Definition of NetBIOS Name Resolution in Network Encyclopedia.
What is NetBIOS Name Resolution?
On TCP/IP internetworks, NetBIOS Name Resolution is the process by which the NetBIOS name of a computer is resolved to its IP address.
NetBIOS name resolution enables NetBIOS hosts to communicate with each other using TCP/IP. Once a host’s name has been resolved to its IP address, the address resolution protocol (ARP) can then be used to resolve the IP address into its corresponding physical layer or MAC address.
Once the physical address of a host is known, frames may be placed on the wire and targeted to this address.
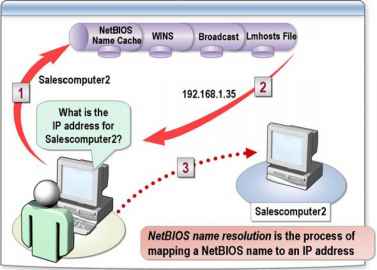
How It Works
When you go to the command prompt of a machine running Microsoft Windows and type a Net Use command to map a drive to a network share, you type the NetBIOS name of the target host in the command (for example, net use x: \server7\pub ). For this command to be fulfilled, the NetBIOS name of the remote host must first be resolved into its IP address so that it can be contacted on the network. This process is called NetBIOS name resolution.
You can use a number of different methods to perform NetBIOS name resolution. The following table shows the order in which these are attempted when the hosts are H-node types. Each method is successively tried until the name is resolved into its IP address or name resolution fails. Some methods will not be available – for example, if there is no NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS) or DNS server on the network.
NetBIOS Name Resolution Methods
| Method (in the Order Applied) | Comments |
| Check local NetBIOS name cache | The cache contains recently resolved NetBIOS names. |
| Contact NBNS | This method works only if NBNS is configured. The name server is usually a Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) server on a Microsoft network. The requestor tries three times to contact the name server, and then tries to contact a secondary WINS server three times (if configured with secondary servers). |
| Perform local broadcast | The requestor broadcasts a NetBIOS name query request packet. The requestor tries three times before giving an error. |
| Check local lmhosts file (Unique to Microsoft networks. If all methods fail, an error message states that the computer could not be found on the network.) | The requestor checks if an Lmhosts file exists. |
| Check local hosts file (Unique to Microsoft networks. If all methods fail, an error message states that the computer could not be found on the network.) | On Windows NT the requestor checks the Hosts file if Enable DNS For Windows Resolution is selected on the WINS Address tab of the TCP/IP property sheet. This option is not available for Windows 2000. |
| Contact DNS server (Unique to Microsoft networks. If all methods fail, an error message states that the computer could not be found on the network.) | The requestor contacts the DNS server if Enable DNS For Windows Resolution is selected on the WINS Address tab of the TCP/IP property sheet and the DNS tab has a DNS server specified on it. The requestor also tries 5, 10, 20, and 40 seconds later. |
Resolve Host Names
A separate series of steps is used to resolve host names on a network that uses the Domain Name System (DNS). On IPX/SPX networks, NetBIOS over IPX (NBIPX) resolves NetBIOS names to Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) addresses.