IP spoofing is a technique used to gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks by disguising the source IP address of a packet. This goal is accomplished by altering the source addresses of packets, making them appear as though they came from a trusted user within the network, rather than from a distrusted outside user.
Spoofing is one of the methods by which hackers attempt to compromise a network’s security and is of particular concern when a network is connected to the Internet.
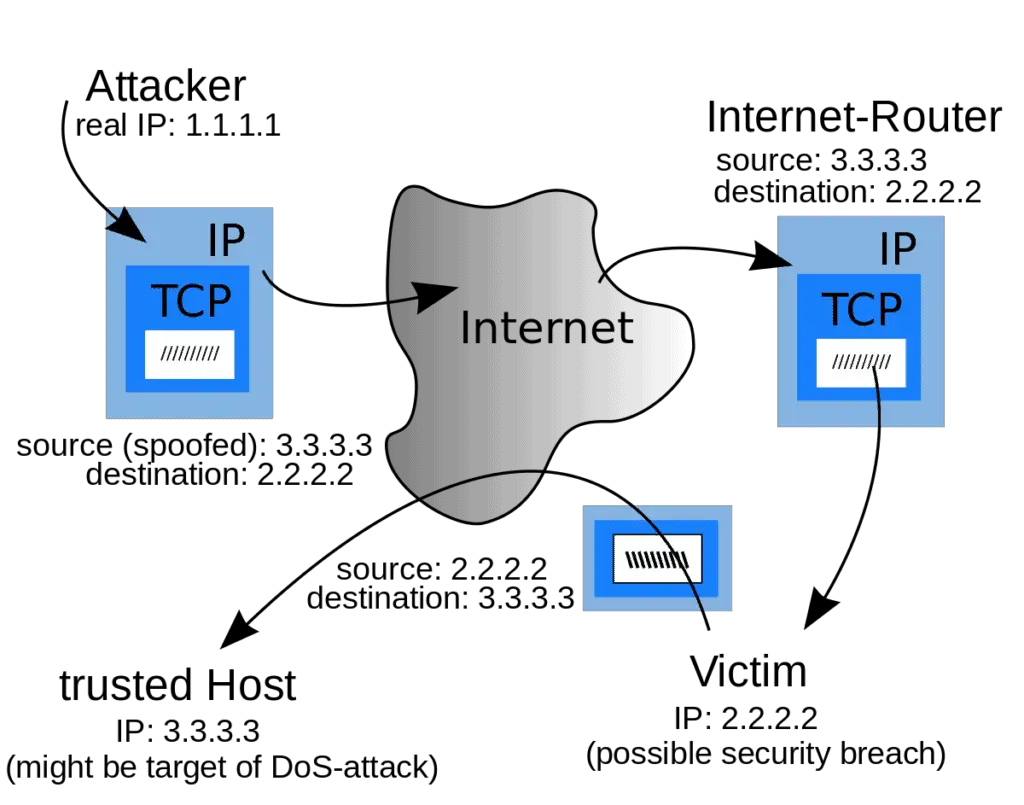
IP spoofing can be used for various malicious purposes, including:
- Hiding the identity of the attacker: By disguising the source IP address, an attacker can obscure their identity and location, making it more difficult to trace the attack back to them.
- Conducting denial of service attacks: By sending a flood of traffic with forged IP addresses, an attacker can overwhelm a server or network, disrupting service and making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Gaining access to restricted networks or systems: An attacker can use IP spoofing to gain access to networks or systems that are restricted to certain IP addresses. For example, an attacker could use IP spoofing to gain access to a corporate network by forging the IP address of an employee’s device.
- Conducting man-in-the-middle attacks: An attacker can use IP spoofing to intercept communications between two parties, allowing them to intercept and potentially alter or steal sensitive information.
How to protect our network against spoofing attacks?
Because of limitations in the design of the current Internet Protocol (IP) standard, IPv4, spoofing of IP packets cannot be prevented, only protected against.
One way to protect your network against IP address spoofing is to use the packet-filtering features of a router or firewall. Configure your packet-filtering router so that the input filter on the external router interface discards any packet coming from the external network whose source address makes it look like it originated from your own internal network. Similarly, configure the output filter on your internal router interface to discard any outgoing packets that have a source address different from that of your internal network to protect against spoofing attacks from within your own network.
Ingress filtering
A very common defense against spoofing is ingress filtering, outlined in BCP38 (a Best Common Practice document). Ingress filtering is a form of packet filtering usually implemented on a network edge device that examines incoming IP packets and looks at their source headers.
If the source headers on those packets don’t match their origin or they otherwise look fishy, the packets are rejected. Some networks will also implement egress filtering, which looks at IP packets exiting the network, ensuring that those packets have legitimate source headers to prevent someone within the network from launching an outbound malicious attack using IP spoofing.