Imagine you’re sitting at your computer, eagerly trying to access a website you’ve been meaning to visit. You type in the website’s URL, hit enter, and within seconds, the webpage magically appears on your screen. Have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes that allow this seemingly effortless process to occur? The answer lies in the world of DNS (Domain Name System) and its vital component, the DNS query.
What is DNS Query?
DNS Query is one of three methods of requesting that name servers handle name lookups. DNS queries can occur between resolvers and name servers, name servers and other name servers.
Queries can be answered by the queried name server from its local DNS database, from previously cached query results, or from a referral to another name server.
A DNS query is like sending out a question into the vast network of interconnected devices, seeking the answer to a crucial piece of information: the IP address associated with a particular domain name.
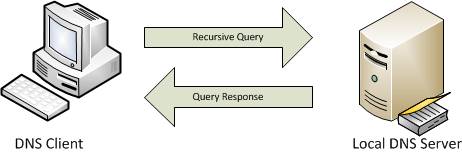
The three basic kinds of DNS queries are recursive queries, iterative queries, and inverse queries.
Recursive Query
The local resolver, acting as a middleman, receives the query and begins the recursive process. It sends the query to one of the DNS root servers, asking for information about the top-level domain (TLD) of the domain name in question, such as “.com” or “.net.”
Iterative Query
The root server, while not providing the IP address directly, responds with a referral to the authoritative server responsible for the TLD. The local resolver then sends an iterative query to the TLD server, seeking information about the next part of the domain name.
Authoritative Query
The TLD server, in turn, provides a referral to the authoritative name server responsible for the specific domain name, such as “example.com.” The local resolver sends yet another query, this time to the authoritative name server.
Common DNS Request Types
| DNS Lookup Type | Description | Function |
| A | IPv4 address record | Returns a 32-bit IP address, which typically maps a domain’s hostname to an IP address, but is also used for DNSBLs and storing subnet masks |
| AAAA | IPv6 address record | Returns a 128-bit IP address that maps a domain’s hostname to an IP address |
| ANY | All cached records | Returns all records of all types known to the name server |
| CNAME | Canonical name record | Alias of one name to another: the DNS lookup will continue by retrying the lookup with the new name |
| MX | Mail exchange record | Maps a domain name to a list of message transfer agents for that domain |
| NS | Name server record | Delegates a DNS zone to use the specified authoritative name servers |
| PTR | Pointer record | Pointer to a canonical name that returns the name only and is used for implementing reverse DNS lookups |
| SIG | Signature | Signature record |
| SOA | Start of authority record | Specifies authoritative information about a DNS zone, including the primary name server, the email of the domain administrator, the domain serial number, and several timers relating to refreshing the zone |
| SRV | Service Locator | Generalized service location record, used for newer protocols instead of creating protocol-specific records such as MX |
| TXT | Text record | Carries extra data, sometimes human-readable, most of the time machine-readable such as opportunistic encryption, DomainKeys, DNS-SD, etc. |