The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Ping utility is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of network administrators and IT professionals managing Microsoft Exchange Server environments. Originating as a means to verify RPC connectivity between Exchange Servers and client workstations, RPCPing helps diagnose and ensure the smooth operation of email communication within a network.
This article explores the utility’s functionality, its relevance in modern Exchange Server management, and provides a detailed guide on leveraging RPCPing to maintain optimal server connectivity. From setup to troubleshooting, we cover all you need to know to master the Remote Procedure Call Ping in your networked environment.
Table of Contents:
- What is RPCPING?
- Setting Up RPCPing for Exchange Server
- How to Use RPC Ping: A Step-by-Step Guide
- RPC Ping in Modern Exchange Environments: Relevance and Updates
- References

1. What is RPCPing?
RPC Ping is a client/server utility included with Microsoft Exchange Server for testing for remote procedure call (RPC) connectivity between two locations on a network. In the context of Microsoft Exchange Server, RPC facilitates critical communications between the server and its clients, including email transmission, calendar synchronization, and other essential functions.
The server portion of RPC Ping runs on an Exchange server and responds to requests from the RPC Ping client. RPC connectivity is essential between all Exchange servers in the same site.
The Importance of RPCPing
The “Remote Procedure Call Ping” utility is invaluable for administrators for several reasons:
- Network Health Check: It serves as a health check, ensuring that the Exchange Server is accessible over the network and can communicate efficiently with client machines and other servers.
- Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues: RPC Ping is crucial for diagnosing connectivity problems within an Exchange environment. It helps pinpoint whether issues are due to network configurations, firewall settings, or the Exchange Server itself.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular use of RPC Ping can aid in monitoring the performance of RPC connections, allowing administrators to preemptively address potential issues before they impact users.
- Security Assessments: By testing RPC connectivity, administrators can also verify that security measures do not inadvertently block legitimate traffic, ensuring that communication remains secure yet fluid.
Understanding and effectively utilizing RPC Ping can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of Exchange Server operations, providing a better experience for both administrators and end-users.
2. Setting Up RPCPing for Exchange Server
Setting up RPC Ping requires a straightforward process, but it’s essential to ensure that your environment meets all prerequisites for successful execution. Follow these steps to set up RPC Ping in your Exchange Server environment:
Prerequisites
- Administrative Access: Ensure you have administrative privileges to the Exchange Server and client machines where you intend to use RPC Ping.
- RPC Ping Utility: Download the RPC Ping utility if it’s not already included with your Exchange Server installation. Microsoft provides this tool as part of its Exchange Server support tools or resource kits.
Installation and Configuration
- Install RPC Ping: Once downloaded, install the RPC Ping utility on the client machine from which you want to test the connectivity to the Exchange Server. Follow the installation prompts to complete the setup.
- Configure Firewall Settings: Ensure that any firewalls between the client machine and the Exchange Server are configured to allow RPC traffic. This may involve opening specific ports or setting up rules to permit traffic from the RPC Ping utility.
- Prepare Exchange Server: On the Exchange Server, verify that the services you intend to test with RPC Ping are running. This includes services like the Microsoft Exchange Information Store and the Microsoft Exchange Directory service.
- Gather Required Information: Collect necessary information such as the IP address or hostname of the Exchange Server and the specific ports or services you want to test with RPC Ping.
Execution
With RPC Ping set up, you can now execute tests to assess the connectivity and responsiveness of your Exchange Server. Detailed instructions on using RPC Ping, including command-line options and parameters, will be provided in the subsequent chapters, guiding you through the process of running connectivity tests and interpreting the results.
By following these setup instructions, you’ll be prepared to utilize RPC Ping effectively, ensuring that your Exchange Server environment is configured for optimal connectivity and performance.
3. How to Use RPCPing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using RPC Ping effectively requires familiarity with command-line interfaces and a basic understanding of network protocols. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of utilizing RPC Ping to test RPC connectivity in your Exchange Server environment.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
- Begin by opening the Command Prompt on the machine where RPC Ping is installed. Ensure you run it with administrative privileges to avoid permission issues.
