In the digital era, the backbone of any efficient and secure IT environment is often its network infrastructure. At the heart of this infrastructure lies the concept of server-based networks, a centralized approach for managing network security and storage. But what exactly is a server-based network, and why is it pivotal in today’s technology landscape?
This article dives deep into the nuances of server-based networks, unraveling their importance in enhancing both security and efficiency. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced benefits, we cover it all. Are you ready to transform your network management strategy?
Table of Contents:
- What is a Server-Based Network?
- How Server-based Networks Work?
- Centralized Security in Server-Based Networks
- Efficient Storage Management
- Scalability and Reliability
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Potential Challenges and Solutions
- Conclusion
- References

1. What is a Server-based network?
A server-based network is a pivotal concept in the realm of modern computing, particularly in the context of organizational IT infrastructure. Unlike peer-to-peer networks, where each device (or ‘node’) acts independently, a server-based network centralizes key functions and resources in one or more servers. These servers become the fulcrum of network operations, managing data, applications, security, and communication protocols.
A Server-based network is a network in which network security and storage are managed centrally by one or more servers.
Fundamental Components of a Server-Based Network
- Servers: At the heart of this network are the servers themselves. They are powerful computers designed to process requests and deliver data to other computers over a local network or the internet. Servers can be dedicated to specific functions like file storage, database management, application hosting, or email services.
- Clients: Clients are devices that access the server for resources. These can be computers, mobile devices, or even IoT devices. They rely on the server for retrieving, storing, and processing data.
- Network Infrastructure: This includes the physical and wireless connections that link clients to servers. Components like routers, switches, and networking cables fall under this category.
- Software: Server software enables the management of resources, user access, and various services the network provides. Client devices also run software that allows them to interact with the server.
- Security Mechanisms: These are integral to a server-based network, involving both hardware and software solutions to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
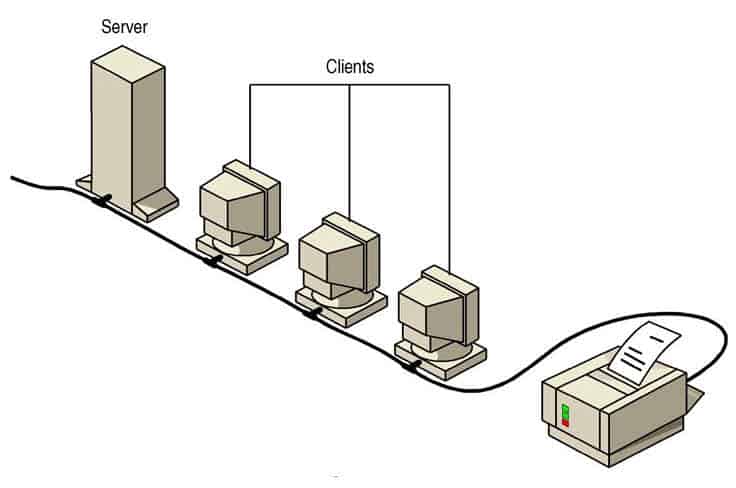
By centralizing network management, server-based networks offer enhanced control, security, and efficiency. They are scalable, allowing for additional resources and users without a significant overhaul of the existing infrastructure. Read also: Client-Server Model.
2. How Server-based Networks Work?
In a server based network, special computers called servers handle network tasks such as authenticating users, storing files, managing printers, and running applications such as databases and e-mail programs. Security is generally centralized in a security provider, which allows users to have one user account for logging on to any computer in the network. Because files are stored centrally, they can be easily secured and backed up.
Server-based networks are more costly and complex to set up and administer than peer-to-peer networks, and they often require the services of a full-time network administrator. They are ideal for businesses that are concerned about security and file integrity and have more than 10 computers.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 or 2019 are ideal operating systems for server-based networks. They offer centralized network administration, networking that is easy to set up and configure, NTFS file system security, file and print sharing, user profiles that allow multiple users to share one computer or allow one user to log on to many computers, Routing and Remote Access for supporting mobile users, and Internet Information Services (IIS) for establishing an intranet or Internet presence.
3. Centralized Security in Server-Based Networks
In a server-based network, security management is centralized, offering a comprehensive approach to protecting data and resources. This centralization brings several advantages, ensuring a robust defense against potential threats.
How Server-Based Networks Manage Security
- Centralized Access Control: Servers manage user authentication and authorization. By having a single point of control, it’s easier to monitor and regulate who accesses what data and when. This method simplifies the management of user permissions and roles.
- Unified Threat Management: Centralized security allows for consolidated threat detection and response. Servers can run advanced security software that monitors network traffic for suspicious activities, providing real-time threat intelligence and rapid response to potential breaches.
- Data Encryption: Central servers can encrypt data both at rest and in transit. This encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable and secure.
- Regular Updates and Patches: With a server-based network, updating security protocols, software patches, and system upgrades can be done centrally. This ensures all devices and applications are up-to-date with the latest security measures.
Advantages of Centralized Security
- Enhanced Security: Centralized control allows for a more rigorous and consistent security posture across the entire network.
- Efficiency: Administrators can implement and update security policies across the network from a single location, saving time and resources.
- Compliance: It’s easier to ensure compliance with various regulatory standards, as centralized security offers better control over data handling and user activities.
- Scalability: As the network grows, maintaining security standards becomes more manageable when all security measures are centralized.
In conclusion, centralized security in server-based networks provides a robust framework for protecting sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of network operations. This security model is crucial for organizations handling large amounts of data and requiring strict control over their IT environments.
