Our Latest Articles
-

Domain Forest
DOMAIN FOREST is a logical structure formed by combining two or more domain trees.
-
DNS Database
DNS Database is the collection of database files, or zone files, and associated files that contain resource records for a domain.
-

DNS Client: Navigating the Digital Sea
DNS Client is a client machine configured to send name resolution queries to a DNS server. A DNS client is also called a resolver. When a client needs to resolve a remote host’s name into its IP address, it sends a request to the DNS server, which returns the IP address of the remote host.…
-
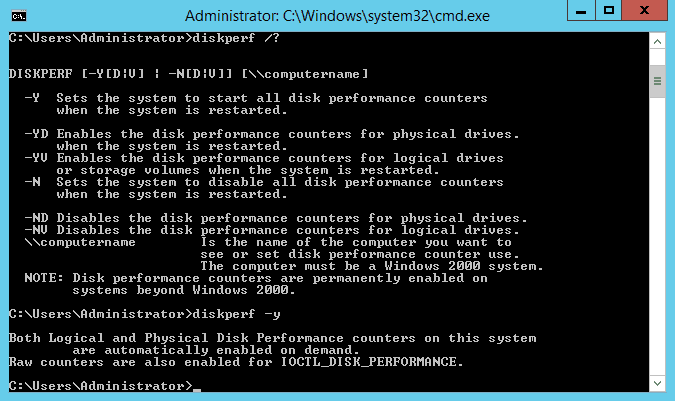
Diskperf Command
Learn about Diskperf, the essential command-line tool for enabling or disabling disk performance counters in Windows. Perfect for those who use Performance Monitor.
-
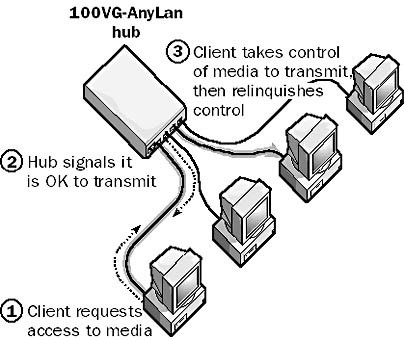
Demand Priority
Demand Priority is a media access control method for 100VG-AnyLan networks.
-

Understanding Data Terminal Equipment: 7 Crucial Points
Discover the crucial aspects of Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) in this in-depth exploration. Understand its role in modern networking and why mastering DTE is essential for IT professionals.
-
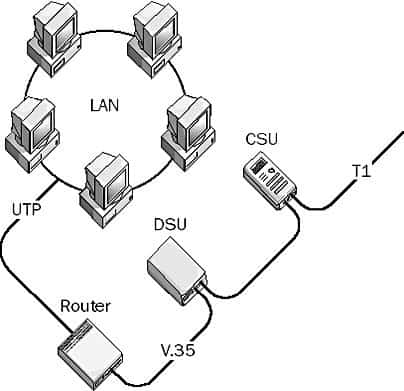
Data Service Unit (DSU)
DSU, or Data Service Unit, is a digital communication device that works with a Channel Service Unit (CSU) to connect a local area network (LAN) to an external communication carrier service.
-

Network Coupler
Discover everything you need to know about network couplers. From types like RJ-11 and RJ-45 to their advantages, disadvantages, and alternatives, this guide covers it all.
-
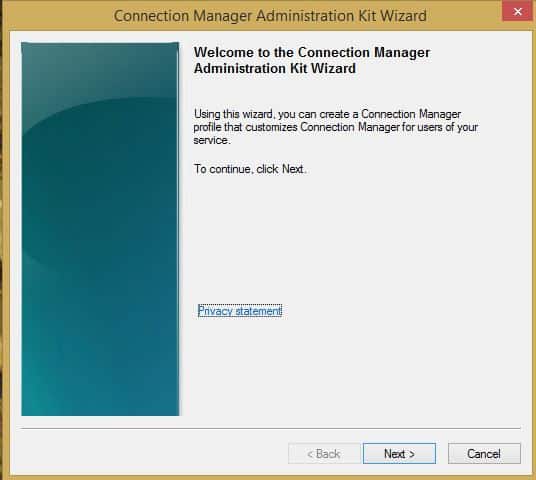
Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK)
Learn about Microsoft’s Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK)—a customizable network connectivity solution for remote access and VPNs.
-
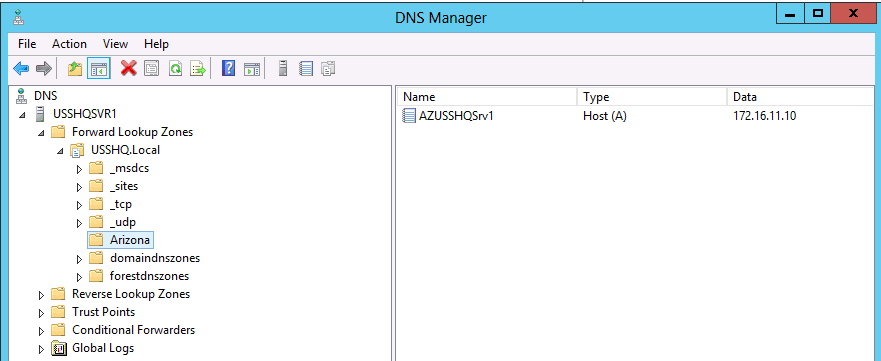
Child Domain
Child Domain is a domain in a domain tree in Microsoft Windows Server whose Domain Name System (DNS) name is a subdomain of a parent domain.
-

Understanding the CHAP Protocol: Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol, or CHAP, is an encrypted authentication scheme in which the unencrypted password is not transmitted over the network.