In the realm of computer networking, understanding various topologies is key to grasping how networks are structured and function. Among these, Bus Topology stands out for its simplicity and historical significance. This article aims to demystify Bus Topology, delving into its core principles, advantages, limitations, and its evolution in the networking landscape. We’ll navigate through its conceptual framework, practical applications, and reasons for its decline in favor of more advanced topologies. By the end of this exploration, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of Bus Topology and its place in the history and future of network design.
Table of Contents
- What is Bus Topology?
- Historical Background and Evolution of Bus Topology
- Comparing Network Topologies: Choosing the Right One
- Common Challenges and Solutions in Bus Topology
- The Decline of Bus Topology: Why It’s No Longer Favored
- Current Trends in Network Topologies: What’s Dominating Today?
- Conclusion: The Enduring Lessons of Bus Topology
- Video
- References
1. What is Bus Topology?
Bus Topology, in the context of network design, is not just a concept but a physical topology. This distinction is crucial as it refers to the actual layout of the network – how devices are physically connected and the tangible structure it takes. Understanding physical topology is fundamental, as it dictates the network’s performance, capabilities, and limitations.
Defining Physical Topology
The term physical topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically. Two or more devices connect to a link; two or more links form a topology. The topology of a network is the geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and linking devices (usually called nodes) to one another.
Behrouz A. Forouzan, “Data Communications and Networking” (1)
A network that uses a bus topology is referred to as a “bus network.” Bus networks were the original form of Ethernet networks, using the 10Base5 cabling standard.
Key Characteristics
- Simplicity: The straightforward design of Bus Topology makes it easy to set up and understand, ideal for small networks.
- Linear Structure: In a Bus Topology, all devices are connected to a single central cable, known as the ‘bus’ or backbone. This linear arrangement forms the physical backbone of the network.
- Economy: With minimal cabling and no need for additional hardware like switches or hubs, it’s a cost-effective solution.
- Broadcast Nature: Messages sent over the bus are available to all devices, but only the target device processes them, ensuring efficient communication.
- Terminators at Each End: To prevent signal reflection, which can cause transmission errors, terminators are placed at both ends of the bus cable.
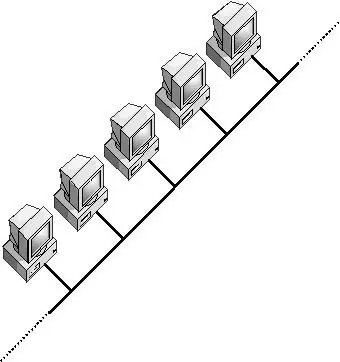
How it Works
In a Bus Topology, when a device transmits data, the signal travels along the bus until it reaches every connected device. Each device examines the signal and determines if it’s the intended recipient. If not, the device ignores the data. This process continues until the data reaches its destination. However, if two devices send data simultaneously, it leads to a collision, disrupting the network communication.
Limitations
While Bus Topology is efficient in certain contexts, it has limitations, especially in scalability and collision management. As the network grows, the risk of data collisions increases, and the bus becomes a bottleneck, limiting the overall network performance.
In summary, understanding Bus Topology is vital for grasping fundamental networking principles. Its simplicity and cost-effectiveness made it popular in early network designs, setting the stage for more complex topologies. However, its limitations in handling larger, more demanding network environments led to its decline in favor of more robust alternatives.
2. Historical Background and Evolution of Bus Topology
Inception and Inventors
The concept of Bus Topology originated in the early days of computing and networking. It was a brainchild of the collaborative efforts of multiple researchers and engineers striving to simplify network communication. The exact origins of Bus Topology are diffuse, as it evolved through collective innovation rather than a single inventor’s breakthrough. However, its roots can be traced back to the development of early computer networks in the 1960s and 1970s, particularly the pioneering work on Ethernet technology by Robert Metcalfe and David Boggs at Xerox PARC. (2)
Early Adoption and Growth
In its infancy, Bus Topology was revolutionary, offering a simple yet effective way to connect multiple computers. Its adoption was accelerated with the advent of Ethernet technology in the 1970s, which utilized a bus layout for connecting devices within a Local Area Network (LAN). Ethernet’s standardized approach to networking and its use of Bus Topology played a pivotal role in the topology’s widespread adoption.
