Category: Letter E
-

Ethics in Machine Learning: Navigating the New Frontier
Dive into “Ethics in Machine Learning: Navigating the New Frontier,” a manual exploring the ethical challenges of AI. From bias and privacy to accountability, learn to harness AI’s power responsibly. Perfect for pioneers eager to ensure technology enhances humanity without crossing dark borders.
-

Decoding EAP Protocol: A Guide to Extensible Authentication
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a network authentication framework used to control access to both wired and wireless networks.
-

Why Encrypted Passwords Are Non-Negotiable
Discover why encrypted passwords are crucial for safeguarding data. Learn about encryption methods, vulnerabilities, and best practices in this comprehensive guide.
-

Edge Computing: The Frontier of Modern Data Processing
Explore the transformative world of edge computing. Understand its role in modern data processing, how it differs from traditional and quantum computing.
-
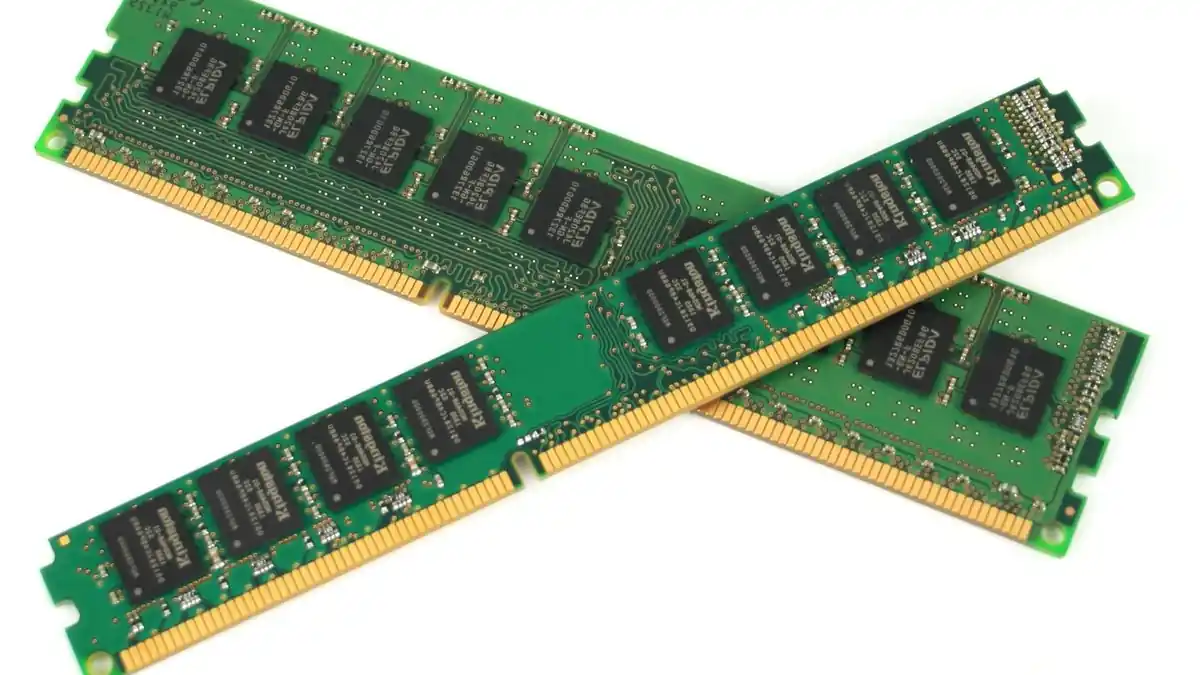
ECC RAM
ECC RAM stands for Error-Correcting Code RAM. It’s a specialized form of computer memory that integrates sophisticated error detection and correction functionalities.
-

Edge Traversal
Edge Traversal refers to the ability of a packet to pass from one network to another network at the edge or boundary of the first network.
-

