Welcome to the world of Home Area Networks (HAN) – the cornerstone of a connected, smart, and efficient home. In this digital age, understanding and mastering HAN is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity. From streaming your favorite shows seamlessly to ensuring your smart devices communicate flawlessly, a well-set-up HAN is the invisible hero of your home’s connectivity. Dive into our comprehensive guide to not only grasp the basics but also to discover the advanced capabilities that a HAN network can offer.
In this article:
- What is a Home Area Network (HAN)?
- Setting Up Your HAN Network
- Advanced Features and Setup
- Troubleshooting Common HAN Issues
- References

1. What is a Home Area Network (HAN)?
A Home Area Network (HAN) is a localized network that connects digital devices within a residential premise. It enables the sharing of internet access, media files, and other digital resources among multiple devices. Key components of a Home Area Network include:
- Networking Router: The core of HAN, directing traffic and connecting devices to the internet.
- Modem: Facilitates internet connection from your ISP.
- Switches and Hubs: Used for connecting multiple devices, enhancing network management.
- Wireless Access Points: Extend the wireless coverage area.
- Networked Devices: Computers, smart TVs, smart home devices, etc.
Today, almost every house have a router who provides internet access to all devices with TCP/IP connection. That includes the traditional computer or laptop, smartphones, smart-TVs, game consoles, security cameras, and even the latest home appliances (IoT).
A typical architecture of a Home Are Network:
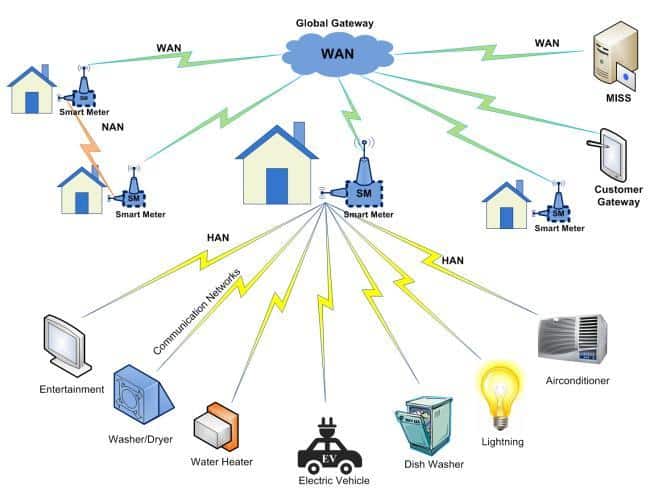
Currently (2024), Internet Service Providers offer fiber-optic network directly to our home providing a very fast service for TV streaming, gaming and VoIP services. All communications run through a TCP/IP connection between our home router and our Internet Service Provider.
Inside our home, we usually have one or more wireless access points to ensure full wi-fi signal coverage.
Comparing HAN with Other Types of Networks
- LAN (Local Area Network): Similar to HAN but more commonly used in business environments. LANs are typically larger and support more devices.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): Spans a large geographic area, like a city or region. Used by businesses and governments to connect smaller networks (LANs, HANs).
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Larger than LAN but smaller than WAN, covering a city or town.
2. Setting Up Your HAN
Step-by-Step Guide on Setting Up a Basic HAN
- Choose an Internet Service Provider (ISP): Select based on speed, reliability, and cost.
- Install a Modem: Connects your home to your ISP.
- Set Up a Router: Central point for managing your HAN.
- Connect the router to the modem.
- Configure the router settings (Wi-Fi name, password).
- Expand with Switches/Hubs (if needed): For more wired connections.
- Add Wireless Access Points: To increase Wi-Fi coverage.
- Connect Devices: Computers, smartphones, smart home devices.
- Secure Your Network: Set a strong password, update firmware, and enable encryption.
Discussing Different Networking Equipment and Their Roles
- Modems: Bridge between your home network and the internet.
- Routers: Distribute internet to various devices, provide security layers.
- Switches: Expand the number of available wired connections.
- Wireless Access Points: Boost Wi-Fi signal strength and range.
- Network-Attached Storage (NAS): Centralized storage for files, accessible by all networked devices.
Remember, a robust Home Area Network setup caters to your specific needs, ensuring all devices are seamlessly connected and the network is secure.
Devices and Services
- Computers such as desktops, laptops, netbooks, and tablets
- Network-attached storage (NAS) device
- Network Printers
- Smartphones connected via Wi-Fi
- Smart speakers
- Smart TV’s and DVRs (access to services such as Netflix and YouTube)
- Stereo systems with network connectivity that allow a user to easily access their music library stored on a PC or NAS
- Video game consoles for multiplayer games and social network integration
- Security alarms
- Garage door and gate openers
- HVAC (keeping your house warm or cold)
- Smoke/CO detectors
- Media Players or Streaming Devices like Apple TV
3. Advanced Features and Setup
Integrating Smart Home Devices
- Understanding Smart Devices: Recognize various smart devices like thermostats, lights, security cameras, etc., and their connectivity requirements (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave).
- Centralized Control Systems: Set up systems like Google Home or Amazon Alexa for unified control.
- Network Configuration for Smart Devices: Ensure strong Wi-Fi coverage, consider dedicated networks or VLANs for smart devices.
- Automating Home Functions: Utilize IFTTT or similar services for home automation.
Network Security and Privacy Concerns
- Secure Wi-Fi Access: Use WPA3 encryption, strong passwords.
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keep router and device firmware up-to-date.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate critical devices on separate networks.
- VPN for Remote Access: Use VPNs for secure remote network access.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Implement network monitoring tools for unusual activity.
4. Troubleshooting Common HAN Issues
Common Problems and Solutions
- Connectivity Issues: Check and restart routers/modems, check cables.
- Slow Internet Speeds: Test speeds, minimize interference, upgrade plan or equipment.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure device and network compatibility, update drivers/firmware.
Maintaining a Healthy HAN Network
- Regularly update software and firmware.
- Monitor bandwidth usage.
- Perform routine security checks.
- Educate family members about safe internet practices.
5. References
- Books:
- “Networking All-in-One For Dummies” by Doug Lowe.
- “Home Networking Do-It-Yourself For Dummies” by Lawrence C. Miller.
- RFCs: