ARPANET, or the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, marks a monumental chapter in the annals of digital communication and technology. Initiated in 1969 under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Defense, ARPANET was conceived to connect supercomputers across various sites nationwide, fostering rapid and reliable data exchange. This groundbreaking network not only revolutionized the way information was shared but also paved the path for the modern Internet.
Join us on an exploratory voyage to the inception of the Internet, delving into the intricate details and fascinating stories behind ARPANET. From visionary concepts to technological breakthroughs, this article promises a comprehensive narrative that keeps you captivated, tracing the evolution from a defense network to the digital lifeline of today’s connected world.
Table of Contents:
- The Genesis of ARPANET
- Technological Milestones and Innovations
- Key Figures Behind ARPANET
- The Network Expands
- Challenges and Solutions
- ARPANET to Internet: The Transition
- Cultural and Social Impact
- Legacy and Lessons Learned
- Conclusion
- References
1. The Genesis of ARPANET
Conceptual Origins
The seeds of ARPANET were sown in the fertile minds of visionaries during the late 1950s and early 1960s, a time when the Cold War loomed large and the race for technological supremacy was in full swing. The concept of a decentralized network, capable of surviving nuclear attacks and ensuring uninterrupted communication, intrigued many within the defense and academic communities. It was Paul Baran and Donald Davies, working independently in the United States and the United Kingdom, who proposed the revolutionary idea of packet switching — a method that could efficiently route digital data in small blocks, or “packets,” across a network. This concept became the cornerstone of ARPANET and, eventually, the Internet.
Funding and Initial Development
The U.S. Department of Defense, recognizing the strategic importance of this innovative communication method, tasked its Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) with the development of a network that embodied Baran and Davies’ ideas. In 1966, Lawrence Roberts, an MIT researcher who had been following developments in packet switching, was appointed by ARPA to lead the project. With funding secured from the Department of Defense, Roberts and his team set about turning the theoretical into the practical. They laid out the plans for a network that would connect computers at research institutions and universities across the country, facilitating resource sharing and collaboration.

The First Nodes and Connections
On October 29, 1969, the ARPANET took its first breath, establishing a connection between the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Stanford Research Institute (SRI). This inaugural link was the culmination of years of planning, development, and testing. It was a modest beginning, with the first message supposed to be “LOGIN.” However, the system crashed after transmitting just “LO” — a humble start to what would become a global phenomenon. Following this initial success, ARPANET quickly expanded, adding the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), and the University of Utah to its network by the end of 1969.

These first nodes and connections were not just technical achievements; they were the first steps towards realizing a vision of a world where information could flow freely and efficiently, regardless of geographical boundaries. The ARPANET’s early days set the stage for the network’s evolution and laid the foundational principles for the modern Internet — connectivity, resilience, and innovation.
2. Technological Milestones and Innovations
Packet Switching: The Core Principle
At the heart of ARPANET’s revolutionary design was the principle of packet switching, a concept that forever altered the landscape of digital communication. This innovative approach allowed data to be broken down into smaller, manageable packets, each independently routed across a network to its destination, where they would be reassembled into the original message. This method contrasted sharply with the then-dominant circuit switching, where a dedicated line was established for the duration of a communication session, an inefficient use of resources for the bursty nature of computer data. Packet switching’s efficiency and resilience, particularly in the face of network disruptions, were pivotal in ARPANET’s success and its ability to lay the groundwork for the future Internet.
The Creation of TCP/IP
As ARPANET grew, so too did the need for a more robust and flexible protocol to manage the increasing complexity and scale of the network. Enter TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), developed by Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn. This suite of protocols, introduced in 1974 and implemented on ARPANET in 1983, provided a set of rules for how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed, and received. This innovation allowed different networks to interconnect and communicate, a concept known as internetworking, which is the essence of the Internet.
Expanding Beyond Academic and Military Domains
By 1971, ARPANET had experienced exponential growth, connecting over 20 prestigious hosts across the United States, including academic giants like MIT, government agencies like NASA, and think tanks like the RAND Corporation. This expansion marked ARPANET’s evolution from a military project to a vital academic and research tool. The network’s reach extended internationally in 1973, with nodes established in Norway and England, symbolizing the beginning of its transformation into a global network.
