Have you ever wondered how your computer knows where to store your files or where to find the programs you need? This seemingly magical knowledge is largely thanks to Environment Variables in Windows operating systems. These variables are not just placeholders; they are the unsung heroes that orchestrate the seamless operation of your OS and applications.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of Environment Variables, exploring their types, purposes, and the vital role they play in the smooth running of Windows OS.
In this article:
- What are Environment Variables in Windows?
- Types of Environment Variables: User vs System
- How Environment Variables Work
- Common Environment Variables in Windows
- Configuring Environment Variables
- Advanced Uses of Environment Variables
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- References

1. What are Environment Variables in Windows?
Definition and Basic Understanding
Environment Variables in Windows are dynamic string variables stored within the system that dictate how the various processes in the operating system (OS) behave. These variables contain information such as data paths, file locations, and system settings. They act like shortcuts, allowing the OS and applications to quickly and efficiently access essential directories and settings without needing to know the exact path or value.
The concept of Environment Variables is not unique to Windows; it’s a common feature in many operating systems, but Windows utilizes them in specific ways. They provide a flexible method of referencing system properties and user-specific settings, making the OS more adaptable and personalized.
The Role in Operating System and Applications
In the Windows operating system, Environment Variables serve two primary purposes:
- Facilitating Configuration: They simplify the configuration of system and application settings. For instance, the ‘PATH’ variable tells the system where to look for executable files, so you don’t have to type the full path every time you run a program.
- User and System Information Storage: Environment Variables store key information about user profiles (like the home directory) and system settings. This storage role is crucial for applications to operate correctly across different user accounts and system configurations.
By using Environment Variables, applications can adapt their behavior based on the user’s environment without hardcoding specific paths or settings. This adaptability is particularly important for applications designed to work across multiple versions of Windows or in networked environments with varying directory structures.
2. Types of Environment Variables: User vs System
Understanding User Environment Variables
User Environment Variables are specific to a user’s profile on a Windows system. They define the settings and paths relevant to the user’s session. For example, the ‘TEMP’ variable for a specific user points to the directory where temporary files for that user are stored. These variables ensure that personal settings and files are kept separate and secure for each user.
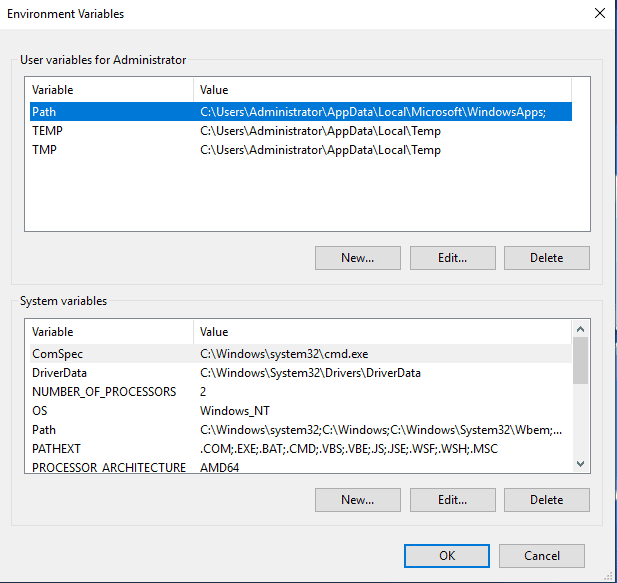
Exploring System Environment Variables
System Environment Variables, on the other hand, are global; they affect all users on the system. These include variables like ‘SYSTEMROOT’, which indicates the location of the Windows system directory, and ‘COMSPEC’, which specifies the command interpreter. Changes to System Environment Variables impact the entire operating system, making them essential for system-wide settings and configurations.
Key Differences and Use Cases
The primary difference between User and System Environment Variables lies in their scope and impact. User variables cater to individual user preferences and settings, while System variables provide information and configurations that are universal across the system.
For example, a software installation might add its executable’s path to the ‘PATH’ System Environment Variable to ensure that all users can access it. In contrast, a user might set a custom ‘TEMP’ directory in their User Environment Variables for their temporary files.
In practice, understanding and correctly using these two types of Environment Variables is key to efficient system administration and software management in Windows. They allow for a high degree of customization and flexibility, accommodating diverse needs and scenarios in a multi-user environment.
3. How Environment Variables Work
Mechanism of Action in Windows OS
In Windows Operating System, Environment Variables function as a bridge between system-level configurations and user-level interactions. When the system boots up or a user logs in, Windows reads a set of predefined Environment Variables. These variables inform the OS and applications about system-wide settings like where to find essential system directories and user-specific settings such as the location of the user’s personal files.
The Windows registry stores these Environment Variables. System Variables are located under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) subtree (specifically in HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment), while User Variables are found under HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU) subtree (in HKCU\Environment). When changes are made to these variables, they are typically reflected after a system reboot or a user logoff/logon cycle.
Interaction with Applications and Services
Applications and services in Windows use these Environment Variables to determine various operational parameters. For example, when a software installer runs, it might use the ProgramFiles Environment Variable to determine the default installation directory.
