Our Latest Articles
-
User Mode
Explore the multi-faceted concept of User Mode in computing and networking. From restricted modes in Microsoft OS to advanced networking scenarios.
-
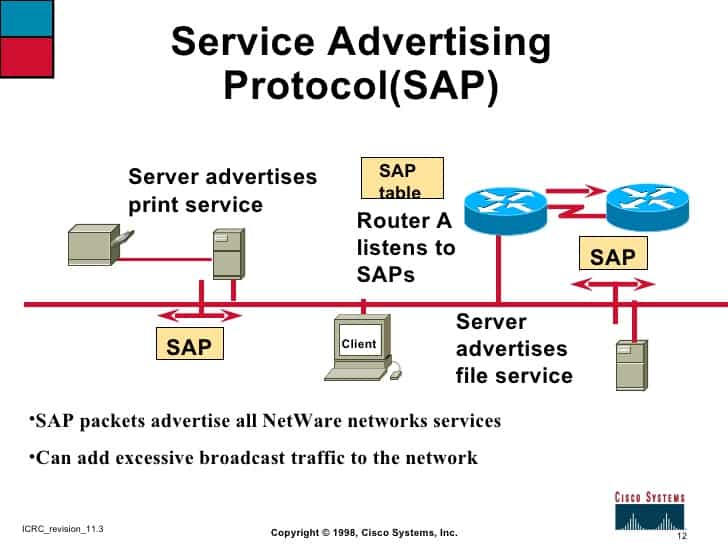
Service Advertising Protocol (SAP)
Service Advertising Protocol, also known as SAP, is a Novell NetWare protocol that is used with Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) to enable file and print servers to advertise their availability to clients on a network.
-
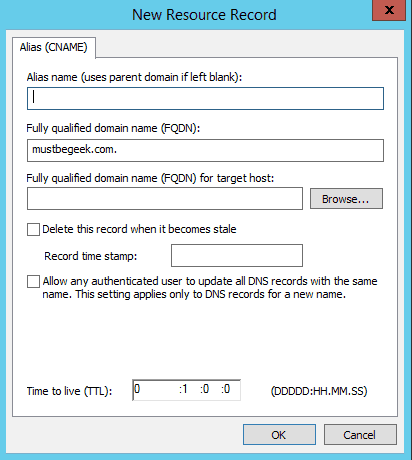
CNAME Record
CNAME Record stands for Canonical Name record, is a Domain Name System (DNS) resource record in a DNS server’s database or zone file. A CNAME record is used to map an alias to the canonical name (true name) of a server.
-
Caching service provider (CSP)
Caching Service Provider, also known as CSP, is a company that maintains caching servers that speed the transfer of information across the Internet’s infrastructure and offers managed access to these servers for a fee.
-

CryptoAPI
CryptoAPI is a core component of the latest versions of Microsoft Windows that provides application programming interfaces (APIs) for cryptographic security services that provide secure channels and code signing for communication between applications.
-
Connection Point Services (CPS)
Explore the functionalities and historical significance of Connection Point Services (CPS) in Microsoft RAS, and discover other meanings of the acronym CPS in networking.
