Definition of Encrypting File System in the Network Encyclopedia.
What is Encrypting File System (EFS)?
Encrypting File System, also known as EFS, is a Microsoft Windows 2000 core technology for storing encrypted NTFS files on disk; designed to protect data on NTFS volumes from local access by unauthorized users.
What is EFS (Encrypting File System)?
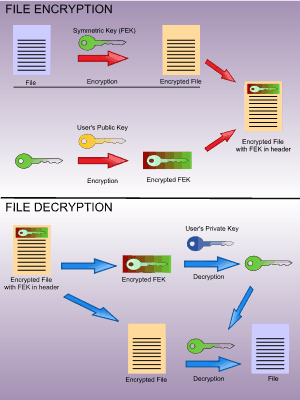
Encrypting File System (EFS) is a public key cryptography scheme based on the Data Encryption Standard (DES) that runs as a Windows 2000 system service and is transparent to the user. EFS is simple to use and automatically generates an encryption key pair for the user who is logged on if one does not already exist. The user’s private key, stored in Active Directory, is used for decrypting encrypted files and folders.
Each time EFS encrypts a file or folder, it generates a random encryption key. EFS encrypts this encryption key using the user’s public key. EFS stores encryption keys in the nonpaged pool of memory.
To access an encrypted NTFS file, the user must meet one of the following criteria:
- Have the private key for the file (in other words, the file was originally encrypted by that user)
- Have permission to share the encrypted file
- Be a registered recovery agent
You can encrypt or decrypt a file or folder on an NTFS volume with the Advanced button on the General page of that file or folder’s property sheet. You can also enable or disable encryption from the command prompt using the cipher command.
Note: EFS does not work on FAT volumes.
Enable encryption at the folder level
If you are working with applications that create temporary files, you might want to enable encryption at the folder level instead of the file level in order to guard against unauthorized access to your temporary files. With folder-level encryption, all files in the folder are encrypted.