Definition of Host Header Names in Network Encyclopedia.
What are Host Header Names?
Host Header Names is a feature of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) version 1.1 supported by IIS that lets multiple Web sites hosted on an IIS 4 (or greater) Web server share the same IP address.
Web browsers such as Microsoft Internet Explorer support host header names and can access these Web sites seamlessly.
How it works
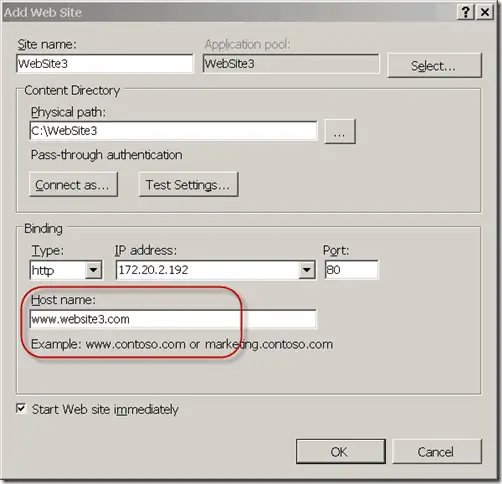
To configure multiple virtual servers (Web sites) on an IIS server to share one IP address and use host header names for client access to them, perform the following steps:
- Open the property sheet for each virtual server in Internet Services Manager.
- Select the Web Site tab and specify the IP address and port number (usually port 80), or select All Unassigned if your server has only one IP address.
- Click the Advanced button, select the identity you want to use from the Multiple Identities For This Web Site list, and add a host header name. Note that each identity can have only one host header name, but each virtual server can have multiple identities.
- Register the host header name with your Domain Name System (DNS) server or Internet service provider (ISP).
Once the IIS server and DNS name resolution environment are configured properly, a Web browser that supports host header names, such as Internet Explorer 4 and later, can use these names to access different virtual servers that have the same IP address and port number and are located on the same machine running IIS. The browser makes an HTTP 1.1-compliant GET request, which contains in its header the host header name being requested.
NOTE
Web browsers that support host header names include Internet Explorer 3 and later or Netscape Navigator 3 and later.
TIP
IIS 4 and later support host header names on older browsers by implementing a mechanism based on cookies. For very old browsers that don’t support cookies, a tool in the IIS Resource Kit called the Cookie Munger enables these browsers to access such sites on IIS 4.
Do not create host header names for the Default Web Site, because this might affect other services installed on the server that expect the Default Web Site to have no host header names.