In the evolving landscape of Windows operating systems, the transition from Scandisk to Chkdsk marks a pivotal advancement in disk diagnostics and repair. The Chkdsk (Check Disk) utility, integral to Windows 10 and Windows 11, embodies the essence of system resilience and data integrity. Originating from the legacy Scandisk tool—once a staple in MS-DOS and early Windows iterations—Chkdsk has risen as its modern counterpart, equipped with enhanced capabilities to scrutinize and mend file systems. This utility not only identifies and rectifies logical filesystem errors but also addresses physical disk issues, ensuring the robust performance of modern computing environments.
As we delve into the functionalities and nuances of Chkdsk, this article also pays homage to Scandisk, offering a nod to those intrigued by the historical evolution of disk repair tools or seeking knowledge out of curiosity. Join us as we explore the intricacies of Chkdsk, from its foundational operations to advanced applications, bridging past and present in disk maintenance technology.
In this article:
- What is Chkdsk?
- Understanding Chkdsk: How It Works
- Running Chkdsk: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Scandisk: A Retrospective
- FAQs and Misconceptions
- References
1. What is Chkdsk?
Chkdsk is a Windows utility that can check the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors. If possible, it also fixes logical errors in the file system. It’s a crucial tool for diagnosing and repairing disk issues, such as bad sectors, cross-linked files, and directory errors.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, Chkdsk can be run from the Command Prompt with administrator privileges. It offers several options that control the degree of the scan and repair process, allowing users to tailor the operation to their specific needs. For example, running chkdsk /f will fix errors on the disk, while chkdsk /r locates bad sectors and recovers readable information.
Furthermore, Windows 10 and 11 include additional features to protect and repair the file system automatically. For instance, the Windows System File Checker (SFC) tool can be used in conjunction with Chkdsk to repair protected system files. Additionally, Windows incorporates Automatic Maintenance, which can automatically run Chkdsk when the system detects certain disk problems.
Despite its longevity, the Check disk utility remains an essential and powerful tool for maintaining the health of hard drives and SSDs in Windows operating systems.
2. Understanding Chkdsk: How It Works
Technical Breakdown of Chkdsk Operations
The Chkdsk utility, short for “Check Disk,” is a Windows system tool designed to verify the file system integrity of a volume and fix logical file system errors. It operates by scanning the disk’s partition for system errors, bad sectors, and other issues that could potentially compromise data integrity. Here’s a breakdown of its core operations:
- File System Analysis: Chkdsk begins by examining the file system’s metadata. This includes checking the file system’s integrity, its directories, and individual file entries against the volume’s master file table (MFT) or file allocation table (FAT), depending on the file system type (NTFS, FAT32, etc.).
- Volume’s Snapshot: For volumes in use, Chkdsk can create a snapshot, allowing it to operate without the need for a system reboot.
- Error Reporting: After the initial scan, Chkdsk reports found errors without fixing them unless instructed to do so. This includes file fragmentation, cross-linked files, and directory errors.
- Error Correction: When run with appropriate parameters (
/ffor fixing disk errors,/rfor locating bad sectors and recovering readable information), Chkdsk attempts to repair file system data, reallocate file fragments, and mark bad sectors to prevent data from being stored there.
Comparing Filesystem Checks and Error Corrections
- Filesystem Checks: Chkdsk’s filesystem checks are largely preventive, identifying potential errors and inconsistencies that might not yet have caused data loss, such as orphaned files, lost clusters, and directory errors. These checks help maintain the overall health and efficiency of the file system.
- Error Corrections: The corrective actions taken by Chkdsk, such as fixing file system errors or recovering data from bad sectors, are reactive measures designed to repair damage and prevent data loss. These operations are crucial after system crashes, malware attacks, or when the disk is improperly disconnected.
3. Running Chkdsk: A Step-by-Step Guide
Instructions for Windows 10 and 11
Using Command Line Options
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Press
Windows + Xand select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” from the menu. - Run Chkdsk: Type
chkdsk C: /f /rand press Enter. ReplaceC:with the letter of the drive you wish to check. The/fparameter tells Chkdsk to fix errors on the disk, and/rlocates bad sectors and recovers readable information. - Restart if Necessary: If the volume is in use, Chkdsk may ask to schedule the scan at the next system restart. Type
Yto confirm.