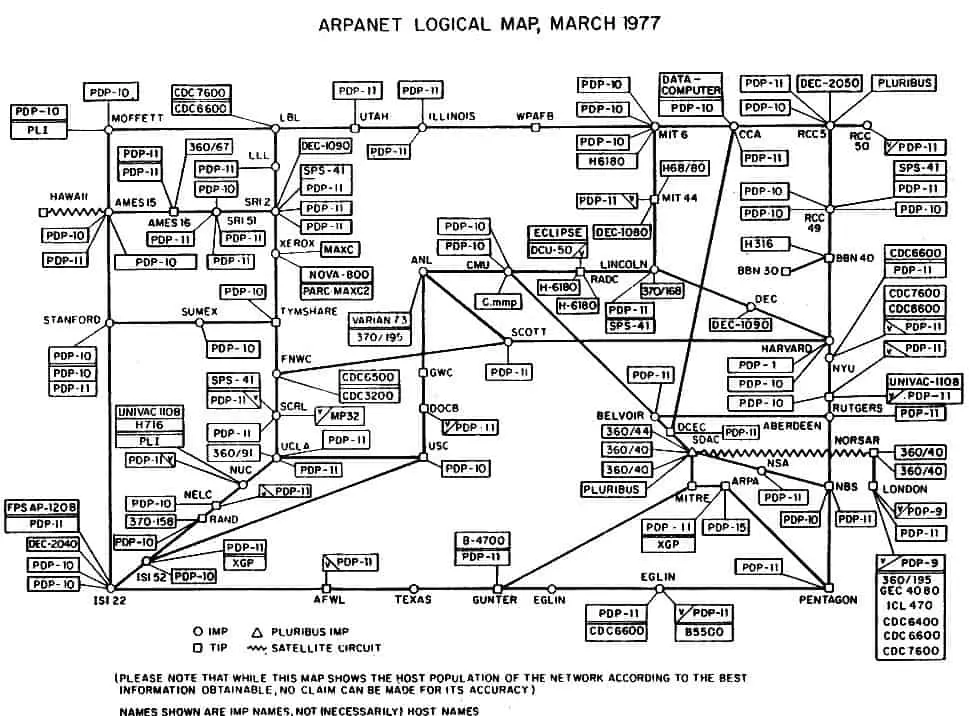
The significant milestone came in 1983 when MILNET, a network for military purposes, was split off from ARPANET, and TCP/IP officially became the standard protocol. This pivotal moment is often regarded as the birth of the Internet as we know it, a network of networks that transcended its original scope to encompass a wide array of academic, government, and later, commercial entities. The establishment of NSFNET in 1986 further expanded this network infrastructure, providing a backbone for interconnecting various regional networks and marking the beginning of the modern Internet era. ARPANET itself was decommissioned in 1989, but its legacy endured, having catalyzed the development of a worldwide network that revolutionized communication, commerce, and culture.

Because ARPA’s name was changed to Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in 1971, ARPANET is sometimes referred to as DARPANET. (DARPA was changed back to ARPA in 1993 and back to DARPA again in 1996.) The history of ARPANET and developments leading up to today’s Internet can be found in Where Wizards Stay Up Late, by Katie Hafner and Matthew Lyon.
3. Key Figures Behind ARPANET
Visionaries and Pioneers
The creation of ARPANET was not just a technological feat; it was a testament to the vision and dedication of a group of pioneers who believed in the power of connectedness. Among them, Lawrence Roberts, often hailed as the architect of ARPANET, saw the potential of packet switching technology to revolutionize computer communications. Working alongside him were Paul Baran and Donald Davies, who independently conceptualized packet switching, laying the theoretical groundwork for ARPANET.
Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn, the fathers of the Internet, developed TCP/IP, the protocol suite that became the lingua franca of the Internet. Their work ensured that disparate networks could communicate, transforming ARPANET from a singular network into a network of networks – the Internet.
Contributions and Legacy
The contributions of these individuals and many others paved the way for a digital revolution. They not only solved complex technical challenges but also foresaw a world where information could be freely exchanged across the globe. Their legacy is the Internet itself—a vast, interconnected network that drives innovation, commerce, and social interaction in the 21st century. Their vision of a networked future has fundamentally changed how we live, work, and communicate, marking them as true pioneers of the digital age.
4. The Network Expands
The Inclusion of International Nodes
ARPANET’s expansion beyond the United States’ borders marked its transition from a national project to a global phenomenon. In 1973, ARPANET went international with connections to University College London in England and the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment in Norway. This groundbreaking expansion demonstrated ARPANET’s potential to facilitate global communication and collaboration, setting the stage for the worldwide web of interconnected networks that would follow.
Growth into a Multifaceted Network
As ARPANET grew, it evolved into a multifaceted network, supporting a diverse range of academic, military, and government institutions. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, the network had burgeoned, linking dozens of institutions across the United States and around the world. This expansion was characterized not just by the addition of new nodes, but by the diversification of its users and uses—from research and education to military communications and beyond.
The network’s growth was propelled further by the development and adoption of TCP/IP, which facilitated the interconnection of other networks with ARPANET, birthing the concept of the “network of networks” that defines the Internet. This period of growth culminated in the establishment of NSFNET, a more powerful network backbone that connected regional networks and academic institutions across the United States, effectively supplanting ARPANET and heralding the modern Internet era.
5. Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Technical Hurdles
As ARPANET grew from a fledgling network into a robust communication infrastructure, it faced numerous technical challenges. The early days were marked by struggles with hardware compatibility, data transmission errors, and the daunting task of establishing reliable communication over long distances. Engineers and researchers collaborated intensively, pioneering solutions that would become staples in network communication. Error correction algorithms, innovative routing protocols, and the development of standardized interfaces facilitated smoother data exchanges and enhanced network reliability, laying down the technical foundations for the future Internet.
