Category: Network Protocols
-
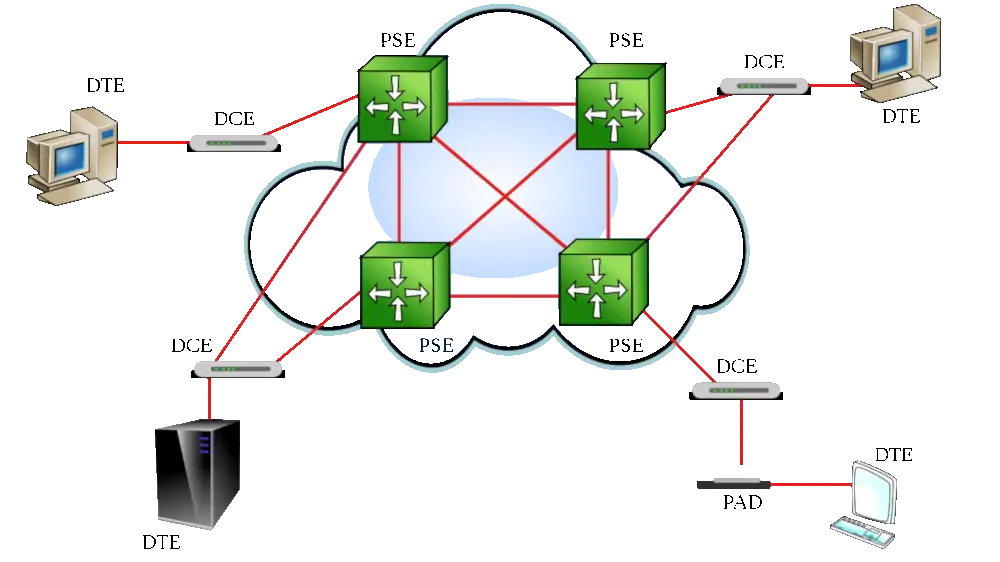
X.25 Protocol
X.25 is a packet-switching protocol for wide area network (WAN) connectivity that uses a public data network (PDN) that parallels the voice network of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
-
TCP Three-Way Handshake: A Comprehensive Guide
TCP three-way handshake is a method of initializing a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) session between two hosts on a TCP/IP network.
-

Statistical Multiplexing
Statistical Multiplexing is a multiplexing technique that allows information from a number of channels to be combined for transmission over a single channel.
-
Bus Topology: A Comprehensive Exploration
BUS is a networking topology that connects networking components along a single cable or that uses a series of cable segments that are connected linearly.
-
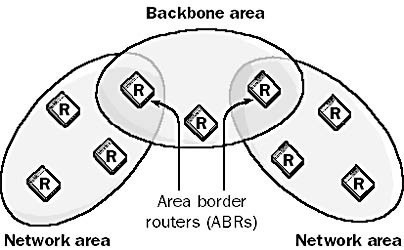
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Protocol
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First, is a link state routing protocol that is used to exchange routing information between dynamic routers.
-

Unraveling the Shortest Path First: The SPF Algorithm
Also called the Dijkstra algorithm, SPF is a routing algorithm in which a router computes the shortest path between each pair of nodes in the network.
-

Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (S-HTTP)
Unveil the essentials of S-HTTP, the protocol for encrypting HTTP traffic. Explore its creation, functionality, current usage, and comparison with HTTPS.
-
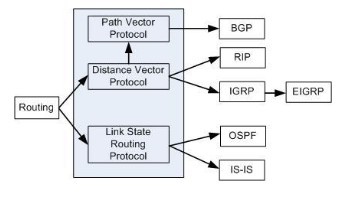
Routing Protocol
Routing Protocol is a protocol that enables the exchange of routing tables between routers in an internetwork.
-

Routing (in TCP/IP Networks)
ROUTING is the process of selecting a path through an internetwork over which to transmit packets to a destination host or hosts and then having devices called routers forward the packets to those hosts.
-
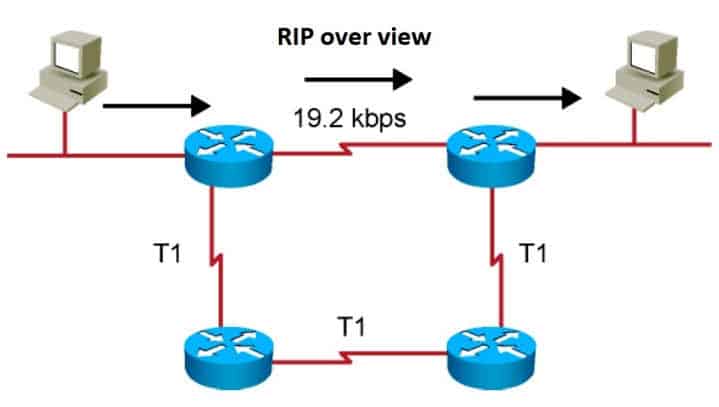
Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
RIP stands for Routing Information Protocol, is a routing protocol that is used to exchange routing information between dynamic routers on IP Protocol or IPX. You should read the article to fully understand this concept.
-
NBNS: NetBIOS Name Server
Uncover the essentials of NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS), its role in network naming services, and its relevance in today’s networking world.
-
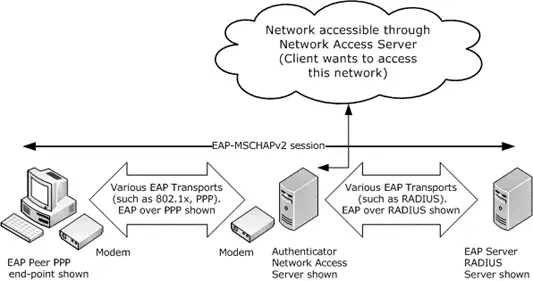
Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (MS-CHAP)
MS-CHAP stands for Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, is an encrypted authentication scheme used in wide area network (WAN) communication.