The Task Manager is a tool created by Microsoft for Windows NT and Windows 2000 that you can invoke by clicking the Task Manager button in the Windows Security dialog box. You access the dialog box by pressing Ctrl+Alt+Del, the secure attention sequence (SAS) keystroke combination.
You can use Task Manager to:
- Start, view, change the base priority of, and terminate processes
- Display CPU and memory usage graphs and data
- Terminate poorly behaving applications
- Assign a process to a particular microprocessor on a multiprocessor system
All Windows Operating Systems offers this tool
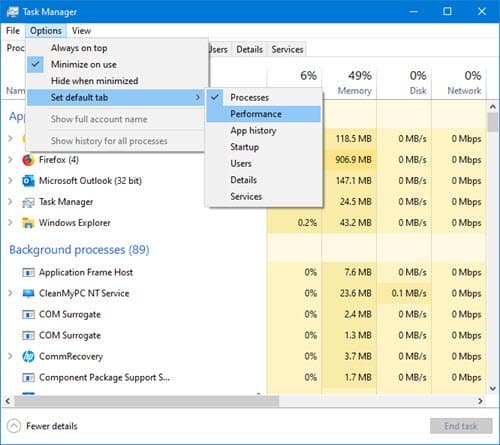
Launch the Task Manager on Windows 10
There are many ways to launch the Task Manager on Windows 10. Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open the Task Manager with a keyboard shortcut or right-click the Windows taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
You can also press Ctrl+Alt+Delete and then click “Task Manager” on the screen that appears or find the Task Manager shortcut in your Start menu.
The first time you launch the Task Manager it will run in Simple View. This window lists the visible applications running on your desktop, excluding background applications. You can select an application here and click “End Task” to close it. This is useful if an application isn’t responding – in other words, if it’s frozen – and you can’t close it the usual way.
You can also right-click an application in this window to access more options:
- Switch To: Switch to the application’s window, bringing it to the front of your desktop and putting it in focus. This is useful if you’re not sure which window is associated with which application.
- End Task: End the process. This works the same as the “End Task” button.
- Run New Task: Open the Create New Task window, where you can specify a program, folder, document, or website address and Windows will open it.
- Always On Top: Make the Task Manager window itself “always on top” of other windows on your desktop, letting you see it at all times.
- Open File Location: Open a File Explorer window showing the location of the program’s .exe file.
- Search Online: Perform a Bing search for the program’s application name and file name. This will help you see exactly what the program is and what it does.
- Properties: Open the Properties window for the program’s .exe file. Here you can tweak compatibility options and see the program’s version number, for example.