Internet Locator Service (ILS) is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol directory service running on a server. While it’s possible that some legacy systems still use ILS, it’s not commonly found in current best practices for network setup and management. Most organizations have moved on to more scalable and secure solutions for directory services and real-time communication.
What is ILS (Internet Locator Service)?
ILS stands for Internet Locator Service, is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory service running on a server that lets users of Microsoft NetMeeting locate and contact other NetMeeting users to conference and collaborate over the Internet or over a private TCP/IP internetwork. The Internet Locator Service (ILS) replaces the earlier User Locator Service (ULS) technology.
How it works
Microsoft Commercial Internet System (MCIS) has an ILS service that functions as a memory-resident database for storing dynamic directory information about NetMeeting users. This information, which includes a user’s name, company, and IP address, is stored in an Active Directory Global Catalog and can be accessed by any LDAP client, such as NetMeeting.
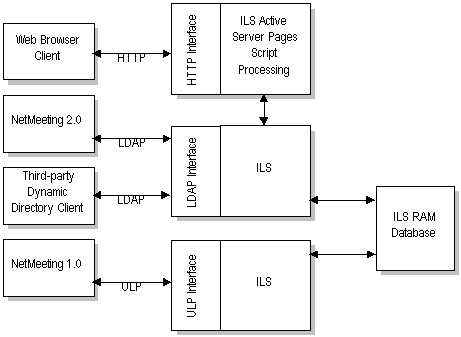
Clients periodically refresh the information in the ILS database. Users can access the ILS using LDAP to place a call to other NetMeeting users and to determine which NetMeeting users are currently logged on to the ILS.
Using Active Server Pages (ASP), you can design a customizable Web interface that displays who is currently online and allows users to search for other users and initiate NetMeeting sessions with them.
Outdated Technology
The Internet Locator Service (ILS) is generally considered to be outdated and is rarely used in modern networking environments. It was initially popular in the late 1990s and early 2000s, particularly for Microsoft NetMeeting and similar applications, but has been largely superseded by more advanced technologies.
ILS uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) for its directory services, but there are now more modern and secure directory services that also use LDAP or other protocols, such as Microsoft’s Active Directory, OpenLDAP, and others.
Read: RFC 4511 – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP): The Protocol