In the world of digital communication, half-duplex mode plays a crucial role in managing how data is transmitted across networks. It allows for the transmission or reception of signals on a single communication channel but not simultaneously.
This article delves deep into the concept of half-duplex communication, comparing it with full-duplex and simplex modes, and examines its practical applications and implications in various technologies.
Index
- What is Half-Duplex Communication?
- Understanding Half-Duplex Operation
- Half-Duplex vs. Full-Duplex: A Comparative Analysis
- Simplex Mode: The One-Way Communication
- Practical Applications of Half-Duplex Communication
- The Technology Behind Half-Duplex: How It Works
- Advantages and Limitations of Half-Duplex Communication
- Transitioning from Half-Duplex to Full-Duplex Systems
- Half-Duplex in Emerging Technologies
- Conclusion
- References

1. What is Half-Duplex Communication?
Half-duplex communication is a transmission method where data flow is unidirectional at any given time. In simpler terms, it’s like a narrow bridge where traffic can flow in both directions, but cars must wait and take turns to cross — they can’t pass each other heading in opposite directions at the same time.
In technical applications, half-duplex allows a device to send information and then switch to receive mode, similar to a walkie-talkie. When one person speaks, they press a button, and their message travels across a single channel. To hear a response, they must release the button, halting their transmission and opening the channel to receive incoming messages. This alternation between sending and receiving happens swiftly, making conversation possible without the need for two separate channels.
This mode is particularly effective in systems where communication is intermittent or where bandwidth conservation is essential. While half-duplex does not support simultaneous bidirectional data flow, its efficiency in channel usage makes it a practical choice in many structured communication scenarios.
2. Understanding Half-Duplex Operation
The simplest example is a walkie-talkie: You have to press a button to talk and release the button to listen. When two people use walkie-talkies to communicate, at any given moment, only one of them can talk while the other listens. If both try to talk simultaneously, a collision occurs and neither hears what the other says.
Communication through traditional Ethernet networks is another example of half-duplex communication. When one station on an Ethernet transmits, the other stations detect the carrier signal and listen instead of transmitting. If two stations transmit signals simultaneously, a collision occurs and both stations stop transmitting and wait random intervals of time before retransmitting.
Half-duplex systems are usually used to conserve bandwidth since only a single communication channel is needed, which is shared alternately between the two directions. For example, a walkie-talkie requires only a single frequency for bidirectional communication, while a cell phone, which is a full-duplex device, requires two frequencies to carry the two simultaneous voice channels, one in each direction.
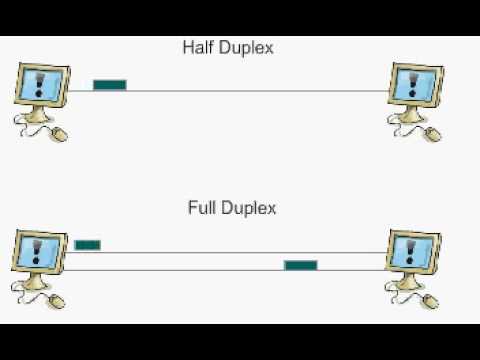
3. Half-Duplex vs. Full-Duplex: A Comparative Analysis
The primary distinction between half-duplex and full-duplex lies in simultaneous communication capability.
In half-duplex systems, if more than one party transmits at the same time, a collision occurs, resulting in lost messages.
In contrast, full-duplex communication enables stations to transmit and receive signals simultaneously, with the advantage of providing twice the bandwidth of equivalent half-duplex technologies. However, full-duplex requires two communication channels to achieve these results – one to transmit and one to receive signals.
4. Simplex Mode: The One-Way Communication
A third mode of communication is called simplex, which involves transmission in one direction only, with one station transmitting signals and the other receiving them.

Simplex communication mode is unidirectional, with signals flowing from a transmitter to a receiver without the expectation of a response, resembling a traditional broadcast.
5. Practical Applications of Half-Duplex Communication
Half-duplex communication, while seemingly a vestige of earlier technology, remains pertinent in various modern applications. In legacy Ethernet networks, for instance, half-duplex mode operates to prevent collisions on the bus topology network, a system where each end system is interconnected with a single cable. Tactical communication systems employed in military operations also utilize half-duplex to maintain robust and secure links while conserving bandwidth, critical in environments where communication infrastructure is limited.
Moreover, certain control systems and industrial networks prefer half-duplex due to its simplicity and lower cost. In these settings, the likelihood of simultaneous communication is rare, making half-duplex a practical choice. Similarly, half-duplex serves well in two-way radio communications, commonly seen in air traffic control systems where clear and controlled communication sequences are paramount.

