Project 802 is a far-reaching effort by the IEEE to create a set of standards for local and wide-area networks. With a series of subsections, Project 802 encompasses a variety of technologies and methodologies that have shaped modern networking. From Ethernet (802.3) to Wireless Networking (802.11), this article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the 802 family.
Table of Contents
- What is Project 802?
- Importance of Project 802
- 802.1: Internetworking Standards
- 802.2: Logical Link Control (LLC)
- 802.3: Ethernet
- 802.4: Token Bus LAN
- 802.5: Token Ring LAN
- 802.6: Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- 802.7: Broadband Technologies
- 802.8: Fiber-optic Technologies
- 802.9: Integrated Voice/Data Networks
- 802.10: Network Security Standards
- 802.11: Wireless Networking
- 802.12: Demand Priority Access
- 802.14: Cable Television Access
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- References
1. What is Project 802?
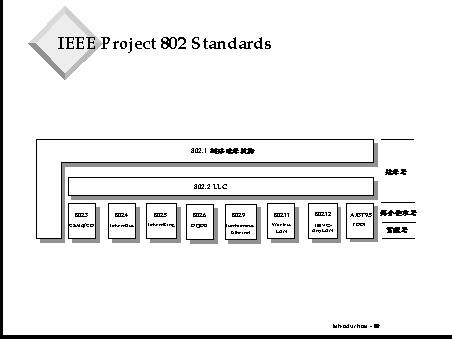
Project 802 is an ongoing project of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for defining local area network (LAN) and wide area network (WAN) standards and technologies. The 802 specifications define the operation of the physical network components – cabling, network adapters, and connectivity devices such as hubs and switches.
2. Importance of Project 802
Understanding Project 802 is essential for anyone involved in network administration, design, or research. It serves as the foundation for how networks communicate, providing a universal language that ensures interoperability among various technologies. In other words, Project 802 makes sure that your devices can talk to each other, regardless of the manufacturer.
3. 802.1: Internetworking Standards
802.1 deals with internetworking standards that provide the architecture and methodologies for the successful operation of networks. It primarily focuses on bridging different LANs and WANs, allowing them to work in a seamless manner. 802.1 is pivotal for network design and plays a crucial role in VLAN (Virtual LAN) configuration.
4. 802.2: Logical Link Control (LLC)
802.2 standardizes the Logical Link Control layer, a part of the Data-Link Layer in the OSI model. It essentially acts as an interface between the Network Layer and the MAC (Media Access Control) sub-layer, facilitating the flow of data across different media types. LLC is responsible for link establishment, maintenance, and termination.
5. 802.3: Ethernet
Perhaps the most commonly known, 802.3 defines the Ethernet standard, which uses a bus or star topology and supports data transfer rates of up to 100 Gbps in its latest versions. Initially using coaxial cables, it now widely utilizes twisted-pair and fiber optic cables. Ethernet has become the de facto standard for LANs worldwide.
6. 802.4: Token Bus LAN
The 802.4 standard defines how Token Bus LANs operate. Unlike Ethernet, which uses a “listen before send” approach, Token Bus uses tokens to manage access to the network. This ensures a deterministic behavior but has become less popular compared to Ethernet due to scalability issues.
7. 802.5: Token Ring LAN
802.5 outlines the Token Ring standard, which, like the Token Bus, uses a token-passing protocol for transferring the data. However, in Token Ring, the topology is set up in a physical ring. Although now largely obsolete, Token Ring offered reliable and deterministic networking and was especially popular in corporate environments in the 1980s and 1990s.
8. 802.6: Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
The 802.6 standard focuses on Metropolitan Area Networks, networks that are larger than LANs but smaller than WANs, generally covering a city or a large campus. These networks serve as a backbone for connecting multiple LANs and offer high-speed and high-capacity data transfer rates.
