Definition of Microsoft Personal Web Server (PWS) in Network Encyclopedia.
What is Microsoft Personal Web Server (PWS)?
PWS (Microsoft Personal Web Server) is a workgroup-level Web server that is installed instead of the full Internet Information Server (IIS) version 4 when IIS is installed on a machine running Microsoft Windows NT Workstation, Windows 95, or Windows 98. Microsoft Personal Web Server (PWS) is suitable for personal publishing, hosting local area network (LAN) intranet sites, development and testing, and performing remote administration of IIS.
When PWS is installed on Windows NT Workstation, it supports all the features of IIS on Windows NT except the following:
- Index Server
- Hosting of multiple Web sites
- ODBC logging
- Domain blocking
- Process isolation
How it works
PWS has two components, a Web or Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) server and a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server, which work independently.
You can run a Web server, an FTP server, or both. PWS creates the \Inetpub\ wwwroot folder for your home page and for the files that you want to make available through FTP. You can create a subdirectory structure under this directory.
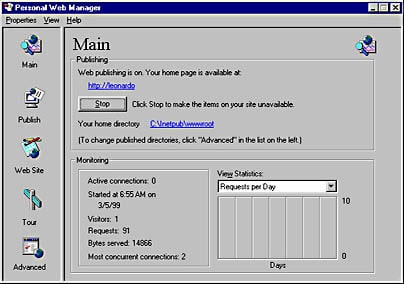
Personal Web Manager
When PWS is installed on Windows 95 and Windows 98, it lacks the NTFS security features. Be sure you don’t accidentally place sensitive data on your site.
Origins of PWS
Personal Web Server was originally created by Vermeer Technologies, the same company which created Microsoft FrontPage, before they were acquired by Microsoft. It was installed by FrontPage versions 1.1 to 98 as well.
Why Personal Web Server was useful?
Before Microsoft Visual Studio 2005, PWS was useful in developing web applications on the localhost before deploying to a production web server. The IDE of Visual Studio 2005 (and later versions) now contains a built-in lightweight web server for such development purposes.
See also: Web Hosting