The Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) by Citrix Systems revolutionized remote desktop and application delivery, providing a robust framework for accessing server-based computing services. Developed in the 1990s, ICA facilitated seamless, efficient remote access to applications, paving the way for flexible, location-independent work environments. This article examines ICA’s core technology, benefits, and its enduring relevance in the era of cloud computing and virtualization.
Index
- What is Independent Computing Architecture (ICA)?
- Core Technology Behind ICA
- Benefits of Using ICA
- ICA vs. RDP: A Comparative Overview
- The Relevance of ICA Today
- Conclusion
- References
1. What is Independent Computing Architecture (ICA)?
Independent Computing Architecture is a proprietary protocol developed by Citrix Systems, designed to facilitate remote access to applications and desktops hosted on central servers. ICA is built to be lightweight and efficient, ensuring that the user experience is smooth and responsive, even over low-bandwidth connections. It encapsulates keyboard, mouse input, and screen updates, delivering them over the network between the client and server.
2. Core Technology Behind ICA
ICA operates by creating a virtual channel—a pathway for transmitting data between the client and server. This channel is optimized for performance, minimizing bandwidth usage while maximizing responsiveness. ICA’s architecture separates application logic, which runs on the server, from the user interface, presented on the client. This separation is key to its efficiency, allowing for scalable, secure, and accessible computing.
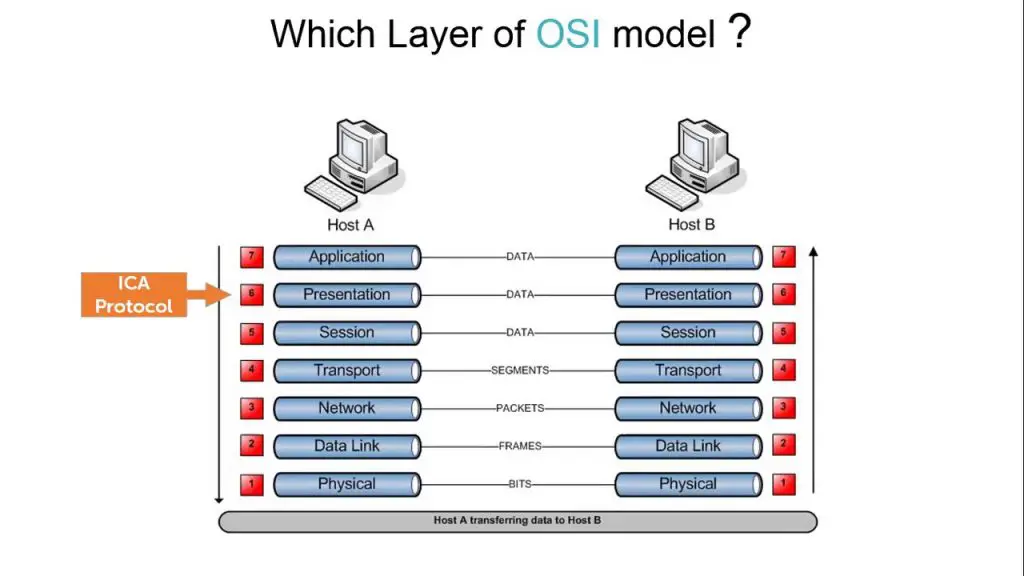
ICA lets the user interface of an application run with minimal consumption of resources on a client device while the actual application logic executes on an ICA-enabled server. In this respect, ICA is similar to the X Windows protocol for UNIX platforms.
Citrix’s ICA is an alternative to Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
The only data transferred between the server and the client device over the network are the user interface, keystrokes, and mouse movements. This results in minimal resource requirements for the client, allowing the use of a «thin client».
ICA also provides location independence because it runs the Windows NT Server operating system and application program at a centralized location while displaying the user interface on any supporting client.
The ICA protocol runs over most industry-standard networking protocols, such as TCP/IP, NetBEUI, IPX/SPX, and Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). It also runs over transport protocols such as Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), frame relay, and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM). Users can access standard Windows applications running on a remote ICA-based server over dial-up, local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN), or Internet connections. Applications can be launched from Web pages or from Windows desktops, making the ICA protocol a platform-independent solution.