Using Graphical Interface Methods
- Open File Explorer: Navigate to “This PC” or “My Computer.”
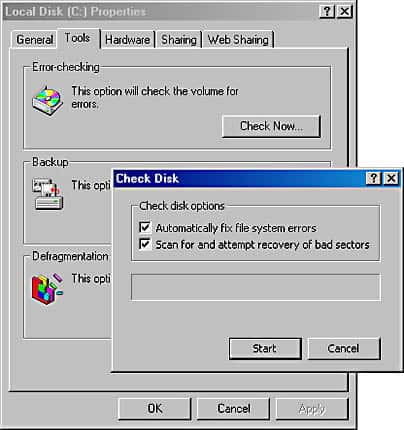
- Right-click the Drive: Select the drive you want to check, right-click it, and choose “Properties.”
- Access Tools Tab: Go to the “Tools” tab and click on “Check” under the “Error checking” section.
- Start the Check: If Windows hasn’t found errors, you can still run a manual check by clicking “Scan drive.” Follow the prompts to start the error checking process.
These step-by-step instructions provide two methods for running Chkdsk, ensuring users can maintain their drives’ health and data integrity, whether they prefer using the graphical user interface or the command line.
4. Scandisk: A Retrospective
Historical Significance of Scandisk
Scandisk was introduced with MS-DOS 6.2 in the early 1990s as a replacement for the CHKDSK utility. Its primary function was to check and repair disk errors on FAT16 and later FAT32 file systems. Scandisk represented a significant advancement over its predecessor by offering a more thorough analysis and repair process, which included the ability to check the surface of the disk for physical errors. It became an essential tool for maintaining the integrity of data storage in the pre-Windows XP era, particularly in environments prone to improper shutdowns, power failures, and system crashes.
Differences between Scandisk and Chkdsk
While Scandisk and Chkdsk share a fundamental purpose—checking and repairing disk errors—their operations differ significantly, primarily due to the evolution of storage technology and file systems:
- File System Support: Scandisk was designed for FAT16 and FAT32 file systems, prevalent in DOS and early Windows versions. Check Disk supports these plus the NTFS file system, which offers enhancements in security, reliability, and efficiency.
- Surface Scan: Scandisk could perform a surface scan to identify bad sectors physically. While Chkdsk also identifies bad sectors, its approach and efficiency are improved, particularly with the NTFS file system’s self-healing capabilities.
- User Interface: Scandisk provided a text-based and later a graphical user interface in Windows 9x, making it accessible to casual users. Chkdsk is primarily a command-line tool, reflecting its use in more recent Windows versions that favor PowerShell and Command Prompt for system maintenance tasks.
- Recovery Capabilities: Chkdsk’s integration with newer Windows versions allows it to recover data in more complex scenarios, thanks to advancements in file system architecture and error correction algorithms.
5. FAQs and Misconceptions
Common Questions and Clarifications
- Q: Does running Chkdsk risk data loss?
- A: There’s a common misconception that Chkdsk can cause data loss. In reality, Check disk is designed to prevent data loss by repairing file system errors. However, in sectors already damaged or corrupt files it cannot fix, it might seem like data is lost because Chkdsk attempts to salvage what it can, moving unreadable content to a different location.
- Q: Is Chkdsk only necessary when you suspect disk problems?
- A: While it’s particularly recommended in cases of suspected disk issues, running Chkdsk periodically can help prevent future problems by catching and fixing errors early.
- Q: Can Chkdsk fix hardware problems?
- A: Chkdsk is designed to identify and correct file system errors, not hardware problems. If it finds bad sectors, it will try to recover readable information but cannot repair the physical disk itself.
6. References
For those interested in exploring more about Scandisk, Chkdsk, and disk maintenance tools, the following resources provide valuable information:
- Russinovich, Mark E., and David A. Solomon. “Windows Internals.” Microsoft Press. This book offers in-depth technical details on Windows operating systems, including file systems and disk management utilities.
- “MS-DOS User’s Guide and Reference.” Microsoft Corporation. This manual covers MS-DOS commands, including Scandisk, providing historical context and usage instructions.
- “File System Forensic Analysis” by Brian Carrier. This book gives insights into the workings of file systems, pertinent to understanding how tools like Chkdsk interact with data.