In the data-driven world of network communications, Full-Duplex Ethernet stands out as a significant advancement, redefining the capabilities of Ethernet technology. Full-Duplex Ethernet transcends the limitations of its predecessors by enabling simultaneous two-way data transmission, effectively doubling the available throughput compared to the conventional half-duplex Ethernet. This technology has revolutionized network infrastructures, allowing for smoother, more efficient communication channels that are pivotal in today’s high-speed, interconnected ecosystems.
In this article, we delve into the workings of Full-Duplex Ethernet, its implementation, and the tangible benefits it brings to modern networks. By dissecting its technical aspects and real-world applications, we will comprehend how Full-Duplex Ethernet achieves superior performance and why it has become the backbone of many contemporary networking solutions.
Table of Contents:
- What is Full-Duplex Ethernet?
- How Full-Duplex Ethernet Works
- The Role of Ethernet Switches in Full-Duplex Networking
- Performance Metrics: The Real-World Throughput of Full-Duplex Ethernet
- References
- Video
1. What is Full-Duplex Ethernet?
Full-Duplex Ethernet is a type of Ethernet that supports full-duplex communication between stations on the network. Full-duplex Ethernet lets stations send and receive data simultaneously, thus giving it twice the maximum throughput of traditional forms of Ethernet.
Technological Breakthrough in Network Communication
Full-Duplex Ethernet represents a significant technological breakthrough in network communication, elevating the standard of data transmission capabilities within network infrastructures. Unlike traditional Ethernet, which operates on a half-duplex basis, Full-Duplex Ethernet allows for simultaneous two-way data exchange. This bidirectional communication mirrors the natural flow of conversation like that in a telephone call, where both parties can speak and listen at the same time. This advancement not only doubles the effective bandwidth but also enhances the overall network efficiency by reducing the time frames spent waiting for a clear signal to transmit data.
Full-Duplex vs. Half-Duplex: The Key Differences
The principal difference between Full-Duplex and Half-Duplex lies in their method of data transmission. In a half-duplex environment, a network device must wait for a clear signal before it can send data because transmission and reception occur on the same channel. This waiting can lead to collisions and network congestion, necessitating a backoff algorithm and retransmission of data packets, which ultimately hinders network performance.
Conversely, Full-Duplex Ethernet eliminates this issue by using two separate channels, typically within the same cable, allowing devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously. This simultaneous communication removes the possibility of collisions, as there is no need to alternate between sending and receiving. The absence of collisions in a Full-Duplex system translates into a more stable and consistent network throughput, making it highly suitable for high-speed networks that demand peak performance at all times.
2. How Full-Duplex Ethernet Works
The Fundamentals of Simultaneous Data Transmission
Simultaneous data transmission in Full-Duplex Ethernet is achieved by splitting the communication into two distinct channels. In twisted pair Ethernet cables, for example, one pair of wires is used exclusively for sending data, while another pair is used solely for receiving. This separation ensures that signals going in one direction do not interfere with those going in the opposite direction. Such a system requires sophisticated hardware capable of managing two-way communication without allowing the signals to cross paths in a disruptive manner.
Infrastructure Requirements for Full-Duplex Operation
To operate in Full-Duplex mode, network infrastructure must meet specific requirements. Primarily, it necessitates the use of Ethernet switches as opposed to hubs. Switches can direct data packets precisely to the intended destination without broadcasting to the entire network, thus preventing the data collisions typical in shared medium networks.
Additionally, both ends of the communication link—typically a server and a network switch—must support Full-Duplex operation and be configured to enable it. This involves setting the network interface cards (NICs) and switches to Full-Duplex mode, which may be done automatically through auto-negotiation or manually through network settings. Network cabling must also adhere to the standards that can accommodate Full-Duplex transmission, such as Cat5e or Cat6 twisted pair cables, which provide the necessary pairs of wires for simultaneous send and receive operations.
