Category: Letter P
-
Physical Medium Dependent (PMD)
Physical Medium Dependent, also known as PMD, defines the details of transmission and reception of individual bits on a physical medium.
-

Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
In this article, we will unravel the layers of Password Authentication Protocol (PAP), exploring its operations, advantages, and its place in the ever-evolving landscape of network security protocols.
-
Power-on Self Test (POST): Ensuring System Integrity from Startup
Power-On Self Test is a special set of ROM routines that run whenever a PC is booted. The power-on self test (POST) is designed to test whether system components are functioning properly before attempting to boot the operating system, and checks such things as the RAM, keyboard, and disk drives.
-
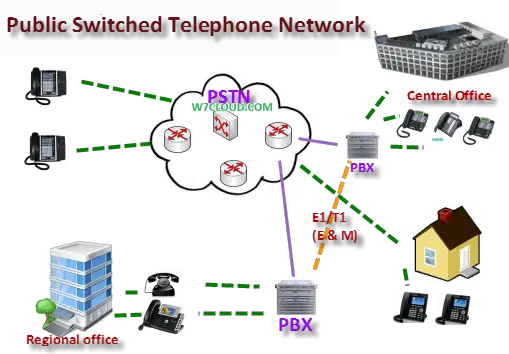
PSTN or Public Switched Telephone Network
Public Switched Telephone Network, also known as PSTN, is the public telephone network managed by the local telco and long-distance carriers. The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) consists of a digital backbone of switched circuits together with the analog local loop wiring still found in many residences.
-
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Cabling
Polyvinyl Chloride cabling, or simply PVC, is a grade of network cabling that uses polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic for its outer protective insulating jacket. Polyvinyl chloride cabling is cheap and flexible but gives off dangerous gases during combustion. Building codes usually require that plenum cabling be used instead of polyvinyl chloride cabling for horizontal runs…
-
Plenum Cabling
Explore the essentials of plenum cable, its safety-centric design, historical context, and ongoing relevance in modern networking.
-
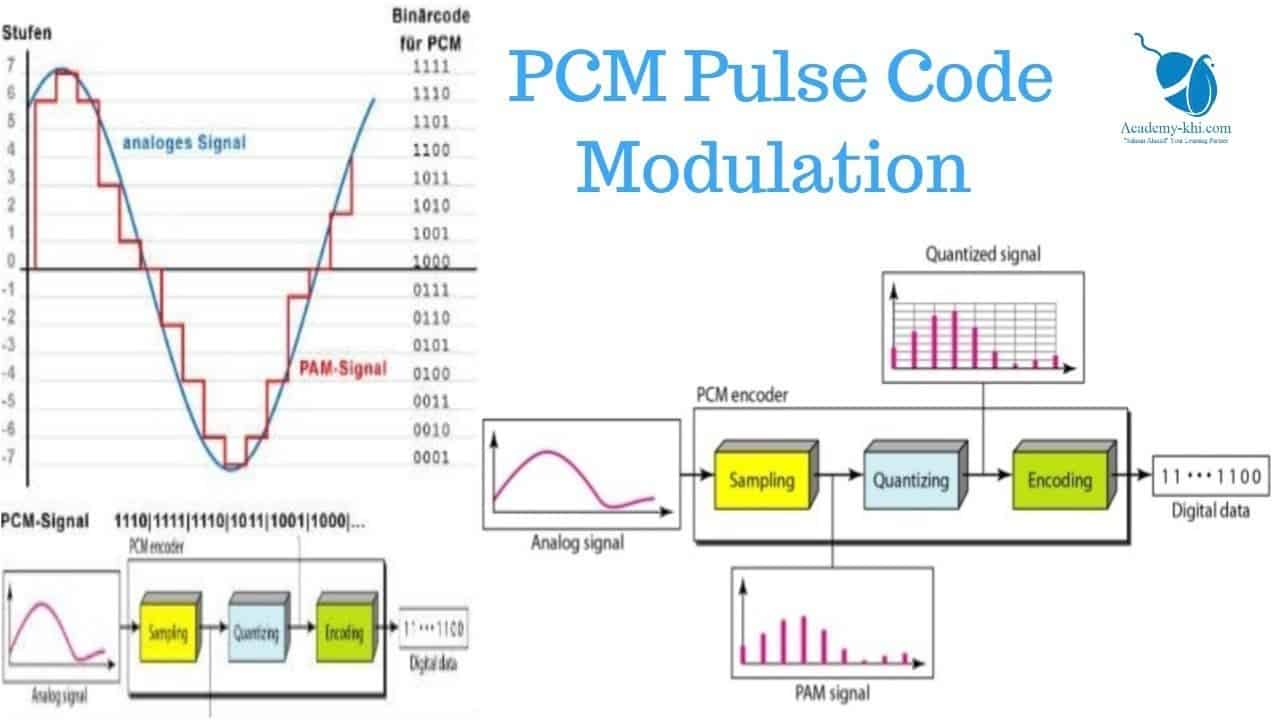
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)
Explore the essentials of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), the cornerstone of digital audio and communication systems.
