Our Latest Articles
-
Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation (CAP)
Carrierless Amplitude and Phase Modulation is a line coding scheme in which data is modulated using a single carrier frequency for transmission over a phone line.
-
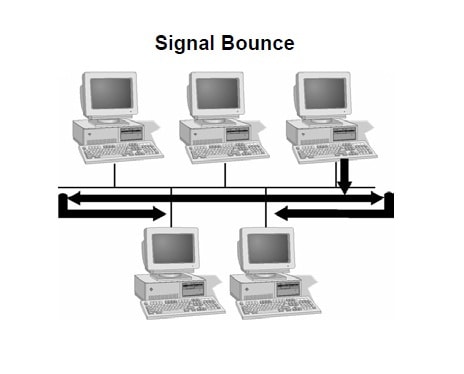
Signal Bounce in Computer Networking: What You Need to Know
Discover the multifaceted world of Signal Bounce, a phenomenon that can drastically impact data integrity and network performance. Learn how to diagnose and mitigate this issue across various industries, from data centers to healthcare systems. This comprehensive guide is your roadmap to understanding Signal Bounce.
-
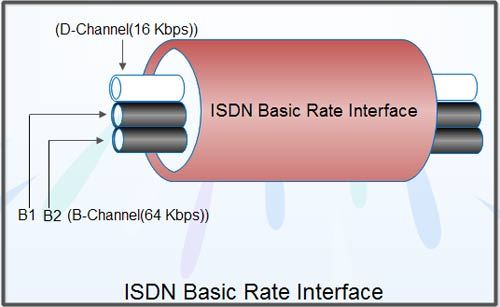
BRI-ISDN: Unpacking the Basic Rate Interface in ISDN Systems
Explore BRI-ISDN, the Basic Rate Interface for ISDN systems, a pivotal technology in telecommunications history, known for its 2B+D channel configuration.
-
Banyan VINES
VINES stands for Banyan Virtual Integrated Network Service, it was a network operating system (NOS) for building enterprise-level networks.
-
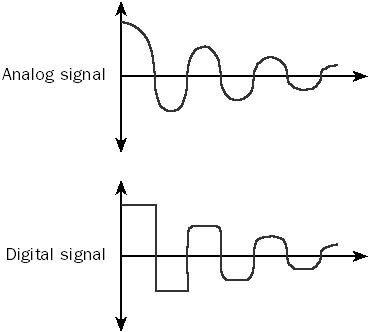
Attenuation in Computer Networking: Understanding Signal Loss
In this article, we will delve into the definition of attenuation, its measurement in decibels (dB), and its implications for different types of cabling media.
-
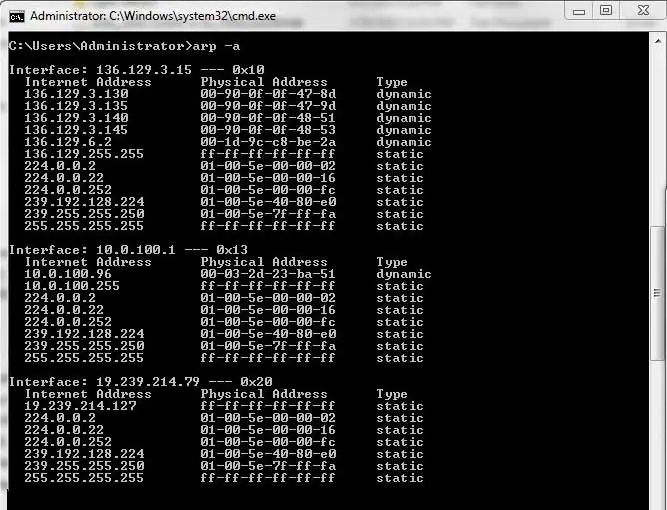
Arp Command
Master the ARP command to manage ARP cache, resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses, and optimize your network configurations. Comprehensive guide on why, how, and when to use the arp command.
-

Application Layer Proxy
Application Layer Proxies are essential tools in modern network architecture, offering deep packet inspection, enhanced security, and content filtering. From understanding its operations, benefits, drawbacks, and comparisons with packet filtering, this article provides an insightful look into the practical applications and setup of these proxies.
