Definition of Fallback Switch in the Network Encyclopedia.
What is Fallback Switch?
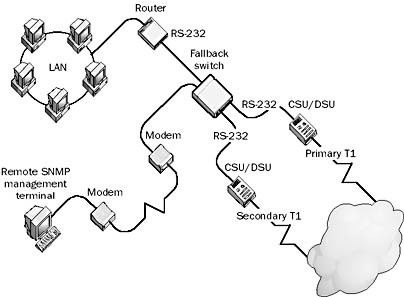
Fallback Switch is a class of switches used to provide failover support for critical network communication lines. Fallback switches are an essential component of a fault tolerant network system with resources that must have a high availability.
How it works
For network resources that require high availability, resources can be connected to your network using two circuits:
- A primary line that normally provides access to the resource
- A secondary line to which the fallback switch reroutes the moment the primary line fails
An example of a resource requiring high availability is a high-speed T1 line that is used by remote clients for accessing a corporate intranet. If the primary T1 line goes down, there must be a backup line that provides instant, transparent failover support for clients. The solution is to use two T1 lines connected to a fallback switch by a serial interface such as RS-232 or V.35.
The fallback switch detects a failure the moment the primary line goes down and can perform a remedial action such as:
- Automatically switching over to the backup line
- Sounding an audible alarm to notify administrators
- Generating an alert to a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) management console.
TIP
Fallback switches can also be used to provide fault tolerance for a high-speed backbone for Fast Ethernet, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), or Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) networking. For example, you can use fallback switches to run two multimode fiber-optic cables between a pair of Ethernet switches, instead of having only one cable connecting them. If one fiber-optic cable goes dark, the fallback switch immediately detects the problem and switches over to the backup cable.
Fallback switches that can be managed using SNMP management consoles are very useful. For example, you could use a remote SNMP terminal to cause a fallback switch to change from a primary to a secondary line if you need to take the primary line down for maintenance. Ganged fallback switches can be used to control multiple serial or local area network (LAN) devices simultaneously. For example, you could schedule a ganged switch to switch over from a set of primary Web servers to a backup Web server every night during a period of low traffic while maintenance or backups are performed on the primary servers. Be sure to use a fallback switch with some form of password protection on its SNMP management functions.