In addition, Bluetooth technology often uses a half-duplex approach for its ad-hoc connections, optimizing the limited spectrum available and ensuring that devices can communicate effectively in a peer-to-peer manner without the need for continuous two-way communication streams.
6. The Technology Behind Half-Duplex: How It Works
The operational essence of half-duplex communication hinges on control mechanisms that effectively manage the alternation of signal transmission and reception. Time-division multiplexing (TDM) plays a pivotal role in this process, dividing the channel into discrete time slots that are allocated for either sending or receiving data. This organized switching prevents collisions and allows for the use of a single channel for bidirectional communication.
Control signals are integral to coordinating the switch between transmitting and receiving modes. For instance, in a half-duplex Ethernet network, the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) protocol governs the timing of data transmission, allowing devices to detect the presence of other signals and to wait for a clear channel before sending data.
7. Advantages and Limitations of Half-Duplex Communication
Half-duplex systems shine in their bandwidth efficiency, utilizing a single channel for both directions of data flow. This efficiency translates to cost savings in both infrastructure and spectrum usage. The simplicity of half-duplex systems also facilitates easier implementation and maintenance, making it a pragmatic solution for certain network environments.
However, the limitations become apparent in high-traffic scenarios. The inability to simultaneously transmit and receive data can lead to delays, as seen in the latency experienced during over-the-air communication like walkie-talkies. Moreover, the risk of collisions, although managed by protocols like CSMA/CD, can lead to packet loss and the need for retransmission, further contributing to potential delays and network inefficiency.
The rise of full-duplex systems, offering double the bandwidth capacity and immunity to collisions, presents a challenge to the viability of half-duplex communication. Yet, the strategic deployment of half-duplex in contexts where its advantages are maximized ensures its ongoing relevance in the network communication landscape.
8. Transitioning from Half-Duplex to Full-Duplex Systems
The transition from half-duplex to full-duplex systems marks a significant milestone in the evolution of network communication. Driven by the escalating demand for higher bandwidth and more efficient data transmission, full-duplex systems are increasingly becoming the standard. The advent of advanced technologies like Gigabit Ethernet and the proliferation of fiber-optic communications have facilitated this shift, offering the necessary bandwidth and eliminating the traditional barriers posed by half duplex systems.
This transition has a profound impact on network design. Full-duplex systems remove the need for collision detection protocols such as CSMA/CD, simplifying network hardware and reducing latency. They also pave the way for more sophisticated network topologies that can handle the high-speed data transfer required for applications such as live streaming, online gaming, and real-time analytics.

The implementation of full-duplex technology necessitates a rethinking of network infrastructure, with a focus on supporting simultaneous two-way communication. This often involves upgrading network components like switches, routers, and interface cards to handle the symmetrical flow of data inherent in full-duplex communication.
9. Half-Duplex in Emerging Technologies
Despite the surge towards full-duplex communication, half-duplex still finds its niche in emerging technologies, particularly where infrastructure constraints or specific application scenarios limit the viability of full-duplex systems. In Internet of Things (IoT) environments, for example, devices often operate on battery power and require low bandwidth, making the simpler and less energy-intensive half-duplex systems more appropriate.
Additionally, in satellite communication, where the delay in signal transmission is inherent due to vast distances, the half-duplex mode can be more practical. It allows for a clear division between uplink and downlink periods, optimizing the use of the satellite channel.
10. Conclusion
Half-duplex communication, with its historical significance and practicality, continues to play a role in the fabric of digital communication. While technology’s relentless march has ushered in the era of full-duplex communication, the principles underlying half-duplex systems remain integral to understanding the foundations of network data exchange. As we advance, the legacy of half-duplex communication endures, influencing the design and operation of current and future communication systems. Its adaptability ensures that it will remain a relevant concept in the lexicon of network communications, bridging the past with the future.
11. References
- RFC 1122: “Requirements for Internet Hosts – Communication Layers”
- “Data Communications and Networking” by Behrouz A. Forouzan
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall