DACL, or Discretionary Access Control List, is an internal list attached to an object in Active Directory that specifies which users and groups can access the object and what kinds of operations they can perform.
What is DACL (Discretionary Access Control List)?
A DACL stands for Discretionary Access Control List, in Microsoft Windows family, is an internal list attached to an object in Active Directory that specifies which users and groups can access the object and what kinds of operations they can perform on the object. In Windows 2000 and Windows NT, an internal list attached to a file or folder on a volume formatted using the NTFS that has a similar function.
How DACL works?
In Windows, each object in Active Directory or a local NTFS volume has an attribute called Security Descriptor that stores information about
- The object’s owner (the security identifier or the owner) and the groups to which the owner belongs.
- The discretionary access control list (DACL) of the object, which lists the security principals (users, groups, and computers) that have access to the object and their level of access.
- The system access control list (SACL), which lists the security principals that should trigger audit events when accessing the list.
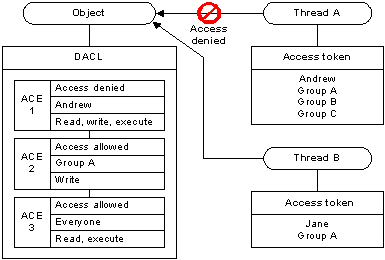
The DACL for an object specifies the list of users and groups that are authorized to access the object and also what levels of access they have. The kinds of access that can be assigned to an object depend on the type of object under consideration. For example, a file object can have read access assigned to a user but a printer object cannot. (You can’t read a printer!)
The DACL for an object consists of a list of access control entries (ACEs). A given ACE applies to a class of objects, an object, or an attribute of an object. Each ACE specifies the security identifier (SID) of the security principal to which the ACE applies, as well as the level of access to the object permitted for the security principal. For example, a user or group might have permission to modify all or some of the attributes of the object, or might not even have permission to be aware of the object’s existence. In common parlance, DACLs are sometimes simply referred to as access control lists or ACLs, though this is not strictly correct.
NOTE
The owner of an object always has permission to modify its DACL by granting permissions to other users and groups.