9. 802.7: Broadband Technologies
The IEEE 802.7 standard pertains to the application of broadband technologies. This standard was formulated to cover the best practices, physical layer specifications, and architectures for broadband. However, it’s worth noting that this section is not as widely cited as others, like 802.3 and 802.11.
10. 802.8: Fiber-Optic Technologies
802.8 deals with the standards and guidelines for fiber-optic technologies. It specifies the physical layer properties, including the type of fiber, signal, and connector used. Fiber-optic technologies are crucial for long-distance and high-capacity networks.
11. 802.9: Integrated Voice/Data Networks
The 802.9 standard focuses on integrating voice and data networks, offering the capacity for both within the same networking architecture. This provides a more seamless communication environment, typically over a high-speed network, and allows for easier management of network resources.
12. 802.10: Network Security Standards and Technologies
This subsection details the standards concerning network security technologies. It outlines the specifications and guidelines to secure network architecture, including methods for secure key management, data encryption, and user authentication.
13. 802.11: Wireless Networking Technologies and Standards
Arguably one of the most popular 802 standards, 802.11 governs wireless LAN technology, commonly known as Wi-Fi. It provides various protocols that extend wireless network capabilities and improve security and efficiency, such as 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax.
14. 802.12: Demand Priority Access Technologies
802.12 focuses on demand-priority access technologies, used mainly for industrial and enterprise-level applications. This standard aims to prioritize data packets based on the urgency of the information they contain, ensuring that high-priority data gets processed faster.
15. 802.14: Cable Television Access
Though now largely deprecated, 802.14 aimed to standardize data delivery over cable television systems. It was developed to facilitate broadband data services over cable networks, providing an alternative to traditional telephone line-based services.
16. Frequently Asked Questions
What is Project 802?
Project 802 is an ongoing initiative by the IEEE to standardize local and wide-area networking technologies. The project encompasses various subcommittees, each focused on a particular area of network technology.
What does 802.11 refer to?
802.11 refers to the IEEE standard for wireless LAN technologies, commonly known as Wi-Fi. It provides different protocols to extend the capabilities of wireless networks, like 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax.
How do 802.1 and 802.2 differ?
802.1 focuses on internetworking standards across all 802 projects, whereas 802.2 focuses on the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer of the OSI data-link layer, facilitating communication between network nodes.
What is 802.3?
802.3 is the standard that specifies the characteristics for Ethernet, the dominant standard for wired local area networks.
Is 802.5 still in use?
802.5, or Token Ring LAN, is mostly considered obsolete but may still be found in some legacy systems.
What is the focus of 802.10?
802.10 concentrates on network security standards, outlining methods for secure key management, data encryption, and user authentication.
What are demand priority access technologies?
Outlined in 802.12, demand priority access technologies prioritize data packets based on their urgency, ensuring that high-priority data is processed faster.
Is 802.14 still relevant?
802.14, focused on cable television access, is largely considered deprecated but served as an important step in the integration of cable networks for data delivery.
What are the latest updates in Project 802?
The most recent updates usually revolve around wireless networking (802.11) and network security (802.10), but it’s essential to keep an eye on the IEEE’s official website for the most current information.
Where can I find more information about Project 802?
The IEEE Standards Association provides comprehensive documentation on Project 802 and its subcommittees, which is available for public access on their website.
Conclusion
Project 802 has been pivotal in standardizing networking technologies. Its various subcommittees have tackled everything from Ethernet to wireless networks, and from network security to metropolitan and wide-area networks. Understanding the different 802 standards can offer a comprehensive view of network types, functionalities, and future possibilities.
References
- IEEE Standards Association. “IEEE 802 Standards.” IEEE Website
- Zimmerman, J. “The Token Ring Network and IEEE 802.5.” Network World.
- Smith, R. “Understanding 802.11 – Wi-Fi’s Inner Workings.” Networking Basics.
- Hall, D. “An Overview of IEEE 802.10 Security Standards.” Cybersecurity Journal.