» To read next: Understanding Quantum Computing in a Simple Way
3. Benefits of Using ICA
- Efficiency Over Low Bandwidth: ICA’s optimization techniques ensure reliable performance over varied network conditions, including low-bandwidth and high-latency environments.
- Scalability: Supports a large number of concurrent users without degrading performance, essential for enterprise-level deployments.
- Security: Centralized application delivery enhances security, as data and applications reside on the server, reducing the risk of data leakage.
- Compatibility: Offers broad compatibility with various operating systems, devices, and network configurations.
4. ICA vs. RDP: A Comparative Overview
Architecture and Performance
- ICA: Citrix’s ICA is renowned for its lightweight architecture and efficiency, particularly in low-bandwidth scenarios. It is designed to minimize latency and optimize the user experience by compressing data and using bandwidth more effectively. ICA’s strength lies in its ability to provide a consistent user experience across diverse network conditions, maintaining performance and responsiveness.
- RDP: Microsoft’s RDP, while also efficient, traditionally lagged behind ICA in terms of performance over low-bandwidth connections. Recent versions of RDP have seen significant improvements, incorporating features like RemoteFX to enhance graphical performance and adaptability to network conditions. However, ICA still often has the edge in highly constrained bandwidth environments.
Application Compatibility and Integration
- ICA: One of the hallmark features of ICA is its extensive support for application compatibility and seamless integration. Citrix has focused on ensuring that applications, regardless of their graphical intensity or complexity, run smoothly over ICA connections. This includes support for specialized or resource-intensive applications that may not perform as well over RDP.
- RDP: RDP supports a wide range of applications and has been increasingly adapted to support more intensive graphical applications. However, some users and administrators report that highly specialized software or applications requiring intensive graphical processing might encounter limitations when used over an RDP connection.
Scalability and Administrative Features
- ICA: ICA shines in scalability and the administrative tools available through the Citrix suite. Citrix provides a robust set of management and monitoring tools that allow IT administrators to fine-tune performance, manage user sessions, and deploy applications at scale. This makes ICA particularly well-suited for large-scale enterprise environments where managing a vast number of concurrent sessions is critical.
- RDP: RDP also offers scalability and has been used successfully in large deployments. However, the management tools and features available natively with RDP may not be as comprehensive or granular as those provided by Citrix for ICA. For organizations that require advanced management capabilities, additional tools or third-party solutions may be necessary to achieve similar levels of control and oversight as with ICA.
Security
- ICA: Citrix has invested heavily in the security of ICA, implementing features like session reliability, secure ICA, and integration with multifactor authentication solutions. Citrix’s approach to security is holistic, encompassing data protection, network security, and access controls, making it a strong choice for organizations with stringent security requirements.
- RDP: Microsoft has also made significant strides in enhancing the security of RDP, introducing features like Network Level Authentication (NLA), RDP Gateway, and Azure Active Directory support for RDP sessions. While RDP provides a secure remote access solution, the perception and historical vulnerabilities have led some organizations to layer additional security measures on top of RDP.
Conclusion
Both ICA and RDP offer robust solutions for remote desktop and application access, each with its strengths and areas of specialization. ICA’s superior performance in low-bandwidth conditions, along with its scalability and comprehensive administrative tools, make it a preferred choice for enterprise deployments with complex needs. RDP, with its improvements and integration into the Windows ecosystem, offers a solid and cost-effective solution for many scenarios. The choice between ICA and RDP ultimately depends on specific organizational requirements, including performance, scalability, application support, and security considerations.
5. The Relevance of ICA Today
Despite the emergence of new technologies and protocols, ICA remains highly relevant. Its efficiency, security, and scalability make it a preferred choice for businesses requiring reliable remote access solutions. With the rise of cloud computing and virtualization, ICA’s ability to deliver a high-quality user experience remotely is more valuable than ever.
6. Conclusion
The Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) by Citrix Systems stands as a testament to innovation in remote computing. Its design principles—efficiency, scalability, and security—remain foundational in today’s digital workspace solutions. As businesses continue to embrace flexible work environments, the relevance of ICA, supported by ongoing developments, is assured.