Digital Data Service is a family of leased line data communication technologies that provides a dedicated synchronous transmission connection at speeds of 56 Kbps.
What is Digital Data Service (DDS)?
DDS stands for Digital Data Service, is a family of leased line data communication technologies that provides a dedicated synchronous transmission connection at speeds of 56 Kbps. Digital data service (DDS) is only one example of a type of digital line; others include Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and T1. DDS can be used in either multipoint or point-to-point communications and requires dedicated digital lines. DDS lines can also be used to connect buildings on a campus, usually with a maximum distance of about 3 miles.
How DDS Works?
“DDS” was originally a trademark for an AT&T all-digital service running at 56 Kbps, but the term has evolved into a general descriptor for a variety of digital services offered by different carriers under various names. DDS is usually available in both a dial-up version called switched 56 and a dedicated leased line service for continuous connections. The dial-up version can serve as a backup for the dedicated version.
Typically, DDS uses four wires to support digital transmission speeds of 56 Kbps, but it is actually a 64-Kbps circuit that uses 8 Kbps for sending signaling information. Some vendors provide a variant of DDS with a data transmission rate of a full 64 Kbps.
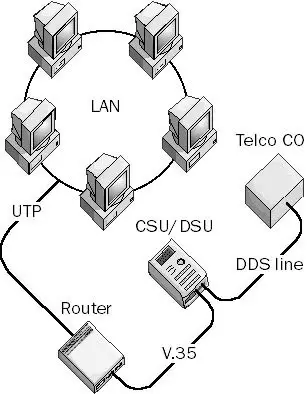
To use DDS services for wide area network (WAN) connectivity, route packets from your local area network (LAN) through a bridge or a router, which is connected by means of a V.35 or RS-232 serial interface to a CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit).
The CSU/DSU is connected to the four-wire termination of the DDS line by means of an M-block connector, a screw terminal block, or some other connection mechanism. The Channel Service Unit (CSU) converts the data signal into a bipolar signal suitable for transmission over the telecommunications link.
The DDS lines themselves use four wires and support speeds of 64 Kbps, but 8 Kbps of bandwidth is usually reserved for signaling, so the actual data throughput is usually only 56 Kbps.
DDS lines are dedicated lines with negligible connection establishment latency; they are always “on” and never “busy”.