In the dynamic realm of telecommunications, adapting to varying bandwidth requirements is crucial for businesses. This is where Fractional T1 lines come into play, offering a versatile and efficient solution. Serving as a middle ground between basic internet connections and full-fledged T1 lines, Fractional T1 represents a significant advancement in how businesses manage their data communication needs.
This article delves into what Fractional T1 is, its technical intricacies, and how it caters to specific business requirements, ensuring a balance between cost and performance.
In this article:
- What is a Fractional T1?
- Technical Aspects of Fractional T1
- Benefits of Using Fractional T1
- Applications and Use Cases
- Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Fractional T1
- The Future of Fractional T1 in Telecommunications
- Conclusion
- References
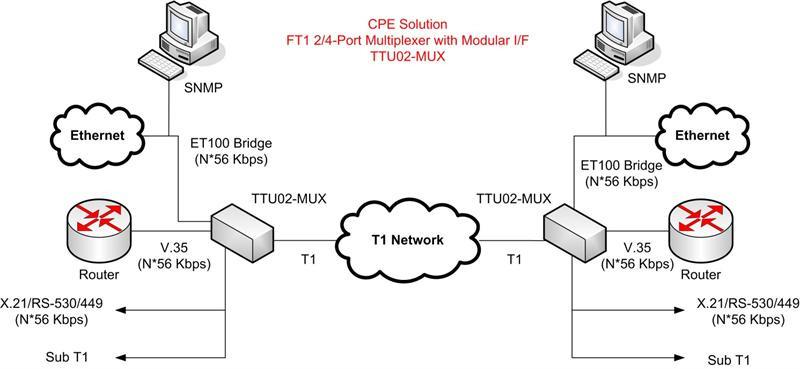
1. What is a Fractional T1?
Fractional T1 is a type of Internet connection. A fractional T1 line is a T1 line, leased by a T-carrier service provider to a customer, that carries only a fraction of the regular T1 bandwidth of 1.544 Mbps.
Regular T1 lines consist of 24 DS0 channels multiplexed together, while fractional T1 lines consists of fewer than 24 channels. Fractional T1 lines typically consist of a combination of nailed-up channels and switched channels.
The technology of fractional T-carrier services is the same as that of regular T-carrier services; the extra channels are simply unused. Customers might want to lease fractional T1 services when they don’t require the entire bandwidth (or cost) of a regular T1 line.
A more secure connection
A T1 line provides a direct connection between the users and the service provider. This connection is considered to be secure because there is a direct link to the provider, whether the connection is fractional or not. These lines are also dedicated communication transmissions. So, unlike with DSL and ISDN, nobody can intervene in your T1 while it’s being used.
Comparison with Standard T1 Line
The key difference between a Fractional and a standard T1 line lies in the bandwidth and cost. A standard T1 line allocates the full 1.544 Mbps to a single customer, which might be excessive and costly for smaller businesses or those with moderate data needs. In contrast, Fractional T1 lines offer a customizable solution, where businesses can choose a specific fraction of the T1 bandwidth, tailored to their requirements. This flexibility makes Fractional T1 a cost-effective and scalable option.
2. Technical Aspects of Fractional T1
How Fractional T1 Lines Work
Fractional T1 lines operate by segmenting the bandwidth of a standard T1 line. This segmentation is achieved through channelization, where the T1 line is divided into multiple channels, each typically providing 64 Kbps of bandwidth. Businesses can lease a specific number of these channels, thereby customizing the bandwidth according to their needs.
Bandwidth Allocation and Configuration
- Bandwidth Allocation: The allocation of bandwidth in a Fractional T1 line is based on the number of channels leased. For instance, leasing three channels would provide a bandwidth of 192 Kbps (3 channels x 64 Kbps each).
- Configuration: The configuration of Fractional T1 lines is handled by the service provider. It involves setting up the T1 line to restrict the bandwidth to the number of channels leased by the customer. This process ensures that customers only pay for the bandwidth they require, while still benefiting from the reliability and stability of T1 technology.
In conclusion, Fractional T1 lines offer a tailored approach to bandwidth management, bridging the gap between limited broadband capabilities and the extensive bandwidth of a full T1 line. This flexibility, combined with the reliability of T1 technology, makes Fractional T1 an attractive option for a wide range of business telecommunications needs.