-
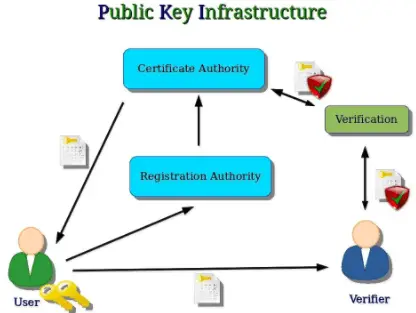
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure, also known as PKI, is a set of services that support the use of public-key cryptography in a corporate or public setting. A public key infrastructure (PKI) enables key pairs to be generated, securely stored, and securely transmitted to users so that users can send encrypted transmissions and digital signatures over distrusted…
-

Proxy Cache Server
Explore the world of Proxy Cache Servers: Unraveling their roles, benefits, comparison with CDNs, and the evolution of Microsoft’s Proxy Server.
-
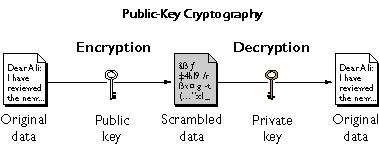
Public Key Cryptography
Public Key Cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a popular encryption method developed by Martin Hellman and Whitfield Diffie in 1976 that is used for securing the transmission of data over distrusted networks such as the Internet.
-
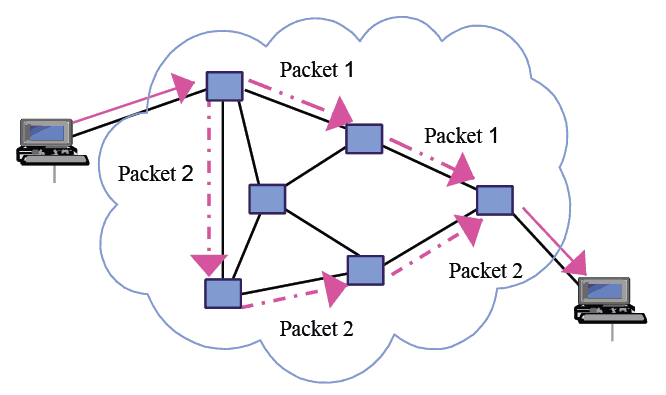
Packet Switching
Packet Switching is the process by which a networking or telecommunications device accepts a packet and switches it to a telecommunications device that will take it closer to its destination. (Learn More)
-
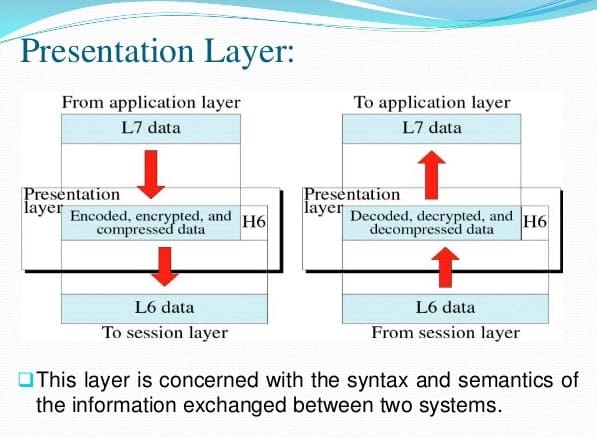
Presentation Layer
Presentation Layer is the Layer 6 of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model.