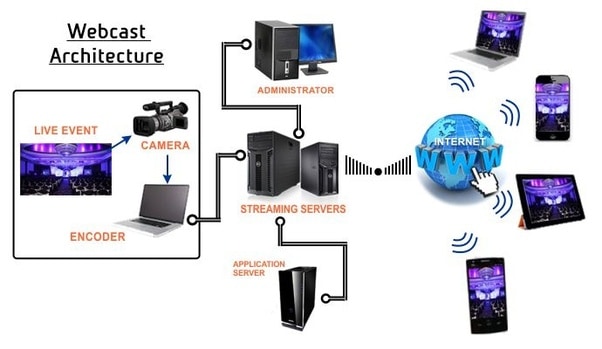
Webcasting is any technology that enables the automatic delivery of information from Web sites on the Internet. For example, you might make use of webcasting to receive a weather report update every 10 minutes. An example of a technology that enables webcasting is the Channel Definition Format (CDF) technology included with Microsoft Internet Explorer versions 4.0 and later.
Examples of Webcasts
Examples of webcasts (live and on-demand) include television programming streamed online, radio content streamed online, and in the commercial sector, investor relations presentations, and e-learning training and seminars. Many companies use webcasting to continue promoting goodwill with their customers. Webcasts can also be monetized through applications like product introductions and client interactions.
Webcasting in Internet Explorer
Webcasting in Internet Explorer can be divided into three categories:
- Basic webcasting: Any existing Web site can be enabled for webcasting without modification to the site format and content. Internet Explorer can be scheduled to “crawl” the site at scheduled time intervals, check for new or updated content, and notify the user of this content or download it for offline browsing. This process is called “subscribing” to the Web site.
- Managed webcasting: An ordinary Web site is turned into an Active Channel Web site when you create a CDF file for the site by using any text editor. The author of the site can optimize and personalize the site and control how it is webcast to users. This is essentially a form of “smart pull” technology.
- “True” webcasting: Uses Internet Protocol (IP) multicasting to push content to the browsers of users who belong to a multicast group. This is an example of true push technology.
Wedcasting
Wedcasting is a webcast of a wedding. Allows family and friends of the couple to watch the wedding in real-time on the Internet. It is sometimes used for weddings in exotic locations, such as Cancun and the Riviera Maya, Hawaii, or the Caribbean, for which it is very expensive or difficult for people to travel to see the wedding in person.
Webcasting explained
Other uses of the term Webcasting
The term “webcasting” is sometimes used to refer to the broadcasting of radio programs over the Internet.
Difference between webcasting and podcasting
Webcasting differs from podcasting in that webcasting refers to live streaming while podcasting simply refers to media files placed on the Internet.
A podcast is more like a portable, downloadable version of a webcast delivered as a series of digital media files (mostly audio) and often downloaded through web syndication. A podcast is like a radio show transmitted across the Internet as a series of episodes.
History of Webcasting
The earliest graphically-oriented web broadcasts were not streaming video but were in fact still frames that were photographed with a web camera every few minutes while they were being broadcast live over the Internet. One of the earliest instances of sequential live image broadcasting was in 1991 when a camera was set up next to the Trojan Room in the computer laboratory of the University of Cambridge.
It provided a live picture every few minutes of the office coffee pot to all desktop computers on that office’s network. A couple of years later its broadcasts went to the Internet, became known as the Trojan Room Coffee Pot webcam, and gained international notoriety as a feature of the fledgling World Wide Web.
On October 31, 1996, UK rock band Caduceus broadcast their one-hour concert from 11 pm to 12 midnight (UT) at Celtica in Machynlleth, Wales, UK – the first live-streamed audio and simultaneous live-streamed video multicast – around the globe to more than twenty direct “mirrors” in more than twenty countries.