Technological Enhancements
Over time, Bus Topology underwent several refinements. The introduction of terminators at each end of the bus cable helped reduce signal reflection and improve data transmission efficiency. Furthermore, advancements in cable technology, like the shift from coaxial cables to more efficient and reliable alternatives, marked significant milestones in the evolution of Bus Topology.
The Decline and Shift
Despite its early success, Bus Topology began to face challenges as network demands grew. The topology’s inherent limitations, such as difficulty in troubleshooting, vulnerability to cable failures, and inefficiency in handling network traffic in larger setups, became more pronounced. The late 20th century saw a gradual shift towards more robust topologies like Star and Ring, which offered greater scalability, reliability, and ease of maintenance. This shift marked a decline in the use of Bus Topology in mainstream networking, relegating it to niche applications or as a foundational concept in networking education.
3. Comparing Network Topologies: Choosing the Right One
Understanding the Landscape
Choosing the right network topology is crucial for building efficient and reliable networks. Alongside Bus Topology, other common topologies include Star, Ring, Mesh, and Hybrid. Each topology has its unique attributes and is suited for different network requirements.
Star Topology
Star Topology, one of the most prevalent in modern LANs, features a central connection point, typically a network switch or hub, to which all network devices are connected. Its key advantages include high reliability – a failure in one cable only affects one node – and ease of setup and troubleshooting. However, it requires more cable than Bus Topology and is heavily dependent on the central hub’s functionality.

Ring Topology
In Ring Topology, each device is connected to two others, forming a closed loop. Data travels in one direction, passing through each device. While it’s efficient in handling data traffic and easy to install, its reliance on the uninterrupted loop makes it vulnerable to disruptions if a single connection fails.

Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology is characterized by its robustness, with each node directly connected to multiple others. This setup enhances fault tolerance and offers multiple paths for data transmission, making it ideal for critical applications. However, its complexity and high cabling requirements can be cost-prohibitive.

Hybrid Topology
Hybrid Topology combines elements of different topologies to leverage their strengths while mitigating weaknesses. It’s adaptable to varied network needs and scales but requires careful planning and management.
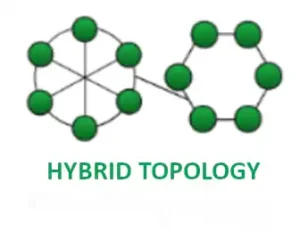
Making the Choice
Selecting the right topology depends on factors like network size, scalability needs, budget, and fault tolerance requirements. For small networks with limited devices, a simple Star or Bus Topology might suffice. In contrast, large-scale or critical operations may benefit from the robustness of Mesh or Hybrid Topologies.
In conclusion, while Bus Topology laid the groundwork for network design, evolving technology and changing requirements have led to a diverse array of topologies. Understanding these options and their suitability for different scenarios is key to building effective and resilient networks.
4. Common Challenges and Solutions in Bus Topology
Identifying the Challenges
While Bus Topology has its advantages, it also faces several challenges, particularly in larger or more complex network environments.
- Data Collisions: With all devices sharing a single communication line, the chances of data collisions are high, especially as the network grows.
- Limited Cable Length and Number of Nodes: The length of the bus and the number of nodes it can support are limited, restricting the scalability of the network.
- Network Disruptions: A single point of failure, such as a break in the bus cable, can bring down the entire network.
- Troubleshooting Difficulties: Identifying and resolving issues can be challenging due to the shared nature of the bus.
Implementing Solutions
To mitigate these challenges, several strategies can be employed:
- Data Collision Management: Using carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) can help manage data collisions. This protocol allows a device to check the bus for traffic before transmitting data.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting a large bus network into smaller, manageable sections using bridges can reduce traffic and collision domains.
- Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: Conducting regular checks and monitoring the network for signs of wear or damage in the cable can preemptively address potential failures.
- Using Reflective Terminators: Implementing reflective terminators at both ends of the bus can help reduce signal degradation and improving network performance.

5. The Decline of Bus Topology: Why It’s No Longer Favored
Shift in Networking Demands
The decline of Bus Topology is closely tied to the evolving demands of network environments. During the late 20th century, as networks grew in size and complexity, the limitations of Bus Topology became increasingly apparent. Its inability to efficiently handle high traffic volumes and its vulnerability to single points of failure started to outweigh its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Key Factors Leading to Decline
- Scalability Issues: Bus Topology struggled with large-scale implementations. As more devices were added, the network’s performance deteriorated due to increased data collisions and network traffic.
