A Virtual Server is a software-based emulation of a physical server, designed to provide a scalable, efficient, and cost-effective computing environment. It operates on a physical server but acts as a separate, independent unit, capable of running its operating system and applications. Virtual servers are pivotal in cloud computing, hosting, and IT infrastructure, offering the flexibility to deploy multiple server environments on a single physical hardware, thus maximizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
This article delves deeper into the intricacies of virtual servers, exploring how they function, why they’re indispensable in current technological realms, and the various forms they can take.
Table of Contents:
- What is a Virtual Server?
- Types of Virtual Servers
- Key Technologies Behind Virtual Servers
- Benefits of Using Virtual Servers
- Choosing the Right Virtual Server for Your Needs
- Setting Up a Virtual Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Future Trends in Virtual Server Technology
- References

1. What is a Virtual Server?
A Virtual Server refers to a software-based simulation of a physical server, a concept at the heart of virtualization technology. Unlike physical servers, which are confined by their hardware components, virtual servers exist as software-defined entities that reside on physical hardware but operate independently of it. This independence allows for multiple virtual servers to coexist on a single physical server, each with its own operating system, applications, and configurations.
The essence of a virtual server lies in its ability to offer the functionalities of a physical server while abstracting the underlying hardware. This abstraction layer enables unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, making virtual servers an integral part of modern data centers, cloud computing environments, and enterprise IT infrastructures.
See also: Virtual Hosting.
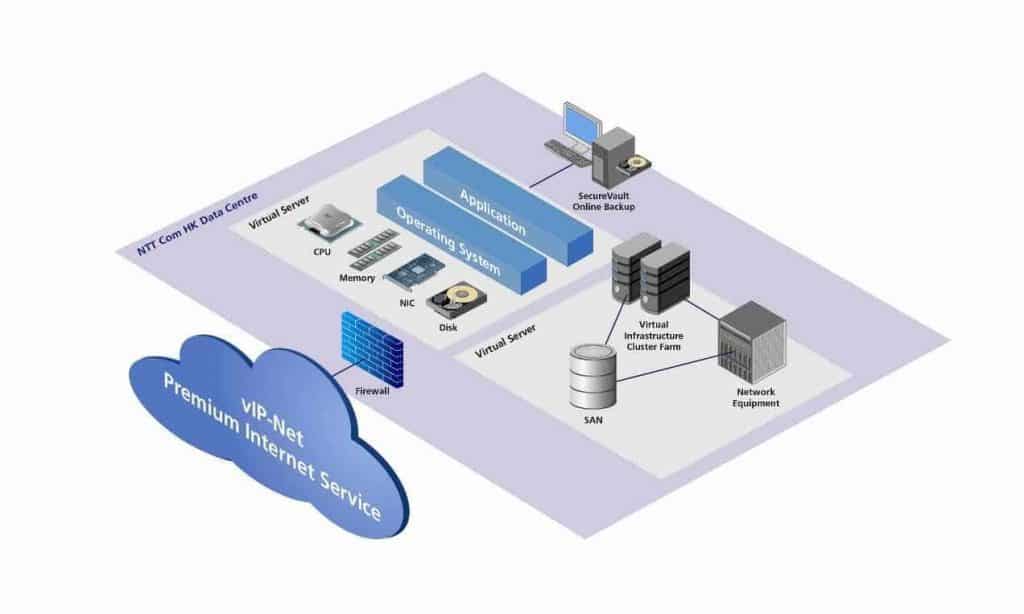
How Virtual Servers Work
The operation of virtual servers is enabled by a layer of software known as a hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM). The hypervisor sits between the physical hardware and the virtual servers, allocating resources as needed from the physical hardware to each virtual server. It manages these resources dynamically, ensuring that each virtual server has access to the processing power, memory, and storage it requires without being directly tied to specific physical resources.
