Certificate Authority is any entity that issues digital certificates to verify the identity of users, applications, or organizations.
What is Certificate authority (CA)?
Any entity (individual, department, company, or organization) that issues digital certificates to verify the identity of users, applications, or organizations.
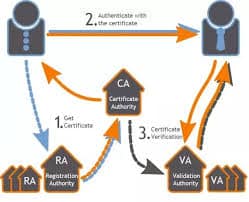
Before issuing a digital certificate to someone, the certificate authority (CA) must verify the user’s identity according to a strictly established policy, which can involve face-to-face communication, examination of a driver’s license with photograph, or another method of establishing a user’s identity.
Once the user’s identity has been verified, the certificate is issued to the user. This certificate can then be presented by the user as a «digital driver’s license» to identify himself or herself during network transactions.
How does Certificate Authority works
CAs can be trusted third parties such as the private companies VeriSign, Inc., CyberTrust, and Nortel; or they can be established within your own organization using Microsoft Certificate Server. CAs can be stand-alone authorities with their own self-signed certificates (that is, they validate their own identity as a root CA), or they can be part of a hierarchy in which each CA is certified by the trusted CA above it (up to a root CA, which must always be self-certified).
For digital certificates to work as an identification scheme, both client and server programs must trust the CA. In other words, when a client program presents a certificate to a server program, the server program must be able to validate that the certificate was issued by a valid and trusted CA. Certificate authorities also maintain a certificate revocation list (CRL) of revoked certificates. Certificates issued by CAs expire after a specified period of time.
Certificate authorities are necessary for the functioning of a public key infrastructure (PKI), which is essential to the widespread acceptance and success of any public-key cryptography system. Microsoft Windows 2000 can use standard X.509 digital certificates to authenticate connections across unsecured networks such as the Internet and to provide single sign-on using smart card authentication systems.
Microsoft Certificate Server (deprecated)
Microsoft Certificate Server, a component of the Windows NT Option Pack (and of Windows 2000, as Certificate Services), is a tool that can be used for issuing, managing, and revoking digital certificates within your enterprise, without the need for third-party CAs.
Microsoft Certificate Server was replaced by Certificate Services.