- Fault Tolerance: The entire network could be disrupted by a single point of failure, such as a break in the main cable or a malfunctioning terminator.
- Maintenance Challenges: Troubleshooting Bus networks was often complex, as identifying the source of a problem could be time-consuming and disruptive.
Notable Shifts in Large Networks
- Educational Institutions: Many universities and colleges that initially adopted Bus Topology for their simplicity transitioned to Star or Mesh Topologies. This shift allowed them to accommodate a growing number of devices and ensure more stable network connections.
- Corporate Networks: Companies like IBM, which initially used Bus Topology for internal networks, gradually moved to more advanced topologies like Ring (with their Token Ring technology) and later to Star Topology, aligning with the introduction of Ethernet switches and routers.
- Government Agencies: Agencies that once relied on Bus networks for internal communications, like the U.S. Department of Defense, shifted to more secure and reliable topologies, especially as cybersecurity concerns grew.
6. Current Trends in Network Topologies: What’s Dominating Today?
Emphasis on Scalability and Flexibility
Today’s network topologies reflect the need for scalability, reliability, and adaptability. The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and distributed computing environments has driven these changes.
Dominant Topologies
- Star Topology: Continues to be widely used, especially in LANs, due to its ease of setup, scalability, and robustness against single failures.
- Mesh Topology: Gaining popularity, particularly in wireless networks, because of its high fault tolerance and redundancy. Mesh networks are integral to IoT applications and smart home technologies.
- Hybrid Topology: Common in large-scale enterprise networks, combining the best features of various topologies to meet specific network requirements.
Real-World Examples
- Google’s Data Centers: Utilize a modified version of Mesh Topology, providing robust fault tolerance and efficient data handling capabilities to manage vast amounts of internet traffic.
- Smart City Projects: Cities like Barcelona and Singapore have implemented Mesh and Hybrid Topologies in their smart city infrastructure to ensure continuous connectivity and resilience in urban networks.
- 5G Networks: The deployment of 5G technology relies on advanced network topologies, often a combination of Star and Mesh, to handle high-speed data transmission and a massive number of connected devices.
The landscape of network topologies is continuously evolving to meet the needs of modern network environments. While Bus Topology laid the foundational principles, the focus has shifted towards more flexible, scalable, and reliable designs. Understanding these trends is crucial for network professionals and organizations aiming to build efficient and future-proof network infrastructures.
7. Conclusion
Bus Topology, a cornerstone in the history of network design, has played a crucial role in shaping modern networking concepts. Despite its decline in favor of more advanced topologies, understanding its principles, challenges, and solutions provides valuable insights into the fundamentals of network architecture. As technology continues to advance, the lessons learned from Bus Topology remain relevant, informing the development of more sophisticated and resilient network structures.
8. Video
9. References
Books
- “Data Communications and Networking” Fourth Edition, by Behrouz A. Forouzan (2007): Presents this highly technical subject matter without relying on complex formulas by using a strong pedagogical approach.
- “Computer Networking – A Top-Down Approach” Seventh Edition, by Ross Kurose (2018): The text works its way from the application layer down toward the physical layer, motivating students by exposing them to important concepts early in their study of networking.
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum: Offers a comprehensive overview of various network topologies, including Bus Topology, with detailed explanations of their operation and applications.
- “Data and Computer Communications” by William Stallings: Provides an in-depth analysis of different network architectures and protocols, with sections dedicated to Bus Topology and its evolution.
- “Networking Essentials” by Jeffrey S. Beasley and Piyasat Nilkaew: A practical guide that covers the basics of network topologies, including the implementation and troubleshooting of Bus Topology.
RFCs
- RFC 1122 – Requirements for Internet Hosts – Communication Layers: Provides insights into network communication protocols that are relevant to understanding Bus Topology dynamics.
- RFC 1149 – A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams on Avian Carriers: While primarily a humorous April Fool’s Day RFC, it provides a unique perspective on alternative data transmission methods, indirectly highlighting the limitations and considerations in traditional network topologies like Bus.
- RFC 826 – An Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol: Offers detailed information on the Ethernet protocol, closely tied to the implementation of Bus Topology in early network designs.
These resources provide a foundation for further exploration into Bus Topology and its role in the broader context of network design and communication. Whether for a seasoned network professional or a newcomer to the field, these references offer valuable insights into the principles and evolution of network topologies.