Virtual servers work by emulating hardware functionalities through software, allowing them to run their operating systems and applications as if they were on their own dedicated hardware. The hypervisor is responsible for handling the creation, execution, and management of these virtual environments, including the execution of instructions, memory management, and I/O operations, ensuring isolation among virtual servers to maintain security and stability.
2. Types of Virtual Servers
Virtual server environments can vary significantly depending on their deployment model and the specific needs they address. The three primary types of virtual servers are dedicated virtual servers, shared virtual servers, and cloud servers.
Dedicated Virtual Servers
A dedicated virtual server, also known as a virtual private server (VPS), is allocated a dedicated portion of a physical server’s resources. Unlike shared servers, a VPS does not compete for resources with other virtual servers on the same physical hardware. This setup offers improved performance, stability, and security, making it suitable for applications requiring consistent resource availability and isolation from other workloads.
Shared Virtual Servers
Shared virtual servers reside on a physical server where resources are not allocated fixedly among the virtual environments. Instead, these servers share the physical server’s resources dynamically, with the hypervisor managing resource allocation based on current demand and predefined policies. Shared virtual servers are a cost-effective solution for hosting websites and applications with variable or low resource requirements, offering the benefits of virtualization without the cost of dedicated resources.
Cloud Servers
Cloud servers represent the evolution of virtual server technology, offering on-demand resource provisioning and scalability. Hosted in cloud computing environments, cloud servers provide greater flexibility than traditional virtual servers, allowing users to scale resources up or down based on real-time needs. This model supports a wide range of applications, from web hosting and database management to complex enterprise applications, benefiting from the cloud’s elasticity, geographic redundancy, and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
3. Key Technologies Behind Virtual Servers
Hypervisors and Virtualization
The foundation of virtual server technology is the hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM). Hypervisors are critical for creating and managing virtual environments, and they come in two main types: Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted).
- Type 1 Hypervisors: These are installed directly on the physical server’s hardware, providing high performance and efficiency by directly managing and allocating the server’s resources to each virtual server. Examples include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen.
- Type 2 Hypervisors: These run on a conventional operating system just like any other software application. While they are easier to set up and manage, they may not offer the same level of performance as Type 1 hypervisors due to the additional layer between the virtual server and the physical hardware. Examples include VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox.
Virtualization enables the division of a single physical server into multiple isolated virtual environments. Each virtual server can run its operating system and applications, operating independently of the others.
Containerization vs. Virtualization
While virtualization involves creating multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a single physical hardware system, containerization encapsulates the application’s code along with its dependencies into a container that can run on any compatible host system.
- Virtualization provides each virtual server with a full set of virtual hardware, allowing it to run an operating system and applications in isolation. This process can be resource-intensive, as each virtual machine includes not only the application and its environment but also an entire operating system.
- Containerization, by contrast, allows multiple containers to share the host system’s kernel but package the application and its libraries, dependencies, and other binaries in a container. This approach is more lightweight and efficient than virtualization, as containers require less overhead than virtual machines.
Both technologies offer advantages depending on the use case. Virtualization is ideal for running multiple different operating systems or when full isolation and security are needed. Containerization is more suited for deploying and managing microservices or other distributed applications that need to be efficiently scaled or replicated.
4. Benefits of Using Virtual Servers
Cost Efficiency
Virtual servers significantly reduce the need for physical hardware, as multiple virtual servers can operate on a single physical server. This consolidation reduces hardware costs, energy consumption, and the physical space needed for server infrastructure, contributing to a lower total cost of ownership.
Scalability and Flexibility
Virtual servers can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. Resources like CPU, memory, and storage can be adjusted quickly to accommodate changing workloads, providing businesses with the flexibility to respond to growth or temporary spikes in demand without the need for physical hardware changes.
Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Virtual servers enhance disaster recovery and high availability strategies. Virtual machines can be migrated from one server to another with minimal downtime, and backup snapshots can be created and restored quickly. This flexibility ensures business continuity by minimizing the impact of hardware failures, maintenance, or other disruptions.
