Name lookup, also known as name resolution or DNS lookup, is the process of translating a human-readable domain name into its corresponding IP address. It is a fundamental function of the Domain Name System (DNS) and plays a crucial role in enabling communication on the internet.
What is Name Lookup?
In the Domain Name System (DNS), Name Lookup is the process of a resolver sending a request to a name server. The resolver sends the host name of a TCP/IP host on the internetwork, and the name server returns the host’s IP address. The name server is said to “resolve” the name of the host into its associated IP address.
Ex:: Type nslookup at the command prompt.
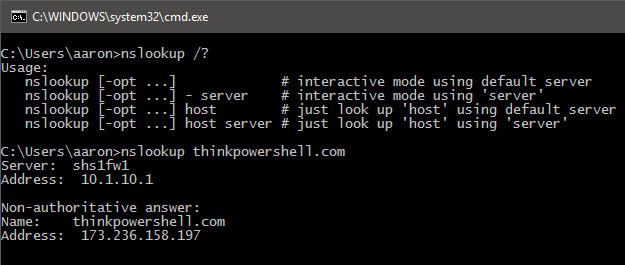
The query sent by the resolver to the name server is most often a recursive query, which returns either the expected IP address or an error. This type of query makes it possible for a name server to forward the request to other name servers if it can’t resolve the name and then return the result of that request to the resolver. If the queried name server is configured to forward requests, it can perform an iterative query, querying several name servers in succession until it resolves the name or runs out of name servers to query.
Name lookup is a critical process that occurs behind the scenes when we interact with websites, send emails, access online services, or perform any network activity that involves domain names. It enables us to navigate the internet using human-friendly domain names instead of having to remember and use IP addresses directly.
Reverse Name Lookup
Reverse name lookup, also known as reverse DNS lookup or reverse DNS resolution, is a process used to determine the domain name associated with a given IP address. While traditional DNS resolves domain names to IP addresses, reverse name lookups work in the opposite direction.
In a typical scenario, when you enter a domain name into your web browser, the DNS system translates it into the corresponding IP address. However, with reverse name lookups, you start with an IP address and seek to find the domain name associated with it.
The reverse name lookup process involves querying the reverse DNS zone, also known as the in-addr.arpa domain, which is specifically designed to store reverse DNS information. This domain is structured in a way that allows IP addresses to be looked up in reverse order.
Example
For example, if you have the IP address “192.0.2.100” and want to perform a reverse name lookup, the process involves reversing the octets to create the corresponding reverse DNS query. In this case, the query would be “100.2.0.192.in-addr.arpa.”
The reverse DNS zone contains PTR (Pointer) records, which store the mapping between IP addresses and domain names. When a reverse DNS query is made, the DNS server responsible for the reverse zone is consulted to retrieve the PTR record associated with the IP address. This record contains the domain name corresponding to the IP address.
What is reverse DNS lookup used for?
Reverse name lookups serve several purposes, including:
- Network Troubleshooting: Reverse DNS can help identify the hostname associated with an IP address, aiding in network diagnostics and troubleshooting. It allows network administrators to gain insights into the origin of network traffic and identify potential misconfigurations or malicious activities.
- Email Server Verification: Reverse name lookups are commonly used in email systems to verify the authenticity of the sending server. By checking whether the IP address has a valid reverse DNS entry matching the hostname in the email’s header, email providers can assess the reputation and trustworthiness of the sender.
- Security and Access Control: Reverse name lookups can be used as an additional layer of security for access control purposes. For example, some systems or applications might require specific reverse DNS entries for incoming connections to prevent unauthorized access or to enforce certain policies.
- Logging and Auditing: Reverse DNS information can be useful for logging and auditing purposes. It allows organizations to track and analyze network activity based on domain names rather than just IP addresses, providing more meaningful insights into network traffic patterns.
It’s important to note that not all IP addresses have corresponding reverse DNS entries. It is up to the organization or entity managing the IP address range to configure and maintain the reverse DNS records.
In conclusion, reverse name lookups enable the identification of domain names associated with IP addresses. They are valuable tools for network troubleshooting, email verification, security, access control, and logging purposes, providing a deeper understanding of network activity and facilitating various administrative tasks.