4. Efficient Storage Management
In server-based networks, servers play a crucial role in storage management, acting as centralized repositories for data and applications. This centralization not only enhances data accessibility but also streamlines the management and security of stored information.
Centralized Data Storage
Servers in a server-based network store all the critical data, which can include files, databases, and application data. This centralization means that clients access and save data to a common location, ensuring consistency and ease of access.
Advantages of Centralized Storage Management
- Data Consistency and Integrity: With centralized storage, data is stored in a single location, reducing the risk of discrepancies or duplications. This ensures data integrity, as the same version of a file or data set is accessed by all users.
- Improved Data Accessibility: Centralized storage allows users to access data from anywhere on the network. This is especially beneficial for organizations with remote or mobile workforces.
- Streamlined Backup and Recovery: Servers facilitate efficient backup and disaster recovery solutions. Centralized data makes it easier to perform regular backups and rapid data recovery in case of a system failure or data loss incident.
- Enhanced Security: Centralizing data storage allows for more controlled and robust security measures. Servers can implement advanced encryption and access controls, providing a higher level of security for sensitive data.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Centralized storage can be more cost-effective, as it reduces the need for multiple storage systems across an organization. It also simplifies maintenance and support.
» Do you know what the UDF File System is? Read our article to learn more!
5. Scalability and Reliability
Server-based networks are designed with scalability and reliability in mind, making them ideal for businesses with evolving needs. The architecture of these networks allows for easy expansion and adaptation, ensuring that the network remains robust and functional as demands increase.
Scalability in Server-Based Networks
- Ease of Adding Resources: As an organization grows, additional servers or storage can be easily integrated into the existing network. This flexibility allows businesses to scale up their operations without overhauling their IT infrastructure.
- Modular Approach: Server-based networks often employ a modular design, meaning components can be added or upgraded individually. This approach allows for gradual expansion, tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
Ensuring Reliability
- Redundancy and Failover Systems: Servers can be configured for redundancy, where critical data and services are duplicated across multiple servers. In the event of a server failure, the network can automatically switch to a backup server, ensuring continuous operation.
- Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: Servers provide the ability to centrally monitor network health and performance. Regular maintenance and proactive monitoring can prevent downtime and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Management: Server-based networks can prioritize certain types of traffic, ensuring that critical services maintain high performance even under heavy load.
- Disaster Recovery Planning: With centralized data and services, implementing comprehensive disaster recovery plans is more straightforward. Servers can be configured for rapid recovery in various scenarios, from data breaches to natural disasters.
In conclusion, server-based networks offer a scalable and reliable solution for businesses looking to grow and adapt in an ever-changing technological landscape. Their ability to efficiently manage storage and scale in line with business needs, all while maintaining high reliability, makes them an essential component of modern IT infrastructure.
6. Cost-Benefit Analysis
When considering the implementation of a server-based network, it’s vital to weigh the associated costs against the potential benefits. This analysis helps organizations make informed decisions about their IT infrastructure investments.
Costs of Implementing a Server-Based Network
- Hardware Investments: The initial cost includes purchasing servers, networking equipment, and backup systems.
- Software Licensing: Costs for operating systems, management software, and security tools are also to be considered.
- Maintenance and Support: Regular maintenance and technical support for servers and network infrastructure incur ongoing costs.
- Training and Staffing: Employees may require training to manage and maintain the new system. Additional or more specialized staff might also be needed.
Benefits of a Server-Based Network
- Enhanced Efficiency: Centralized management leads to streamlined operations, reducing the time and effort required for network administration.
- Improved Security: Centralized security management in server-based networks offers more robust protection against cyber threats.
- Scalability and Flexibility: As the organization grows, the network can be easily scaled to meet increasing demands.
- Data Integrity and Reliability: Centralized storage ensures data consistency and reliability, with improved backup and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Cost Savings Over Time: Although the initial setup has its costs, over time, the efficiency and reduced downtime can lead to significant cost savings.
7. Potential Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a server-based network can present several challenges, but with the right strategies, these can be effectively managed.
1: Complexity in Setup and Management
- Solution: Invest in training for IT staff and consider simplified, user-friendly management tools.
2: High Initial Investment
- Solution: Develop a phased implementation plan to spread out costs and demonstrate ROI at each stage.
3: Scalability Concerns
- Solution: Plan for future growth by choosing scalable hardware and software solutions from the outset.
4: Ensuring Consistent Performance
- Solution: Regularly monitor network performance and invest in quality hardware and efficient software.
5: Data Security and Privacy
- Solution: Implement robust security protocols, regular audits, and stay updated with the latest cybersecurity trends.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, server-based networks represent a significant advancement in managing IT infrastructure. They offer numerous benefits, including enhanced efficiency, improved security, scalability, and data integrity. While the initial setup and ongoing maintenance entail certain costs, the long-term benefits can outweigh these investments.
The challenges associated with server-based networks can be effectively managed with proper planning, training, and the adoption of scalable solutions. Ultimately, server-based networks stand as a testament to the evolution of modern IT infrastructure, offering a robust platform for organizations to thrive in the digital age.
9. References
- “Computer Networks” by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall – A comprehensive guide on networking concepts and technologies.
- “Network Security Essentials” by William Stallings – Offers insights into the security aspects of networking.
- RFC 1157 – Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), a key protocol in network management.
- “The Practice of System and Network Administration” by Thomas A. Limoncelli, Christina J. Hogan, and Strata R. Chalup – Provides practical advice on managing and maintaining IT infrastructures.
- “Data Center Handbook” by Hwaiyu Geng – Provides an overview of data center technologies, including server-based network considerations.
- Windows Server: Cloud Platform