When we venture onto the Internet, we rarely think about the intricate network infrastructure that facilitates this modern marvel. Each Google search, every YouTube video, and all email correspondence traverse an intricate web of digital pathways to reach their destination. Essential to these vast networks are specialized devices known as routers, amongst which, the backbone router holds a unique position.
Acting as a veritable linchpin in network infrastructures, the backbone router orchestrates the ceaseless data flow coursing through the network’s main channels. As gatekeepers of these digital highways, backbone routers are often taken for granted, yet they hold immense significance. This article seeks to bring this unsung hero into the spotlight, providing a comprehensive understanding of its role, its function, and its importance in our increasingly interconnected world.

What is a Backbone Router?
In the expansive lexicon of network terminology, the term ‘Backbone Router’ holds a place of prominence. A backbone router, as the name suggests, serves as a pivotal point in an internet backbone, the high-speed, high-capacity networks connecting different networks globally. Essentially, it’s a router that connects these disparate networks to the internet backbone, facilitating communication and data transfer between networks located vast distances apart.
From a structural perspective, the backbone router operates at the center of a hierarchical network, similar to the spine in vertebrates. Just as the spine serves as the primary conduit for nerve signals to reach different parts of the body, the backbone router routes data packets between networks, acting as the principal gateway.
Backbone routers, unlike standard routers, handle colossal amounts of data, necessitating more sophisticated hardware and software. They need to route traffic quickly, efficiently, and without errors, ensuring that the data packets reach their intended destinations without delay. Consequently, they employ advanced routing protocols and algorithms to manage the sheer volume of data traffic coursing through the internet backbone.
Backbone Router definition
A Backbone Router is a router that is used to connect autonomous systems in a large internetwork such as the Internet.
Multiple data paths
However, the role of backbone routers extends beyond mere data routing. They also play a critical part in maintaining the robustness and reliability of the internet. Through their intricate configuration and interconnections, they provide multiple data paths, ensuring that even if one path fails, data can still reach its destination— a principle known as redundancy.
To sum up, backbone routers are digital maestros, conducting the symphony of data that constitutes our internet experience. By understanding their function, we not only gain insights into how the internet works but also appreciate the complex choreography that underpins our seamless digital interactions.
How does a Backbone Router work?
The working of a backbone router, like the maestro leading a grand orchestra, is a blend of precision, synchrony, and adept handling of complexity. This process involves an interplay of several elements, including Autonomous Systems (ASes), Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs), and Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs), each contributing to the seamless functioning of this digital symphony conductor.
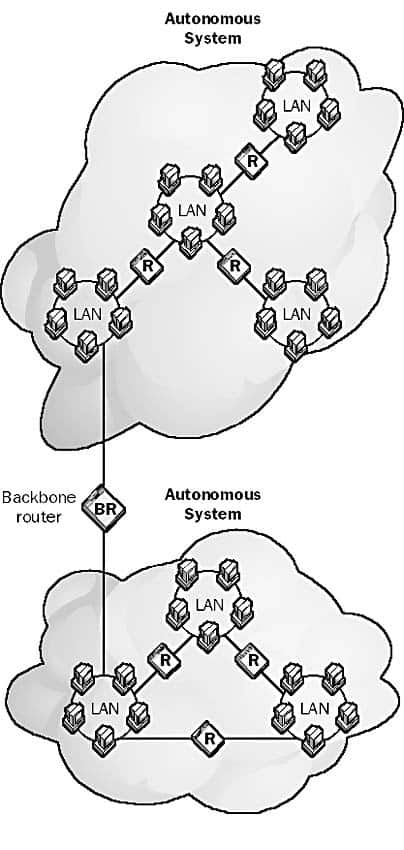
Autonomous Systems, or ASes, form the bedrock of the Internet’s structure. An AS is a network or a collection of networks, that is managed by a single entity and operates under a common administrative protocol. Each AS has a unique identifier, known as the Autonomous System Number (ASN). ASes range from large telecommunication companies to smaller Internet Service Providers (ISPs), each handling its internal routing policies. Backbone routers work within and between these ASes, directing traffic based on the prevailing routing policies and protocols.
Within an AS, the backbone router employs Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) to manage routing. IGPs are a set of routing protocols used within a single AS. They determine how routers communicate with each other within the network, establishing the most efficient route for data packets. Examples of IGPs include Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). IGPs ensure that backbone routers can quickly adapt to changes within the network, maintain routing tables, and provide rapid recovery from failures, contributing to the overall reliability and robustness of the Internet.
Beyond Autonomous Systems
Yet, the realm of the backbone router extends beyond the boundaries of a single AS. They also need to communicate with routers in other ASes, for which they use Exterior Gateway Protocols (EGPs). EGPs govern how data is routed between ASes, with the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) being the de facto EGP used across the Internet. BGP allows backbone routers to share routing information with each other, making decisions based on factors such as policy, network congestion, and the number of ASes data must traverse.
By managing the intricacies of IGPs and EGPs, backbone routers deftly navigate the complexities of the Internet’s structure. They ensure that data packets traverse the labyrinth of networks, keeping the digital world connected. Through their diligent work, the backbone routers truly embody their name, providing the sturdy support that holds the Internet together and enables our digital lives.
In conclusion, the functioning of a backbone router is a testament to the intricate choreography of Internet communication. By understanding this, we gain a profound appreciation for the technological marvel that enables our emails, video streams, and social media interactions to reach across the globe, connecting us in ways that were once the realm of science fiction.
Important Note:
If protecting your network from cyberattacks is your job you should check this out:
- WatchGuard | WGT35641-US | WatchGuard Firebox T35 with 1-yr Total Security Suite (US) – Price and features here