-
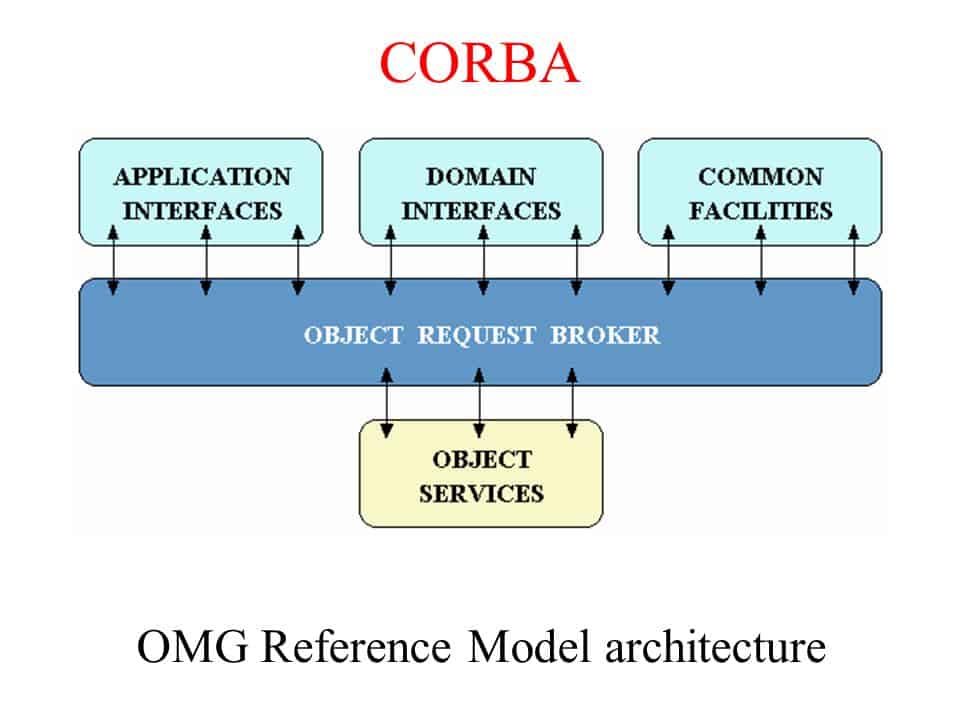
Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)
Common Object Request Broker Architecture, also known as CORBA, is a component architecture developed by the Object Management Group and its member companies that specify technologies for creating, distributing, and managing component programming objects over a network.
-
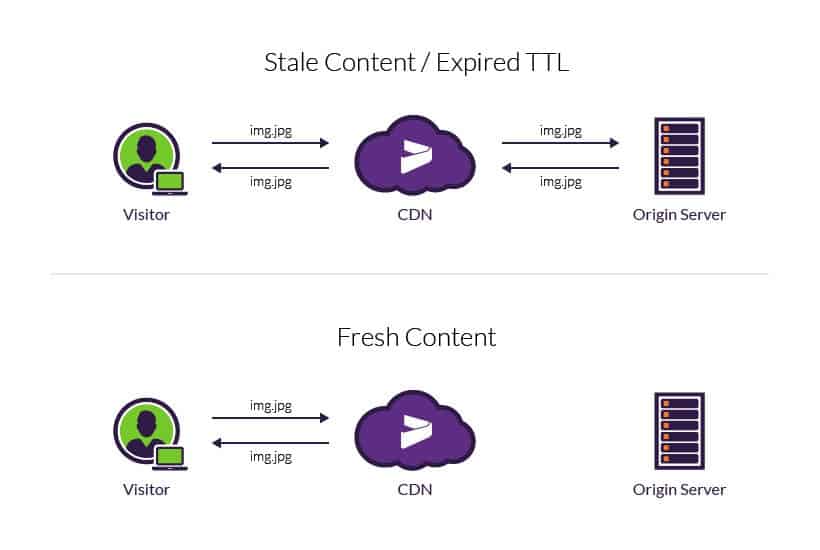
Time to Live (TTL)
Time to live, best known as TTL or Hop Limit, is a mechanism that limits the lifespan or lifetime of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data.
-
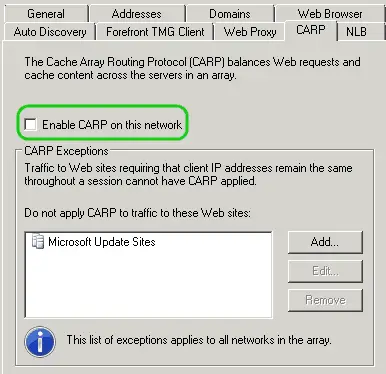
Caching Array Routing Protocol (CARP)
Caching Array Routing Protocol, also known as CARP, is a protocol developed by Microsoft and implemented in Microsoft Proxy Server that allows multiple proxy servers to be arrayed as a single logical cache for distributed content caching.
-

NetWare Protocols
NetWare protocols are the group of protocols developed for and specific to the Novell NetWare network operating system (NOS); popularized in NetWare versions 2 and 3. Some of the networking architecture of NetWare protocols evolved from the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) created in the late 1970s.