-
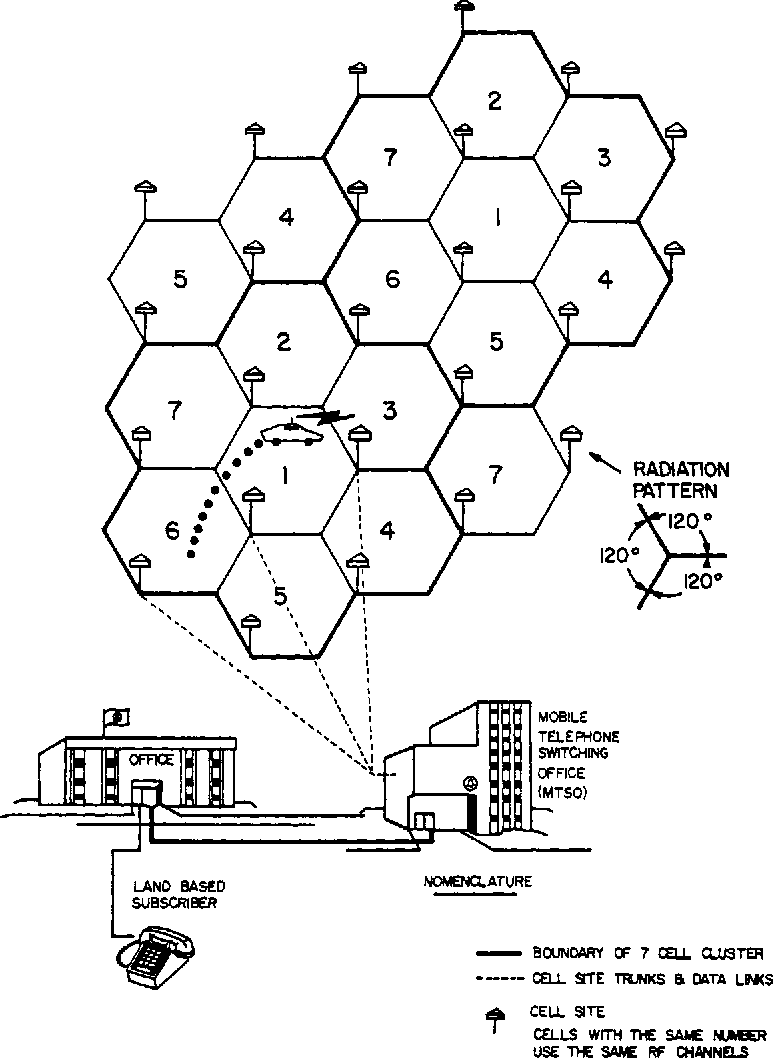
Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS)
AMPS stand for Advanced Mobile Phone Service, is the standard analog cellular phone service used in North and South America.
-
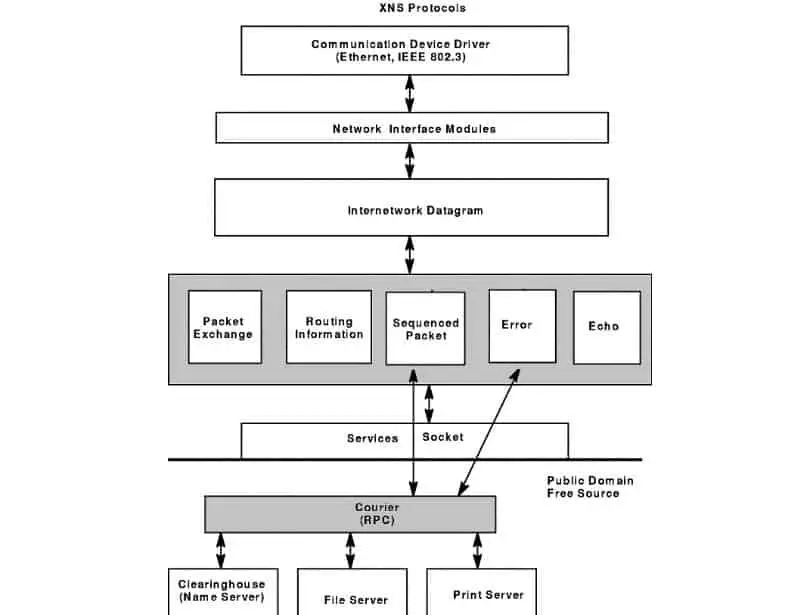
Xerox Network Systems (XNS)
Xerox Network Systems is a suite of networking protocols developed by Xerox Corporation’s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) in the early 1980s.
-
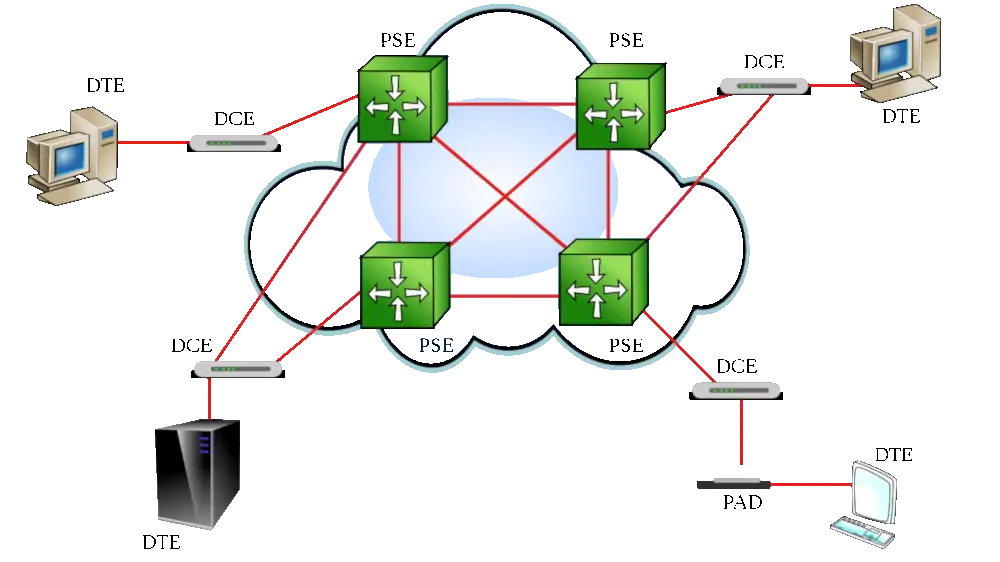
X.25 Protocol
X.25 is a packet-switching protocol for wide area network (WAN) connectivity that uses a public data network (PDN) that parallels the voice network of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).