An Access Point is a type of device that enables wireless stations to connect to a wired local area network (LAN). An access point (AP), therefore, provides wireless stations with access to resources on a network.
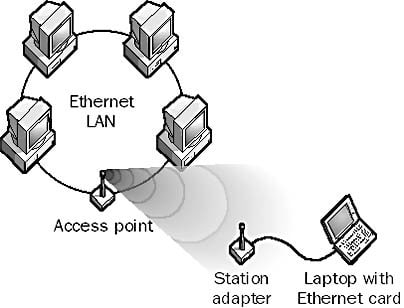
Access Point connection to an Ethernet LAN
How It Works
In typical wireless networking implementations, an access point is a device connected to a wired network, such as an Ethernet network. The AP is a transceiver, transmitting and receiving signals using either direct sequencing or frequency hopping methods in spread spectrum communication technologies. It provides a point of access to the wired network for mobile computers.
To communicate with the AP, a mobile computer can use either a special wireless PCMCIA card or a network interface card (NIC), or it can use station adapters, which are devices that plug into the standard 10BaseT port of the computer’s Ethernet card.
For spread spectrum communication in the 2.4 GHz range, access points typically support 1–3 Mbps communication over distances of up to about 3 kilometers. The area covered by an access point is called a cell. An AP can generally support 15 to 25 wireless stations, while still maintaining optimal data transfer rates. The access points allow wireless stations to be quickly and easily connected to a wired LAN.
Wireless Access Points devices, can benefit from recent Power of Ethernet (PoE) technology. Thus, we are able to place APs in places without power outlets.
Security of Access Point
Many wired networks base the security on physical access control, trusting all the users on the local network, but if wireless access points are connected to the network, anybody within range of the AP (which typically extends farther than the intended area) can attach to the network.
Modern access points come with built-in encryption. The first generation encryption scheme, WEP, proved easy to crack; the second and third generation schemes, WPA and WPA2, are considered secure if a strong enough password or passphrase is used.
Some Access Points support hotspot style authentication using RADIUS and other authentication servers.