Definition of Host Name Resolution in Network Encyclopedia.
What is Host Name Resolution?
Host Name Resolution is the process by which a host determines the IP address of another host given its host name or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) on a TCP/IP network.
How it works
Suppose you go to the command prompt of a machine running 32-bit Microsoft Windows NT and type ping followed by a host name or FQDN of another host on the network. The host name or FQDN of the target host must first be resolved into its IP address before the TCP/IP utility ping can occur. This process is called host name resolution.
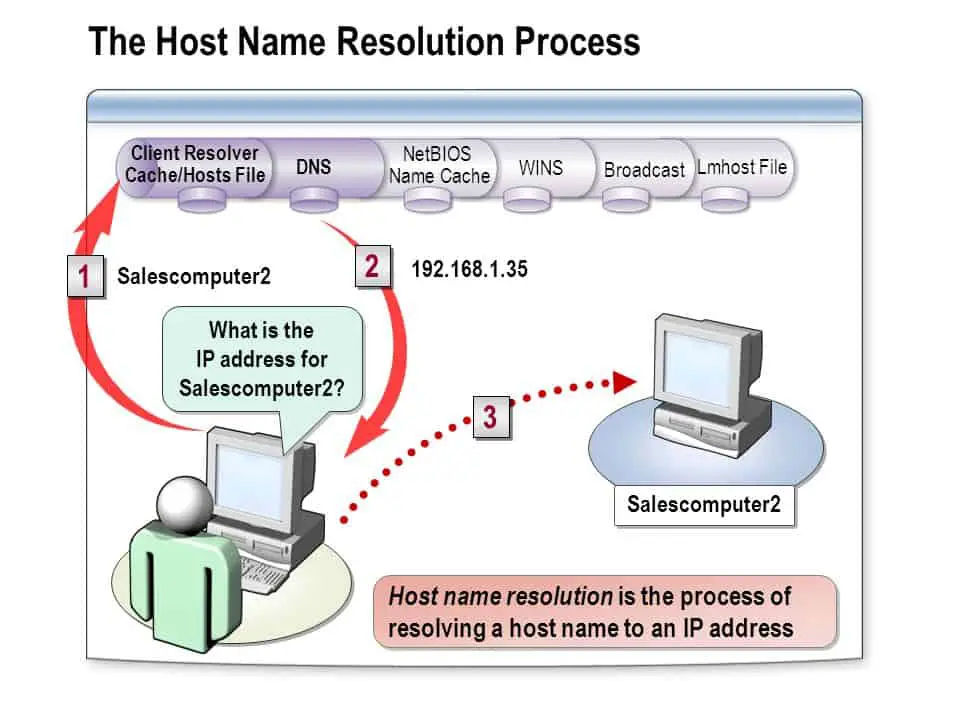
A number of different methods can be used to perform host name resolution. The following table shows the order in which these are attempted on a Microsoft network.
The methods are tried in succession until the host name is resolved into its IP address or until name resolution finally fails. Some methods will not be available – for example, if there is no DNS server or NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS) on the network.
Host Name Resolution Methods in the Order Applied
| Host Name Resolution Methods | Comments |
| Check whether the target host is the local host. | The local host knows its own host name! |
| Check local hosts file. | This check is performed only if a hosts file has been configured. |
| Contact DNS server. | This check is performed only if the DNS tab of the TCP/IP property sheet has a DNS server specified on it. The local host tries again at intervals of 5, 10, 20, 40, 5, 10, and 20 seconds. |
| Check local NetBIOS name cache. (Unique to Microsoft networks.) | The cache contains recently resolved NetBIOS names. (On Microsoft networks, NetBIOS names and host names are usually the same.) |
| Contact NBNS. (Unique to Microsoft networks.) | This check is performed if NBNS has been configured by creating a Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) record within the DNS database. On a Microsoft network, this is usually a WINS server. The local host tries three times to contact the WINS server and then tries secondary WINS server three times if configured. |
| Perform local broadcast. (Unique to Microsoft networks.) | Local host broadcasts a NetBIOS name query request packet three times. |
| Check local lmhosts file. (Unique to Microsoft networks.) | This check is performed if an lmhosts file has been configured. |
If all methods fail, an error message states that the computer could not be found on the network.
NOTE
There is a separate series of steps for attempting to resolve NetBIOS names on a network that uses WINS. For more information, see the entry on NetBIOS name resolution elsewhere in this work.