Through a combination of appropriate hardware, correct cabling, and precise configuration, Full-Duplex Ethernet achieves a collision-free, high-efficiency communication environment, making it an indispensable technology in modern high-performance networks.
3. The Role of Ethernet Switches in Full-Duplex Networking
Switching vs. Hub-Based Networks: Avoiding Collisions
Ethernet switches have been pivotal in the transition from half-duplex to full-duplex networking by providing dedicated pathways for data packets between devices. Unlike hubs, which broadcast incoming data packets to all ports, switches intelligently direct packets to the specific port connected to the destination device. This point-to-point connection between devices on a network switch facilitates full-duplex communication, eliminating the possibility of collisions that are common in hub-based, shared-medium environments. In full-duplex mode, the switch and the network interface card (NIC) work together to transmit and receive data simultaneously without interference, thus maintaining network integrity and enhancing performance.
Configuring Switches for Full-Duplex Efficiency
To achieve full-duplex efficiency, switches must be correctly configured. Modern Ethernet switches are typically designed to auto-negotiate the operating mode of the link (full or half-duplex) and the speed of the connection. However, in environments where auto-negotiation is not possible or not preferred, the network administrator can manually configure both ends of the link to operate in full-duplex mode. Proper configuration is vital to prevent duplex mismatches, which can occur if one end of the link is set to full-duplex and the other to half-duplex, leading to severe network performance degradation.
4. Performance Metrics: The Real-World Throughput of Full-Duplex Ethernet
Theoretical vs. Actual Throughput
While full-duplex Ethernet has a theoretical bandwidth of twice the nominal rate, actual throughput is often less. For instance, a 100BaseT network has a theoretical maximum speed of 200 Mbps in full-duplex mode. However, factors such as protocol overhead, network congestion, and hardware limitations can prevent the network from achieving this theoretical maximum. Actual throughput is typically gauged under real-world conditions and reflects the efficiency and performance of the network in operational environments.
Factors Affecting Full-Duplex Performance
Several factors can affect the performance of a full-duplex Ethernet network. These include the quality and length of the cabling, the capacity and processing power of the switches and NICs, and the network architecture’s overall design. Additionally, the type of traffic and network protocols in use, as well as the presence of any errors or retransmissions on the network, can also impact throughput. It is essential to conduct regular performance testing and network monitoring to identify and address any issues that could be affecting the network’s efficiency.
5. References
Technical Standards, RFCs, and IEEE Documents
- IEEE 802.3: The set of standards governing Ethernet networks, including provisions for full-duplex operation.
- RFC 2819 (Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base): Provides information on network management and monitoring, which can help in understanding and optimizing full-duplex Ethernet performance.
Industry Whitepapers and Performance Analyses
- “Ethernet: The Definitive Guide” by Charles E. Spurgeon and Joann Zimmerman: Offers insights into the configuration and performance optimization of Ethernet networks, including full-duplex settings.
- “Performance Analysis of Full-Duplex Ethernet Networks”: A research paper or industry analysis that studies the performance characteristics of full-duplex Ethernet networks under various conditions and loads.
NOTE
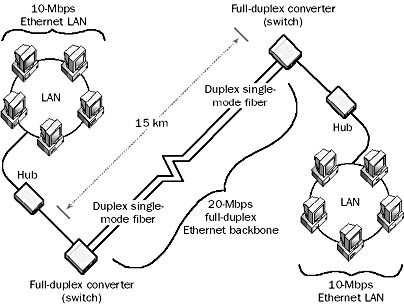
Full-duplex Ethernet does not use the traditional Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) media access control method of traditional Ethernet since collisions cannot occur on a full-duplex, point-to-point link between two stations. Because of this, the distance limitations between two stations in full-duplex Ethernet depend only on the strength of the transceivers with respect to the medium used. Thus station-to-station distances for full-duplex Ethernet connections can be much greater than for traditional Ethernet networks. For 100-Mbps full-duplex links, this is generally around 2 kilometers over fiber-optic cabling.