Developers can also access and manipulate these variables through programming languages and scripts. This flexibility allows for dynamic application behavior based on the user’s environment or system settings. Additionally, command-line tools like Command Prompt and PowerShell can directly use and modify Environment Variables, making them powerful tools for system administration.
4. Common Environment Variables in Windows
PATH: The Journey Finder
The PATH Environment Variable is one of the most critical in Windows. It specifies the directories where the OS should look for executable files when a command is given. By including directories in the PATH, users can run programs and scripts from the command line without specifying the full path. It’s a fundamental variable for system navigation and software execution.
TEMP: The Temporary Custodian
The TEMP (or TMP) Environment Variable points to the directory where applications can store temporary files. This variable is crucial for both system operations and third-party applications, as it provides a designated space for temporary data storage. Different users can have their own TEMP directories, as defined in their user-specific Environment Variables, ensuring that temporary files are managed securely and efficiently.
USERPROFILE: Personal Space in OS
USERPROFILE is an Environment Variable that denotes the path to the current user’s profile folder. This folder contains personal documents, settings, and other user-specific files. Applications often use USERPROFILE to store user-specific configurations and data. For instance, web browsers might store bookmarks and history in a subfolder within the USERPROFILE directory. This variable is fundamental in maintaining a personalized and secure user environment within the Windows OS.
5. Configuring Environment Variables
Step-by-Step Guide to Set and Modify Variables
Configuring Environment Variables in Windows is a straightforward process, but it requires administrative privileges for modifying system variables. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Accessing Environment Variables:
- Right-click on ‘This PC’ or ‘My Computer’ on your desktop or in File Explorer.
- Select ‘Properties’, and then click on ‘Advanced system settings’.
- In the System Properties window, click the ‘Environment Variables’ button.
- Modifying User Variables:
- In the Environment Variables window, under ‘User variables for [your username]’, select the variable you want to modify, or click ‘New’ to create a new one.
- Enter the name of the variable and its value. For a new variable, provide a unique name and specify its value.
- Modifying System Variables:
- Under ‘System variables’, follow the same process as for User Variables. Remember, modifying system variables affects all users and requires administrative access.
- Applying Changes:
- After making changes or adding new variables, click ‘OK’ in each open window.
- For the changes to take effect, you may need to restart your computer or log off and log back on.
Best Practices for Configuration
- Backup First: Before making changes, especially to system variables, back up your current settings.
- Use Descriptive Names: For new variables, use names that clearly describe their purpose.
- Test Changes: Test the effects of changes with a single application or process before applying them system-wide.
- Avoid Overwriting: Be cautious not to overwrite essential system variables, as this can cause system instability.
- Limit Size: Keep the total length of the PATH variable under the maximum limit (which varies by Windows version) to prevent issues.
6. Advanced Uses of Environment Variables
Scripting and Automation
Environment Variables can be incredibly useful in scripting and automation. For instance, in batch scripting or PowerShell, Environment Variables can be used to create scripts that adapt to the user’s environment, like scripts that change behavior based on the user’s profile or system settings. This adaptability makes scripts more robust and portable across different machines and environments.
Customizing User and System Environments
In more advanced scenarios, Environment Variables can be used to customize environments for specific tasks or projects. For example, developers can use Environment Variables to switch between different toolchains or development environments. By altering variables like PATH, you can change which version of a compiler or scripting language is used by default.
System administrators can also use Environment Variables to enforce certain configurations or policies. For example, setting a TEMP directory on a faster storage drive or network location can improve performance for temporary file operations.
By leveraging the flexibility of Environment Variables, both users and administrators can significantly enhance the functionality, efficiency, and customization of Windows operating systems.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and Resolving Variable-Related Errors
Environment Variable-related errors can manifest in various ways, from applications failing to launch to incorrect file paths being accessed. To troubleshoot:
- Check Variable Values: Ensure that the values of critical Environment Variables like
PATH,TEMP, andUSERPROFILEare set correctly. Use the Environment Variables dialog in System Properties to verify and correct these values. - Syntax Errors: Watch out for syntax errors, especially in the
PATHvariable. Even a missing semicolon can cause problems. - Length Limitations: For the
PATHvariable, be aware of its length limitations. Exceeding the maximum length can lead to parts of it being ignored. - User vs System Variables: Ensure that variables are set at the correct level (User or System). Setting a variable at the user level when it should be at the system level (or vice versa) can lead to unexpected behaviors.
- Restart and Test: After making changes, restart your computer or log out and back in to ensure the changes take effect, then test the application or service again.
Ensuring Stability and Security
- Regular Audits: Regularly audit your Environment Variables to ensure they are not being misused by malicious software.
- Use Secure Locations: Ensure that paths in Environment Variables, especially in
PATH, point to secure and trusted locations to prevent security risks. - Limited Editing: Restrict the editing of critical system variables to administrators to prevent accidental or malicious changes.
8. References
Books
- “Windows Internals” by Mark Russinovich and David Solomon
- “Windows System Programming” by Johnson M. Hart
Academic and Technical Articles
- “How To Manage Environment Variables in Windows XP” – Microsoft Learn
- “NVM#: Effective Environment Variables Manager” – Ratish Philip, CodeProject.com