Security, Scalability, and Protocol Evolution
With ARPANET’s expansion came concerns over security and scalability. The open nature of the network, while fostering collaboration and information sharing, also exposed vulnerabilities to unauthorized access and data breaches. In response, encryption techniques and secure communication protocols were developed, setting early precedents for cybersecurity. The introduction of TCP/IP was a watershed moment for scalability, enabling the network to grow beyond its original confines and connect with myriad other networks. This protocol suite not only addressed ARPANET’s immediate scalability issues but also provided a flexible architecture that could support an ever-expanding web of interconnected networks.
6. ARPANET to Internet: The Transition
The Decommissioning of ARPANET
By the late 1980s, ARPANET had fulfilled its mission. It had proven the viability of packet-switched networking and catalyzed the development of protocols and technologies essential for the Internet. As newer, more advanced networks like NSFNET took on the mantle, ARPANET’s role began to diminish. In 1989, ARPANET was officially decommissioned, but its legacy was far from over. The infrastructure, knowledge, and community it fostered formed the bedrock upon which the Internet was built.
Birth of the Modern Internet
The transition from ARPANET to the Internet was not a moment but a process, marked by gradual evolution rather than abrupt change. The adoption of TCP/IP as the standard networking protocol on January 1, 1983, often dubbed “flag day,” was a significant milestone in this transition, signaling the shift towards an interconnected network of networks. The establishment of NSFNET, with its high-speed backbone, facilitated the connection of regional academic networks across the United States, accelerating the growth of the network and its adoption beyond the academic and military domains. This period saw the explosion of network services like email, file transfer, and eventually the World Wide Web, transforming the Internet into a global phenomenon.

The story of ARPANET’s transition to the Internet is a tale of innovation, collaboration, and vision. It showcases how a project designed to connect a handful of research institutions sparked a revolution in communication, leading to the creation of a digital universe that connects billions of people worldwide. This transition underscores the importance of adaptability and foresight in technology’s evolution, principles that continue to drive the growth of the Internet today.
7. Cultural and Social Impact
Influence on Popular Culture and Society
ARPANET’s emergence not only marked a technological revolution but also heralded a significant shift in popular culture and societal interaction. It introduced the concept of digital connectivity to the masses, paving the way for the social media platforms, online communities, and virtual workspaces we engage with today. The network’s influence extended beyond the realms of science and academia, inspiring movies, literature, and art that explored the potential and perils of interconnected digital worlds. ARPANET’s legacy is evident in the way we perceive and interact with technology, shaping our expectations of instant access to information and seamless global communication.
The Foundation for the Digital Age
By connecting disparate computers and networks, ARPANET laid the groundwork for the digital age, an era characterized by the omnipresence of digital technology in everyday life. It transformed the way we learn, work, and entertain ourselves, making digital literacy a cornerstone of modern society. The proliferation of the Internet, spurred by ARPANET’s innovations, has democratized information, empowered individuals with unprecedented access to knowledge, and fostered a new economy centered around digital goods and services.
8. Legacy and Lessons Learned
Enduring Impacts on Technology and Communication
The legacy of ARPANET extends far beyond its physical network. It fundamentally changed our approach to technology and communication, demonstrating the power of a decentralized, packet-switching network in facilitating resilient and flexible communication. The principles and technologies developed for ARPANET, from TCP/IP to the concept of email, have become integral components of today’s Internet infrastructure. Its legacy is a testament to the enduring impact of visionary thinking and collaborative innovation in shaping the future of technology.
Insights for Future Innovations
ARPANET’s journey offers valuable insights for future technological innovations. It underscores the importance of open standards and interoperability in fostering growth and inclusivity in digital ecosystems. The project also highlights the pivotal role of government and academic collaboration in advancing technological frontiers. As we navigate the challenges of privacy, cybersecurity, and digital divide in the Internet era, ARPANET’s history serves as a reminder of the need for ethical considerations and proactive governance in technology development.
9. Conclusion
Reflecting on ARPANET’s journey from a defense project to the foundation of the Internet, its indelible mark on history is clear. It was more than just a network; it was a catalyst for change, driving the evolution of digital communication and shaping the contours of the modern world. As we stand on the cusp of new digital horizons, from quantum computing to the Internet of Things, ARPANET’s legacy reminds us of the transformative power of connectivity and the endless possibilities that arise when we dare to reimagine the future.
10. References
- Internet History Timeline: ARPANET to the World Wide Web
- The Birth and Development of the ARPANET
- “Where Wizards Stay Up Late“, by Matthew Lyon, Katie Hafner.
- Abbate, Janet. “Inventing the Internet.” MIT Press, 1999.
- Cerf, Vinton G., and Robert E. Kahn. “A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication.” IEEE Transactions on Communications, May 1974.
- Leiner, Barry M., et al. “A Brief History of the Internet.” Internet Society, 2003.
- Waldrop, M. Mitchell. “The Dream Machine: J.C.R. Licklider and the Revolution That Made Computing Personal.” Viking, 2001.
- RFC 675 – Specification of Internet Transmission Control Program, December 1974.