5. Choosing the Right Virtual Server for Your Needs
Assessing Workload and Performance Requirements
Selecting the appropriate virtual server environment begins with a thorough assessment of your application’s workload and performance requirements. Considerations include the amount of CPU, memory, and storage needed, as well as network bandwidth and latency requirements. Understanding these needs will help determine the type and configuration of the virtual server that can best support your applications.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Security and compliance are paramount when deploying virtual servers. Evaluate the security features offered by the hypervisor and the hosting provider, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption capabilities. Ensure that the provider complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, to protect sensitive data and maintain regulatory compliance.
Vendor Selection and Migration Strategies
Choosing the right vendor involves comparing the features, performance, cost, and support options of potential providers. Look for vendors with a proven track record in virtualization technology and those that offer the scalability, reliability, and security features your applications require. Developing a comprehensive migration strategy is also crucial for transitioning to a virtual server environment. This plan should include data migration, application testing, and contingency plans to minimize downtime and ensure a smooth transition.
6. Setting Up a Virtual Server: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the Right Platform and Tools
- Assess Your Needs: Evaluate your specific requirements for computing resources, performance, security, and scalability to determine the most suitable virtualization platform for your environment.
- Choose a Hypervisor: Based on your assessment, select a Type 1 (bare-metal) hypervisor for performance and scalability or a Type 2 (hosted) hypervisor for ease of use and flexibility. Popular options include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V (Type 1), and Oracle VirtualBox (Type 2). (1)
- Virtualization Software: Decide on virtualization management software that can help you manage your virtual environment efficiently. Tools like VMware vCenter or Microsoft System Center offer advanced features for managing multiple virtual machines (VMs).
Configuration and Deployment
- Install the Hypervisor: Follow the installation guide for your chosen hypervisor. Ensure that your physical server meets all hardware requirements.
- Create Virtual Machines: Use your virtualization software to create new VMs. Assign resources (CPU, memory, storage) to each VM based on your prior assessment.
- Install Operating Systems and Applications: For each VM, install the necessary operating system and applications. Ensure each VM is configured according to its intended role and performance expectations.
- Network Configuration: Set up virtual networks to allow your VMs to communicate with each other and with external networks securely.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Monitoring Tools: Implement monitoring tools to track the performance and health of your virtual servers. Many hypervisors include built-in monitoring capabilities, but third-party tools can offer more comprehensive insights.
- Regular Updates: Keep your hypervisor, virtualization software, and VM operating systems and applications updated with the latest patches to ensure security and performance.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establish a regular backup schedule for your VMs and test your disaster recovery plans to ensure you can quickly restore operations in case of failure.
7. Future Trends in Virtual Server Technology
Innovations in Virtualization
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Storage (SDS): These technologies provide more flexibility and efficiency in resource management, enabling more granular control over network traffic and storage allocation.
- Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI): HCI integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single system. This simplifies the data center architecture and enhances scalability and performance.
The Role of AI and Automation in Server Management
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze patterns in server performance and utilization, predicting potential issues before they impact operations, enabling proactive maintenance.
- Automated Configuration and Deployment: AI and automation tools can streamline the setup and scaling of virtual servers, reducing the potential for human error and freeing IT staff for strategic tasks.
- Self-Healing Systems: AI-driven tools can automatically detect and correct failures in virtual servers, minimizing downtime and improving reliability.
8. References
Books
- “Mastering VMware vSphere 6.7” by Nick Marshall, Grant Orchard, et al.
- “Windows Server 2019 Inside Out” by Orin Thomas
RFCs
- RFC 2764 – A Framework for IP Based Virtual Private Networks.
- RFC 2917 – A Core MPLS IP VPN Architecture.
Online Resources
- VMware Documentation: https://docs.vmware.com
- Microsoft Hyper-V Documentation: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/virtualization/hyper-v/hyper-v-on-windows-server