Step 2: Navigate to RPC Ping Location
- Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the directory where RPC Ping is installed. If installed in the default location, you might find it within the Exchange Server support tools directory.
Step 3: Construct Your RPC Ping Command
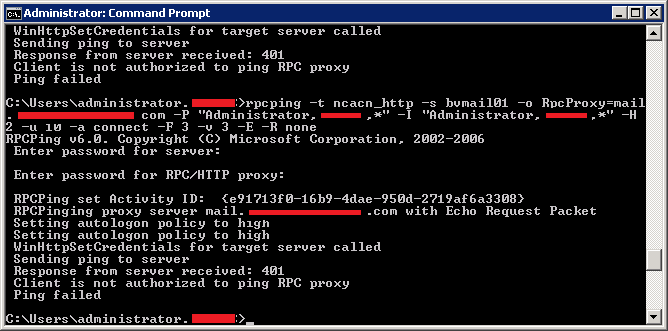
- The basic syntax for RPC Ping is as follows:
rpcping -s [ServerName or IP] -o RpcProxy=[ProxyServer]:[Port] -P "[Username],[Domain],[Password]" -H 1 -u 10 -a connect -F 3 -v 3 -e [Endpoint]
- Replace the placeholders with your actual server details, proxy information (if applicable), user credentials, and the specific endpoint you wish to test.
Step 4: Execute the Command
- After constructing your command, press Enter to execute it. RPC Ping will attempt to establish an RPC connection to the specified server and return the results.
Step 5: Interpret the Results
- The output will include information about the attempt to connect to the server, including any errors or the successful establishment of a connection. A quick response indicates good connectivity, while errors can help pinpoint issues in the network configuration or server setup.
Tips for Effective Use
- Test Multiple Endpoints: Run RPC Ping against different services on the Exchange Server to comprehensively assess connectivity.
- Document Results: Keep a record of test results for future reference, especially if you’re troubleshooting an ongoing issue or monitoring network performance over time.
- Combine with Other Tools: Use RPC Ping in conjunction with other diagnostic tools for a thorough analysis of network and server health.
4. RPCPing in Modern Exchange Environments: Relevance and Updates
Despite the evolution of Microsoft Exchange Server and network technologies, RPCPing continues to hold significant value in modern IT infrastructures. Its capability to precisely diagnose connectivity issues in RPC-based services ensures it remains relevant, especially in complex, hybrid, and cloud-based environments.
Updates and Enhancements
- Integration with Newer Protocols: As Microsoft Exchange has evolved, the Remote Procedure Call Ping utility has been updated to support newer protocols and authentication methods, ensuring compatibility with current Exchange versions.
- Cloud and Hybrid Environments: With the adoption of cloud services and hybrid configurations, RPC Ping helps verify connectivity between on-premises Exchange servers and Office 365 components, ensuring seamless integration.
The Role of RPCPing Today
- Troubleshooting Tool: RPC Ping remains a go-to tool for diagnosing connectivity issues, particularly in environments where legacy and modern systems coexist.
- Performance Monitoring: It serves as a critical component in performance monitoring strategies, offering insights into the latency and reliability of RPC communications.
5. References
To deepen your understanding of RPC Ping and its applications in network diagnostics, the following resources are invaluable:
Books
- “Microsoft Exchange Server PowerShell Cookbook – Third Edition“ by Jonas Andersson and Mike Pfeiffer: Offers insights into managing Exchange Server, including advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting techniques.
- “Networking and Internetworking with Microcontrollers“ by Fred Eady: While not directly related to RPC Ping, this book provides a solid foundation in network protocols and communications.
Relevant RFCs
- RFC 1831 – “RPC: Remote Procedure Call Protocol Specification Version 2”: Provides a comprehensive overview of the RPC protocol, essential for understanding the mechanics behind RPC Ping.
- RFC 1035 – “Domain Names – Implementation and Specification”: Useful for understanding DNS, often involved in configuring network services for Exchange.