Starting to understand Encryption
Encryption is the principal application of cryptography; it makes data incomprehensible in order to ensure its confidentiality.
-
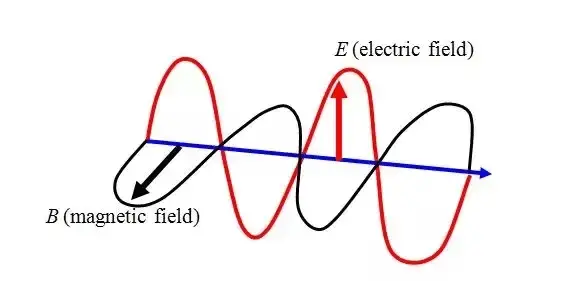
Electromagnetic Waves
An electromagnetic wave is a fluctuation of energy consisting of electric and magnetic fields. The electric and magnetic fields oscillate or move back and forth at right angles to each other, and the wave moves out from the propagating antenna in a direction related to the shape of the antenna, which you will learn about…
-
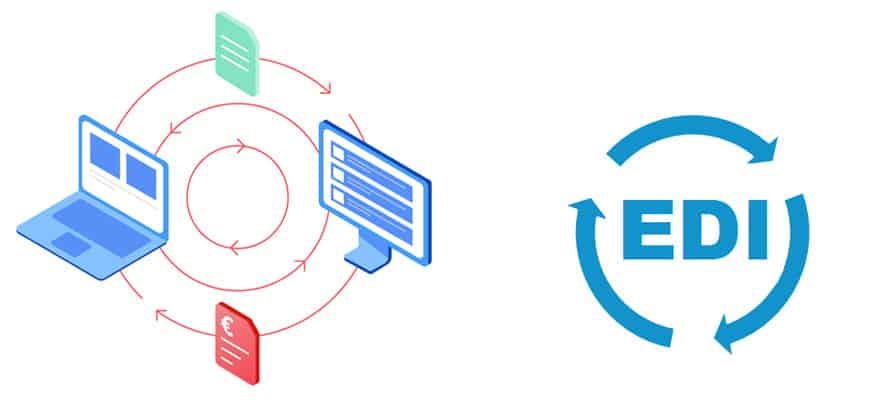
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Electronic Data Interchange, also known as EDI, is a standard format developed by the Data Interchange Standards Association (DISA) in which companies can exchange business data and financial transactions. Electronic data interchange (EDI) is defined in the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard called X.12.
-
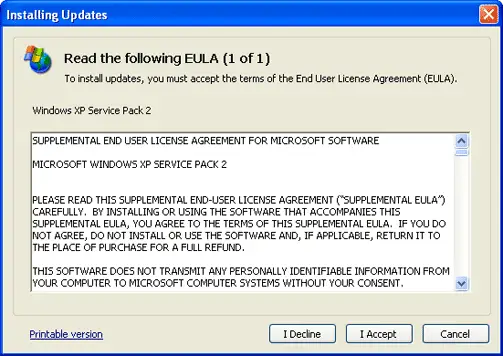
End-User License Agreement (EULA)
End-User License Agreement, also known as EULA, is a type of contract between a computer software publisher and the purchaser of the software that outlines the various rights granted to the purchaser for the legal use of the software.
-
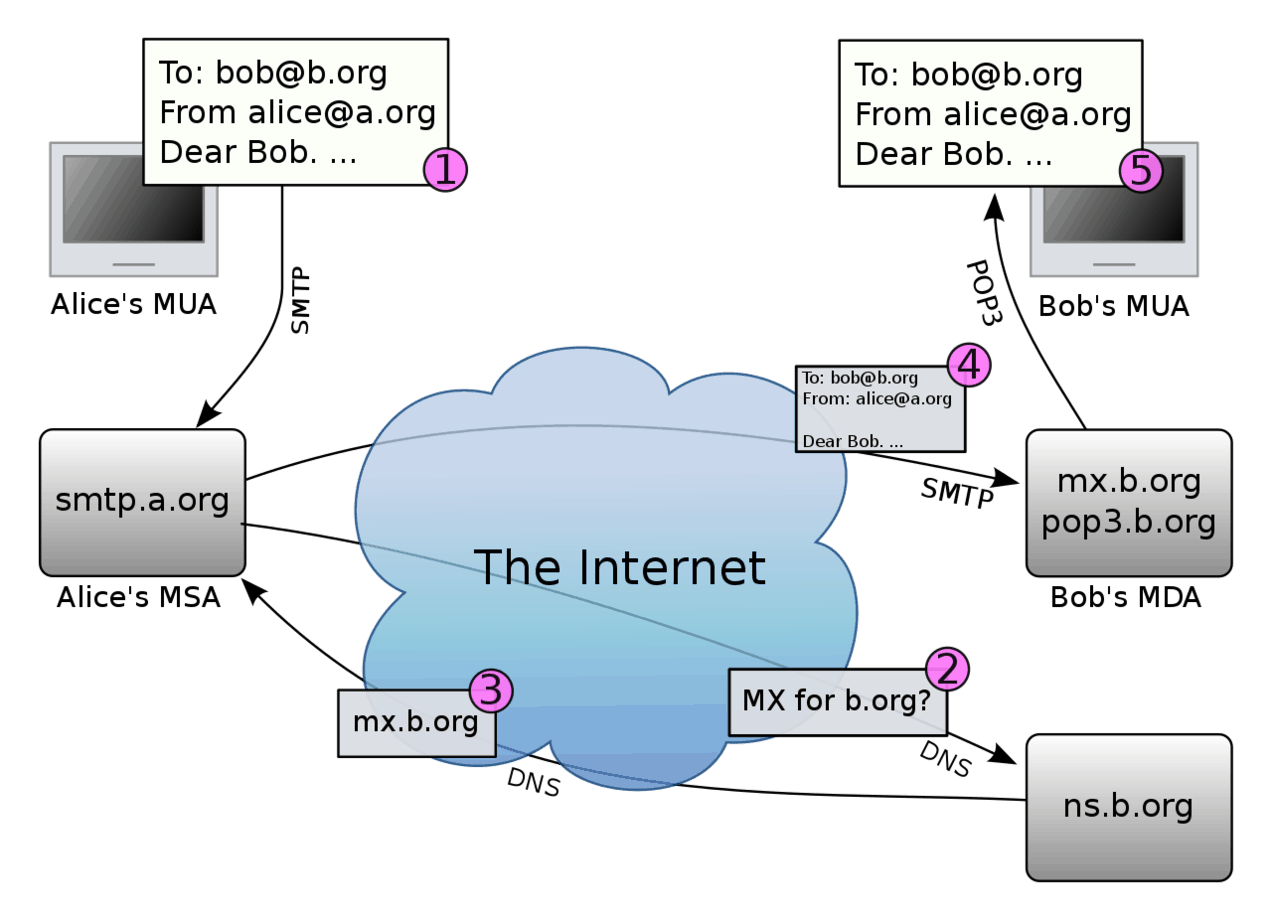
Electronic mail (Email)
Email stands for electronic mail is any system for sending and receiving messages over a network. The email originated in the early 1970s with ARPANET and is now the primary method of business communication today.