3. Benefits of Using Fractional T1
Advantages for Businesses
Fractional T1 lines offer several benefits that make them an attractive choice for many businesses:
- Scalability: Businesses can scale their bandwidth up or down based on their evolving needs, ensuring they have just the right amount of data capacity without overpaying.
- Reliability: Fractional T1 lines inherit the reliability of standard T1 lines, offering consistent and dependable service with less downtime compared to traditional broadband.
- Simplicity and Convenience: Managing a Fractional T1 is simpler than handling multiple broadband connections, as it provides a single, streamlined source of connectivity.
- Higher Quality of Service (QoS): T1 lines typically offer better QoS than standard broadband, which is crucial for applications requiring consistent bandwidth, like video conferencing or VoIP.
Cost-Efficiency and Flexibility
The major draw of Fractional T1 is its cost-efficiency and flexibility:
- Customized Bandwidth Usage: Businesses only pay for the portion of the T1 line they use, making it a cost-effective solution for those who don’t need the full bandwidth of a standard T1.
- Flexibility in Upgrading: As the business grows, upgrading the service to include more channels (and therefore more bandwidth) is usually straightforward and does not require a complete overhaul of the existing setup.
4. Applications and Use Cases
Real-World Scenarios
Fractional T1 lines are beneficial in various scenarios:
- Small to Medium-Sized Businesses: For businesses that have outgrown their broadband but are not yet ready for a full T1, a Fractional T1 provides the perfect middle ground.
- Remote Workforce Connectivity: Companies with remote employees can use Fractional T1 lines to ensure stable and reliable connections for their off-site workers.
- Temporary Projects: For short-term projects requiring reliable internet access, such as construction sites or temporary offices, Fractional T1 can be an ideal solution.
Industries Leveraging Fractional T1
Various industries find Fractional T1 lines beneficial:
- Healthcare: For transmitting patient records or telemedicine where consistent connectivity is vital.
- Finance and Banking: Where secure and reliable data transmission is essential.
- Retail: Especially for online operations requiring stable internet connectivity without the high cost of a full T1 line.
5. Challenges and Considerations in the Implementation
Common Challenges
Implementing Fractional T1 lines can present certain challenges:
- Technical Compatibility: Ensuring existing network infrastructure is compatible with T1 technology can be a hurdle for some businesses.
- Cost vs. Benefit Analysis: For some small businesses, the cost of even a Fractional T1 might be higher compared to other alternatives, making the cost-benefit analysis crucial.
Considerations for Effective Implementation
To effectively implement Fractional T1, businesses should:
- Assess Current and Future Needs: Evaluate current bandwidth requirements and future growth to determine the right level of service.
- Choose a Reputable Provider: Partner with a reliable service provider that can offer good support and service quality.
- Plan for Scalability: Consider the ease of scaling up the service as the business grows.
In summary, Fractional T1 lines offer a blend of reliability, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making them a suitable choice for a wide range of businesses and applications. However, careful consideration of the specific business needs and potential challenges is essential for maximizing the benefits of this telecommunications solution.
6. The Future of Fractional T1 in Telecommunications
Evolving Role in Telecom Landscape
As the telecommunications landscape continues to evolve rapidly, the role of Fractional T1 also adapts. With the advent of newer, faster technologies like fiber optics and 5G, the traditional T1 lines, including their fractional counterparts, face stiff competition. However, Fractional T1 still holds a unique position in certain scenarios, especially where high-speed alternatives are not feasible or cost-effective.
Future Trends and Developments
Looking ahead, potential developments in Fractional T1 technology might include:
- Integration with Advanced Technologies: There could be a trend towards integrating Fractional T1 lines with newer technologies to enhance reliability and service quality.
- Cost Reductions: Technological advancements might lead to reduced costs for T1 technologies, making Fractional T1 more accessible for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Customization and Flexibility: Future iterations of Fractional T1 might offer even more customization options, catering to a broader spectrum of business needs.
7. Conclusion
Fractional T1 lines represent a significant technological solution in the field of telecommunications, especially for businesses seeking a balance between bandwidth requirements and cost-effectiveness.
Despite the emergence of faster internet technologies, Fractional T1 remains relevant for its reliability, scalability, and quality of service. Its future in the telecom landscape will likely be shaped by its adaptability to changing business needs and integration with newer technologies. Understanding its benefits and potential limitations is crucial for businesses making informed decisions about their telecommunications infrastructure.
8. References
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan.
- “Telecommunications Essentials” by Lillian Goleniewski.