In computer networking, a bidirectional path switched ring (BPSR) is a type of network architecture that uses a ring topology to transmit data between nodes. In a BPSR network, data is transmitted in both directions around the ring, allowing for communication between any two nodes on the network.
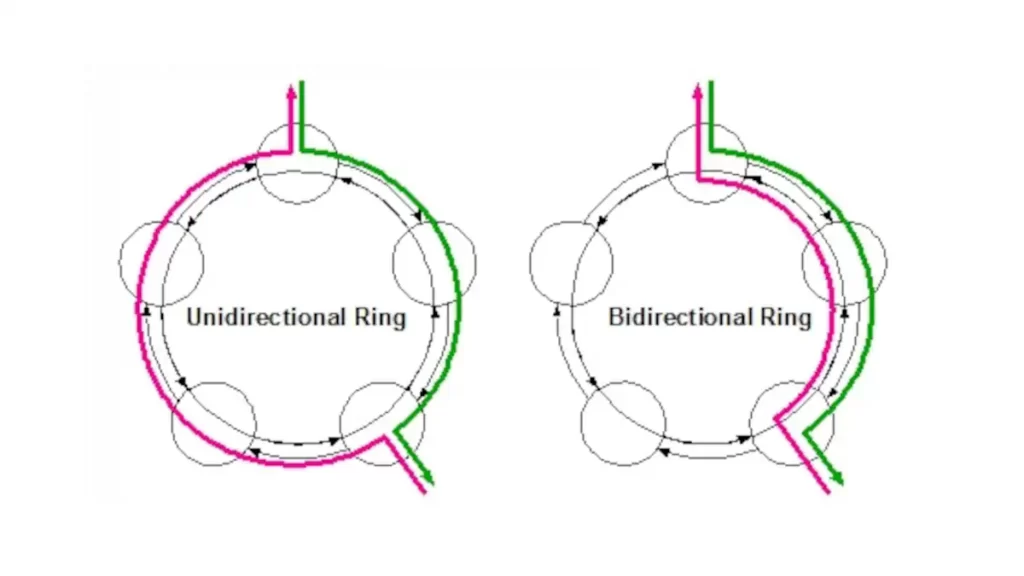
In a BPSR network, each node on the ring is connected to two other nodes, one on either side. When a node wants to send data to another node on the network, it sends the data to its left neighbor, which then forwards the data to its left neighbor, and so on, until the data reaches its destination. The data is then transmitted back to the sender in the same way.
One of the benefits of BPSR networks is that they can recover from failures quickly, as data can be transmitted around the ring in either direction. This makes them well-suited for mission-critical applications that require high availability. Additionally, BPSR networks are relatively simple to implement and manage, making them a popular choice in certain types of networks.
Bidirectional path switched ring networks limitations
However, BPSR networks do have some limitations. They can be slower than other types of networks, and they may not be suitable for larger networks with many nodes, as the time it takes for data to travel around the ring can increase with the number of nodes. Additionally, BPSR networks may not be as flexible as other types of networks, as nodes must be connected in a specific order to form the ring.
Difference between BPSR and UPSR
Bidirectional path switched ring (BPSR) and unidirectional path switched ring (UPSR) are both types of network architectures that use a ring topology. However, they differ in the way that data is transmitted around the ring.
In a Bidirectional Path Switched Ring network, data is transmitted in both directions around the ring, allowing communication between any two nodes on the network. When a node wants to send data to another node on the network, it sends the data to its left neighbor, which then forwards the data to its left neighbor, and so on, until the data reaches its destination. The data is then transmitted back to the sender in the same way.
In contrast, in a UPSR network, data is transmitted in only one direction around the ring. This means that communication is only possible between nodes that are located in the same direction on the ring. For example, if two nodes are located on opposite sides of the ring, they cannot communicate directly, as the data must travel all the way around the ring to reach its destination. Instead, the data must be transmitted to a node that is located between the two nodes, which can then forward the data to its destination.
One of the main differences between BPSR and UPSR networks is the level of redundancy and fault tolerance. BPSR networks are more redundant and can recover from failures more quickly, as data can be transmitted around the ring in either direction. UPSR networks are less redundant, as they rely on a single direction for data transmission, and may take longer to recover from failures. However, UPSR networks may be simpler to implement and may be more efficient in certain situations.
